Showing Full Message Headers in Microsoft Outlook 2007
Outlook 2007 Message Headers
Simple Message Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and internet Message format are defined in RFCs 5321 and 5322. E-mail servers are required to append routing information in the SMTP headers. In addition, optional information can be added to the headers using the letter X. These X-Headers provide information such as anti-spam actions taken or whether the message as scanned with an anti-virus application. X-Headers can also be stripped by e-mail servers en route.
Each message will have its own unique header information. E-mail messages arriving in Outlook that originated from the internet have complete headers that are not visible by default. If an e-mail message is delivered where the sender and recipient reside on the same internal server, especially and Exchange Server, then the header information may be abbreviated or absent, depending on the client protocols used.
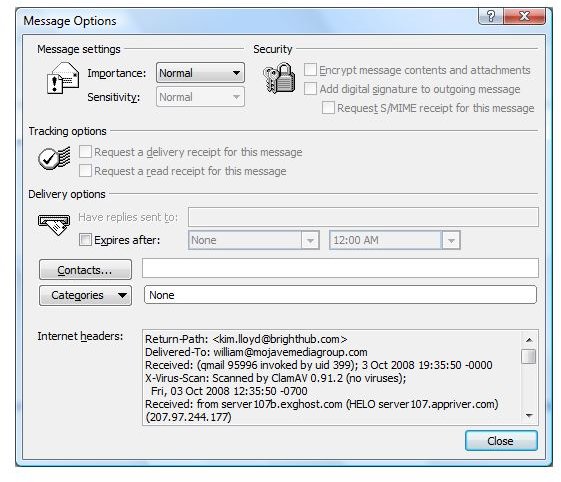
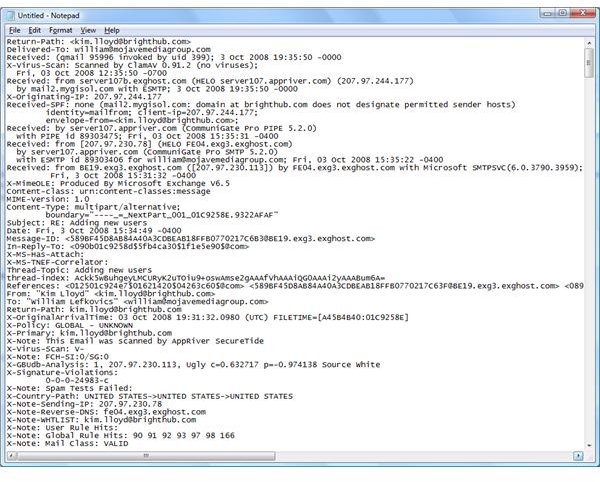
Header information is more than basic headers identifying the addressing of To, Cc, and Bcc. To view the header information of an e-mail in Outlook 2007, you must first open the e-mail in its own window. Outlook 2007 uses the new Office 2007 Ribbon for messages. The Message tab should be selected already (you may have a Developers tab also). You then click on the little arrow at the bottom right corner of the Options section of the ribbon. This opens the Message Options window [See Figure 1]. At the bottom of the Message Options window is a section of text labeled Internet Headers. Yyou can work with this text from this limited window or highlight, copy and paste to a text editor, such as Notepad or Wordpad. Figure 2 shows an example of complete message headers from an inbound e-mail copied to Notepad.
We can see the e-mail servers involved in the transaction with thie IP addresses and the unique message ID for this e-mail. We can also see that the message was scanned by at least 2 anti-virus agents and one anti-spam application. There are several X-headers that describe actions and assessments of this e-mail message. Checking message headers is a valuable tool for troubleshooting or validating message transport.
Screenshot
This post is part of the series: Microsoft Office Outlook 2007 Tips
A series of Tips and Tricks for working with Microsoft Outlook 2007 both as a user and an administrator.
- New E-mail Account Configuration in Microsoft Outlook: Tip #1
- Use AutoComplete “Nickname” Cache in Outlook: Tip #2
- Configure Outlook Custom Message Views: Tip #3
- How to Configure RSS Feeds in Outlook: Tip #4
- Tip #5 - Making Changes to the Custom Dictionary in Microsoft Outlook 2007
- Tip #6 - Configure Outlook Autosave Settings
- Microsoft Outlook Keyboard Shortcuts: Tip #7
- Microsoft Outlook 2007 Tip #8 - Outlook.exe Startup Switches
- Microsoft Outlook Instant Messenger Addons: #9
- Tip #10 - Using Outlook 2007 to Access GMail
- Showing Full Message Headers in Microsoft Outlook 2007: Tip #11
- How to Re-Send an E-mail Message in Outlook: Tip #12
- How to View Animated GIFs Embedded in an E-mail in Microsoft Outlook 2007: Tip #13
- Telling Outlook How to Handle Messages: Tip #14
- Microsoft Outlook 2007 Tip #15 - How to Color Code the Task List in the To Do Bar
- Tip #16 - Importing from Incredimail to Microsoft Outlook 2007
- Viewing Multiple Outlook Calendars: Tip #17
- Removing Cancelled Future Appointments in Microsoft Outlook 2007: Tip #18
- Tip #19: How to Create New Outlook E-mail from the Command Line
- How to Configure Outlook AutoArchiving: Tip #20
- Using Custom Categories in Microsoft Outlook 2007: Tip #21
- How to Manage Outlook Add-ins: Tip #21
- Microsoft Outlook 2007 Tip #23 - Attachment Previewing Options