What is a Database Server? Introduction and Overview
Raw Data
If you have ever watched Criminal Minds or NCIS on TV, they will invariably contact a computer specialist who is tasked with finding out information about a suspect or a criminal incident in question. They pull up their computer and start typing. Often the operations are very fast to the point of exaggeration. It is hard to get that kind of information that fast, but they have the right idea. If you have data, then you can process the data to turn it into information. That is what computers are really designed for – taking raw data and combining it with other data to produce meaningful information. To do that, there are two different elements needed, a database server that holds the data and a database engine that will process it.
For example, a telephone book contains raw data, the name, address and phone number. But a database organizes the raw data; it could be used to find all of the people that live on Main Street and their phone numbers. Now you have information. Turning raw data into information is what a database is designed to do. There are database engines and servers that help provide that service.
Hardware
Servers are typically computers with extra hardware attached to them. The processors will be dual or quad core. This means that instead of one CPU, the CPU has a dual or quad core system to double or quadruple the processing power. They will also have more memory (RAM) this makes their processing faster. It is standard for servers to start with at least 4 gigabytes of RAM and go higher, to 32 or 64 gigs. The more RAM, the better the CPU can perform the data processing.
Another feature of the hardware is the RAID system that usually comes with a server. RAID is a backup-redundancy technology that is used with hard drives. RAID 5 is the standard technology and it uses a minimum of three hard drives. The idea is that if one drive fails, you can replace the hard drive on the fly, rebuild the lost drive, and be operational in minutes. You don’t even need to power down the server.
Servers and Database Servers
A database server is a computer. It can have special hardware added to it for purposes of redundancy and control. A server usually is tasked to perform special functions. For example, a domain controller is a server that manages a network. An Exchange Server manages the e-mail operations for an organization. You can have a financial server that will host accounting, tax, and other financial software. But often, a hardware server can perform multiple roles if the roles are not too tasking.
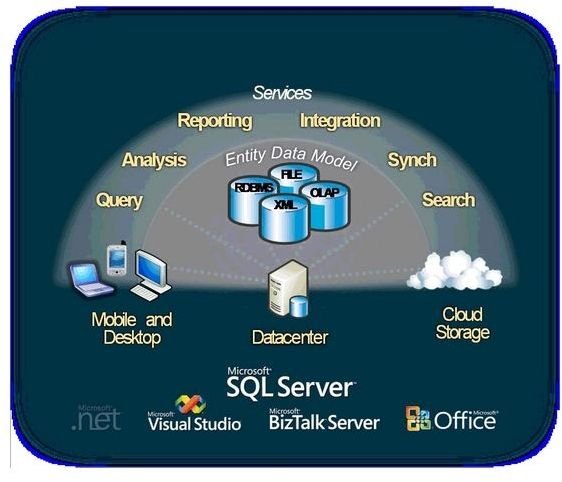
In this example, there is a database that is connected to multiple servers. The policies that control them make their operation a complete database system.
Image: Microsoft Database Roles
A database server will perform operations for the database that it is designed for. However, it is the data that makes the database server; it is a repository of a large collection of data. In this sense a financial server can also be a database server.
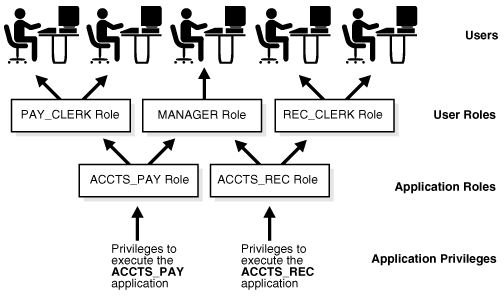
A hardware server can have multiple databases on it. But if the database takes up a large amount of space or is frequently used, like an e-mail database, then it would be better to have it operate on a separate hardware device.
Server Types
There are several kinds of database servers that support different types of database models:
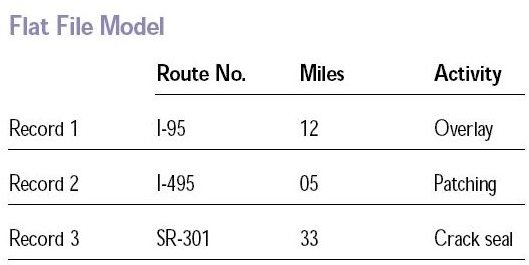
- The flat file database model consists of a single, two-dimensional array of data elements. An Excel spreadsheet is one example of a flat file.
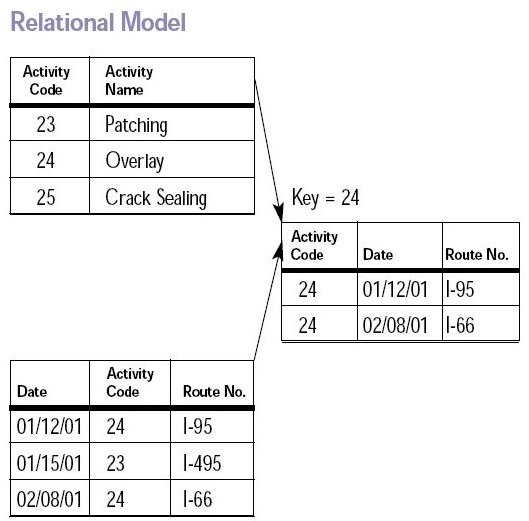
- Relational database models are designed to make database management systems more independent of any particular application. Sales, inventory, and customers brought together have different raw data elements, but together they can work to produce many different reports.
- Object database models work to bring the database world and the application programming world closer together. SQL and Visual Studio programming would apply here.
- In hierarchical relational database models, data is organized into a tree-like structure. A financial database could apply here. The example below shows accounting, loans, and taxes information and how each is related to the other.
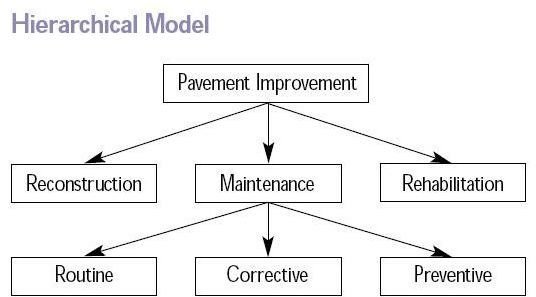
Image Credit: Wikipedia
Database Engines
In order to process the raw data, a database engine must be available to perform the organizational task. One common engine comes from Oracle. This company specializes in producing a high level engine that will handle millions of records of data.
Oracle is designed for medium to large companies that have very large databases to work with. It is a highly scalable engine.
Source: Oracle
Another database engine is Oasis.

Oasis’s claim to fame is that you don’t need to know database theory in order to have a functional database operational. This is intended for small to medium size companies that don’t have a lot of data.
There is one other engine that is quite popular now, and that is the SQL Server engine. Microsoft has made SQL the database engine for its products. It’s proprietary software is called SQL Server, and there are the 2000, 2005 and 2008 editions.
Summary
In this introduction to Database Servers, you can see that they can perform a variety of different tasks related to the data that is collected. They all have one thing in common, they hold a lot of raw data. This data gets processed using a database engine that helps convert the raw data into meaningful information. They are also placed on special computers whose hardware is designed to handle large volumes of information. Dual or quad core CPUs with multiple gigabytes of RAM make the processing faster. RAID 5 hard drive hardware is designed to provide redundancy and on-the-fly support.
For a short collection of database servers, look here.
This post is part of the series: How Servers Work - Bringing Together Different Applications
Servers are the workhorses of a network. There are different kinds of servers,application, file, print; and there are specialized servers like finance, engineering, or database. In this series we look at different servers and their function.