Learn About Building with Adobe: Building Methods for Adobe for a Better Environment
An Introduction to Building with Adobe
Construction of adobe buildings can be traced back to 500BC, and the method of construction has changed little during the intervening 2000 years or so, except that nowadays, the adobe mixture can have asphalt added and then be hydraulically pressed into brick molds. But the traditional method of packing the mix into the brick molds by hand is still widely used and a more satisfying method.
The brick molds are usually made from wood, to the required size of the brick.
The components comprising of clay, sand, straw and animal dung are mixed with the water then packed into the mold, ensuring that all the air has been pressed out of the mix. Once this has set, the mold is removed leaving a formed adobe brick, which will be left for up to a week to harden, depending on the weather.
Once sufficient quantities of bricks have been prepared, (a single storey house can require 6,000 bricks) the construction of the building walls can be commenced.
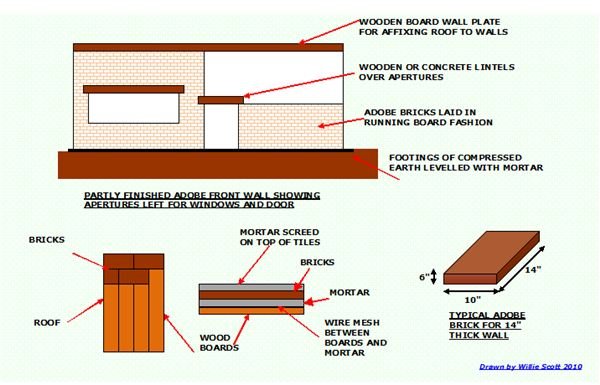
The bricks are laid in the traditional fashion known as a running bond, the mortar being made from the same mix as the bricks, but of a more watery consistency and without the straw component. The foundations can comprise of poured concrete or the traditional method of footing which is to compress the earth to support the weight of the walls above it.
This is the fourth in a series of articles on natural green materials for buildings, the previous ones being on straw, logs and rammed earth.
As with the previous articles, the descriptions and method used for the buildings is to illustrate the aesthetic quality, durability and suitability of the material, and not to be used as a technical construction manual.
We shall begin with the components of the mixture used when building with adobe.
Components of the Brick Mixture
The components of the usual mix are as follows,
- Clay – The mixture contains about 50% clay, bonding the material components together, and the clay used should be able to pass the following simple sediment test:
-A handful of clay is added to a glass jar of water and vigorously shook until the contents are well mixed. It is then left for an hour or so on a level surface. Upon examination, the water should not be cloudy; the clay lying at the bottom of the water indicating the clay is suitable for brick formation. A cloudy mixture indicates clay which would produce weak inferior bricks, liable to crack.
- Sand – 30% of the mixture is ordinary sand. This is used to bulk out the mixture acting as a filler to the mix and bonding to the clay.
- Dung or Straw - This makes up the last 10% of the mixture, and either one can be used as a bonding agent. I wondered about the straw used for bedding for cattle in barns, this would be a combination of both. But I am sure the dung would need to be dried before use so it crumbles into the other mixtures. The straw or dung is used to strengthen the bricks and help dry them out evenly avoiding cracking or crumbling.
Note
These percentages vary for different countries, for instance adobe building construction companies in Canada recommend up to 70% soil content in the mix.
Manufacturing of the Frame Molds and Bricks
A typical frame mold measures about 10" x 14" and is made from 6" x 4" sections of wood, but these dimensions can be altered to suit the size of bricks required. The frame is laid on a firm, level plane where the mix is shoveled into it and tamped down until level with the top of the wood frame. This ensures all the unnecessary air and water is expelled.
After a short time, the frame is removed and the formed brick left in the sun to dry for a few hours. Once set enough to lift, the bricks are brought into shade for final drying, lying on their side. It takes about a week in the hot weather for the bricks to harden and be ready for the wall construction. A DIY family can produce 200 bricks per week. (Why not have a few brick building parties or barbeque parties – where everyone constructs 20 bricks!) Remember to have plenty of mixture and molds ready.
Please read on to find out more about adobe building construction methods.
Wall Building Technique
Foundations or Footings
The foundations are excavated to a depth of at least 24" by 18" wide. The loose earth is then shoveled back into the excavation and well compacted to form a firm footing for the walls, mortar being used to make up the shortfall of soil after compaction, while ensuring the footings are level.
Mortar Formation
The mortar used to bond the bricks together is made from the same mix as the bricks except that the straw is omitted and a little more water is added.
Wall Construction Method
Walls are constructed from the well-seasoned bricks in the normal running board method, where the bricks are laid on their sides in course, giving a wall thickness of 14".
As the wall progresses, apertures are left to accommodate the fitting of the doors and windows. These apertures must be spanned across the top with a strong wooden or concrete lintel to support the weight of the bricks above. If an lintel is not used, the layers of bridging bricks are liable to sag in the middle and crumble at the edges.
Lengths of wood should also be incorporated into the last layer of the bricks and the top layer for use as wall plates, to give support and attachment for the roof. Insulation may be required and this is usually attached to the inside of the building boundary walls, the outsides of the walls rendered with the mortar mix. Some people add lime or linseed oil to the mix for waterproofing purposes.
Roof and Floor Construction (Traditional Method)
The almost flat roof is constructed by laying wooden beams known as Vigas the full length of the building, overhanging the walls at the sloping end of the roof. These beams support the bricks used to line the roof, with the overhang allowing water to run off clear from the walls to prevent erosion.
Chicken wire can be nailed to the wood beams to provide a key for the mortar then, the roof is secured to the wooden wall plates fitted earlier to the top of the walls.
The mortar can now be laid onto the wire mesh as the bricks are laid. The bricks for the roof construction can be wider than the ones used for the walls, as this will help distribute the load evenly along the beams.
As the work progresses, the mortar should be spread on top of the bricks about an inch thick, much like traditional plastering methods. Once all the bricks have been laid and the mortar layer plastered onto the top of the bricks and left to dry, this will form a waterproof and strongly bonded brick roof.
An alternative would be to use recycled shingles which are more aesthetic and a lot lighter.(But more expensive) This would require the wooden beams to be sheeted with 15mm plywood, the shingles being fixed to this.
Floor Construction
Once again, the floor area can be screeded with adobe mix mortar, leveled, and left to dry out.
Once dry, the mortar floor can be wire brushed by hand or mechanically, to give a long-lasting polished floor, requiring no carpeting.
Summary
Adobe buildings have been around a long time, the traditional methods of construction reaching as far back as several thousand years.
Bricks are used in the construction of the adobe buildings, these bricks being made from a mix of clay and sand, strengthened with straw and mixed with water.
When building with adobe, the outer walls are constructed first, then the roof goes on and all the adobe surfaces are rubbed down and linseed oil is applied.
This will not only give the walls and roof a weatherproof coating but will improve the buildings aesthetic qualities.
Finally, once the adobe building has been completed, consideration should be given to reusing recycled construction materials, such as doors, windows and plumbing items (as seen in the next article).
Sketches of Adobe Construction Methods
Internet Sites Visited
https://www.greenhomebuilding.com/adobe.htm
This post is part of the series: Green Construction Materials
Here we look at different green construction materials and rate their durability, insulation capability, aesthetic qualities and more. We will take a closer look at using materials such as logs, straw and rammed earth, and adobe, as well as the use of recycled building materials.