Endoplasmic Reticulum. Where is the Endoplasmic Reticulum Located? And Other Questions
What is the Job of the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum has many functions to perform in the cell. There are two main types of endoplasmic reticulum - the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum and both have different jobs to do.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Manufacturing and Packaging of Proteins (the rough ER is studded with ribosomes, the protein making factories of the cell)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Storage of steroids and ions
- In muscle cells the smooth ER stores calcium ions and releases them when the muscles contract
Other general functions of the endoplasmic reticulum include drug metabolism, storage of glycogen, facilitating the transport of proteins and protein folding.
Where is the Endoplasmic Reticulum Located?
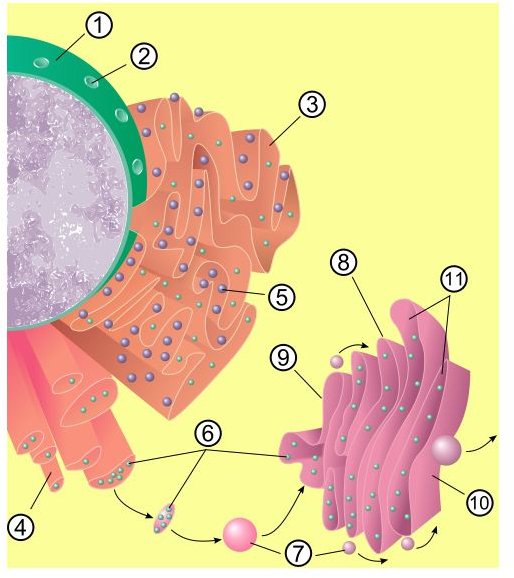
Although from some diagrams the endoplasmic reticulum appears to be situated around the nucleus it really doesn’t have one specific base or point in a cell, as it extends a network of membranes, tubules, vesicles, and sacs throughout the cell.
The ER is a phospholipid membrane enclosing an internal fluid filled sac called a cisternal space or lumen. The membranes are folded and stacked on top of each other and connected to the nucleus.
The rough ER with ribosomes attached is closest to the nucleus.
What Does the Endoplasmic Reticulum Look Like?

The endoplasmic reticulum has a few different ’looks.’ The rough ER appears as lumpy sheets of folded membranes; the lumps are the ribosomes. They are not permanently attached, adhering only when there is protein manufacturing work to be done.
The smooth ER which isn’t coated with ribosomes looks like smooth tubes. And sometimes the ER resemble flat balloons.
Who Discovered the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum was discovered by Belgian biologist Albert Claude (1899-1983), a man who is considered by many to be the ‘father of cell biology.’ One of his main achievements was to demonstrate that the interior of the cell was not a haphazard place, but a highly organised area. He used the newly developed electron microscope to explore the interior of cells and along with his associate Keith Porter in 1945 observed the presence of a ’lace-work structure.’ It not only helped to give shape to the cell but it also housed many granular components, including ribosomes. They had detected the endoplasmic reticulum.
It was really this discovery that convinced scientists that cells were not merely ‘bags of stuff.’