What is the Function of the Chipset - What is a Chipset?
Millions of transistors exist within the computer (specifically, the motherboard), but you would still need something to help the CPU perform its task better. Even the best of the workers would do well with assistants, don’t they?
The CPU still needs help before it can handle every specific input, output, and control signal that it exchanges with the computer memory, input, and output devices. Each motherboard also has a set of Integrated Circuit Chips called a chipset that converts all these generic CPU signals to and from the instructions and data that each component expects. Think of a chipset as a gatekeeper which aides the CPU in deciding what has to be done with each block of data. It also directs the inputs and outputs to the right destinations at the right speeds in an appropriate, prioritized sequence.
One of the most important characteristics is what type of chipset is being used with what type of CPU for the particular compatible motherboard. However, many motherboard manufacturers may offer several models that support the same CPU with various chipsets.
Intel is the only company that manufactures its own chipsets. Most motherboard manufacturers don’t make their own chipsets and are sourced from third-party chipset manufacturers. So, next time you see the same chipsets in two different brands, models or makes of a computer, don’t be surprised. Some of the well-known chipset manufacturers are NVIDIA and VIA technologies. As mentioned earlier, Intel makes its own chipsets for their CPUs. Of course, other chipsets are being made for Intel CPUs by companies like Silicon Integrated Systems (SiS) and VIA Technologies.
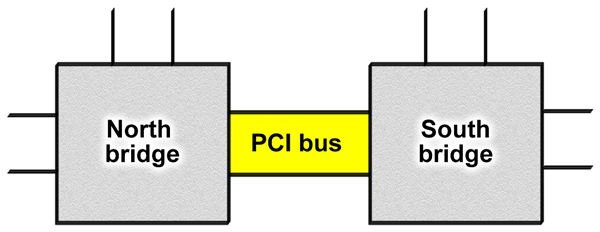
One of the most common terms you will read about and encounter when learning about chipsets are terms “northbridge” and “southbridge” which helps us recognize their respective distinct functions and also help explain their internal architecture. As you can see, this design has two distinct parts (as seen in most Intel and AMD processors); the southbridge part of the chipset manages relatively slower devices such as the network interface and the USB ports, while the northbridge part controls the high-speed channels such as communicating with RAM , Cache (Level 1 and 2) and the graphics controller.
[Img Courtesy : karbosguide.com]
Suggested Reading
For More information about the Latest on Motherboards and Chipsets, processors and the like, Please read the following links:
Choosing a Chipset For Penryns and Phenoms - An Introduction By JeanFA @ Brighthub.com
X58 Tylersburg: Big Changes to Motherboards are Coming By JeanFA @ Brighthub.com
<strong>Chipsets and Hubs @ karbos Guide</strong>
This post is part of the series: Beginner’s Guide to Hardware
Not knowing about computers can make US obsolete. It is critical for us to develop an understanding of how these computers work since we have to make decisions about buying, repairing, selling, and using them. This continuing series is all about that and much more.
- An Introduction to Hardware for Beginners: A Primer
- An Introduction to Hardware for Beginners: Bits, Bytes and Beyond
- An Introduction to Hardware for Beginners: The Motherboard
- An Introduction to Hardware for Beginners: The Central Processing Unit
- An Introduction to Hardware for Beginners: The Chipset
- An Introduction to Hardware for Beginners: Understanding BIOS and Memory
- An Introduction to Hardware for Beginners: What Goes In and What Goes Out?