How to Use Microsoft SharePoint: Getting the Most Out of SharePoint
How is SharePoint Different From a Project or Document Management Tool?
SharePoint has many features found in a variety of software tools – Powerpoint, InfoPath, Word, Excel, Browsers, and Project. Each has its own function and methods for dealing with the document creation and management process. Certain applications in the MS Office suite do not integrate well with the others. Word documents don’t handle Excel very well. InfoPath and Project together … not really. So if you are using all of these programs, can you find a way to use them together and not lose the data without reinventing the wheel?
The answer is SharePoint, which can help you organize the data from a variety of elements into one point of action. That is what makes SharePoint different.
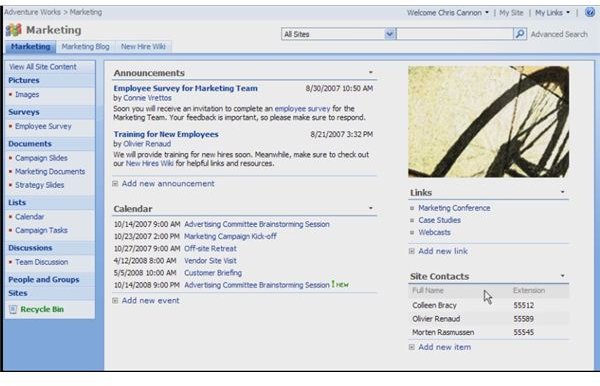
Collaboration: Sites and Pages
In order to get a working understanding of SharePoint, the easiest place to start is by looking at sites. SharePoint is a browser-based application that works with Internet Explorer. The organizational points are sites. Sites are the central storage points where you can create a series of features that different users can work with. For example, let’s say that you want to create a place where your project’s information is stored in one central location, which will be available to everyone. That project location would be a site.
Now you can create columns for your site, such as the departments that are working on your project. You can create a library of documents for your project, and you can add multiple pages to keep separate parts of you project intact.
For some sample sites, refer to the article Showcasing SharePoint 2007 – Top Sites.
Portals and Personalization
Organizations have individuals with a variety of talents – some expert, some novice, and some in-between. How does an expert share information with a novice? How does a novice find out what they need to know…from the expert? With SharePoint, organizations can create portal sites that cross-connect individual sites across an organization and consolidate access to existing business applications. In this way, the left hand can communicate with the right hand. Teams and individuals across an organization can use a portal site to access the expertise, information, and business applications from a variety of locations. Expertise is no longer kept to a select few.
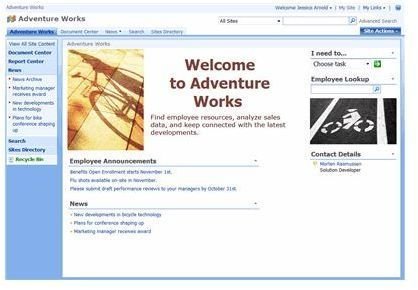
Search
As you probably know, one of the best tools anywhere on the Internet is search. In SharePoint, you have that ability to find information, files, Web sites, and people.
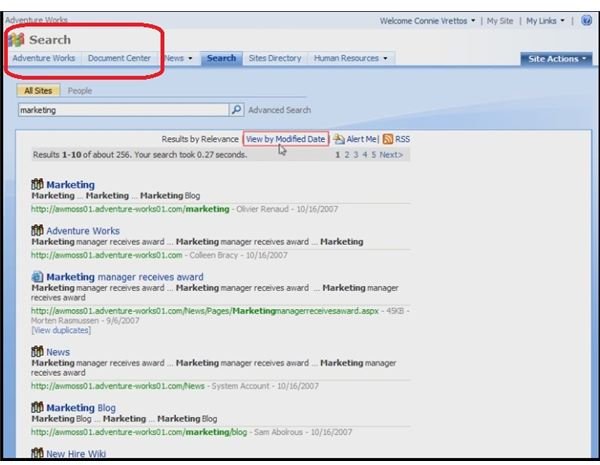
Search allows the users to customize how they will look for information in the site.
Enterprise Content Management
SharePoint wouldn’t be SharePoint without the ability to create, manage, and store content throughout an enterprise. Anyone can create diverse content, but the problem is managing it. Suppose that you have e-mail, blogs, videos, a web site, presentations, worksheets, and a host of other communication or information items. And how long will each of these be relevant?
Administrators can manage content, and decide if it is still relevant or if it should be removed.
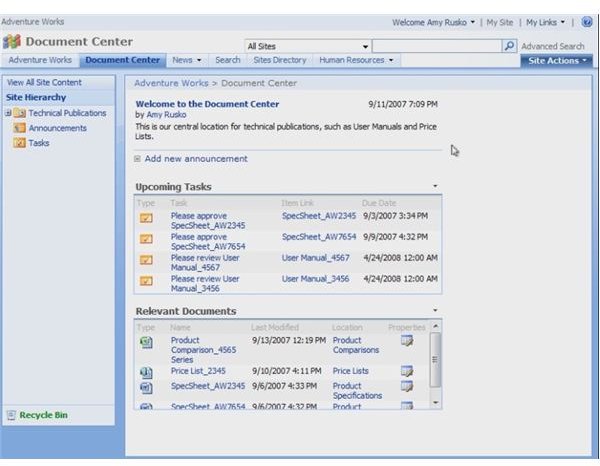
Business Processes and Forms
SharePoint allows you to integrate and streamline your business processes. For example, one process may be to create browser-based forms for use throughout the organization. You don’t need specialized programs like MS InfoPath or Project to get the information.
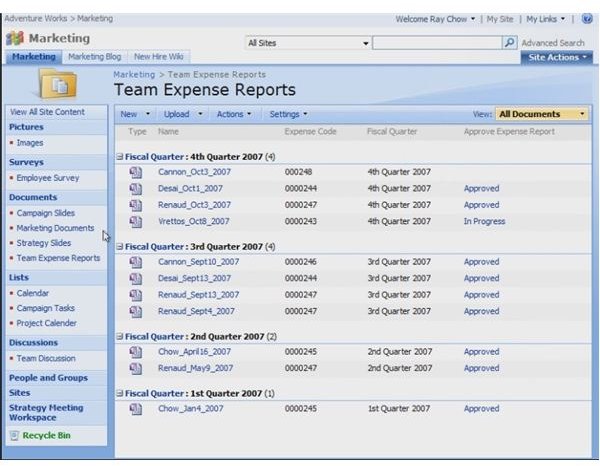
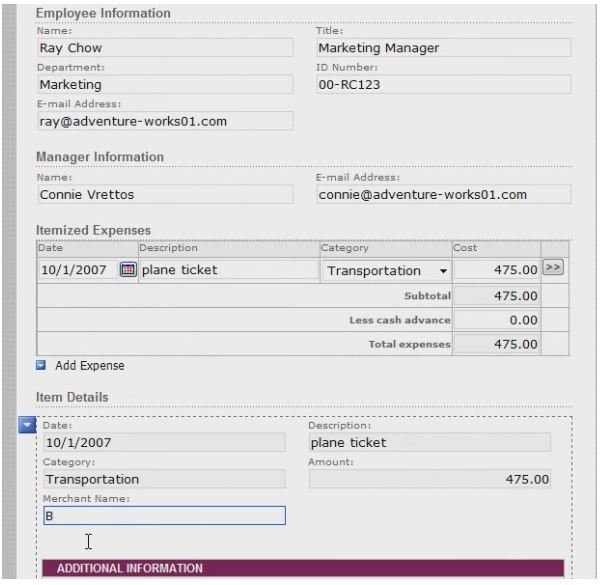
How a work process manifests itself from person to person or department to department is called a workflow. SharePoint can streamline the cost of coordinating common business workflows, like document review or project approval. It can provide a way to track and manage those tasks involved. Here is an example of an expense report workflow.
The workflow, in real time, would be for the employee to find the expense report form and fill it out. Then he must submit it, Then the appropriate parties are notified that an expense report is pending approval. The managers read the expense report and can approve or disapprove the item. If approved, it must be submitted to HR so that a check can be cut for the employee or added to the next payroll check. This series of steps is the workflow for expense reports. SharePoint can automate and streamline the process.
.
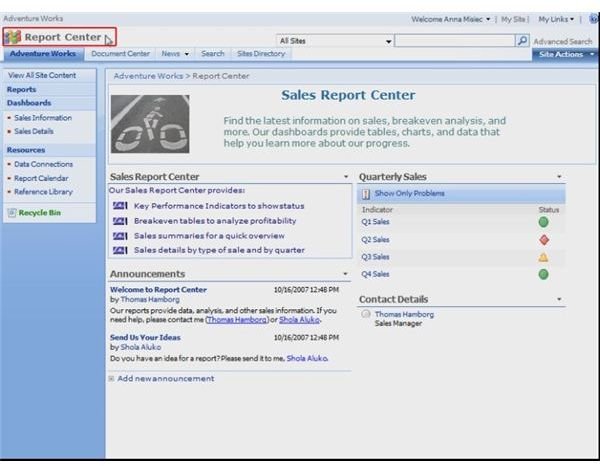
Business Intelligence
Too much data! That is probably what managers say when they look at a project and try to decide to continue or to cut it. To address this problem or its counterpoint, not enough data, business intelligence can be used. Briefly, it is the process of aggregating, analyzing, and reporting on business data to support rational business decisions.
Are there patterns in the data? If not, can we find them? Is the data complete? Is the data reliable?
SharePoint can provide the means to getting business data using reports and dashboards.
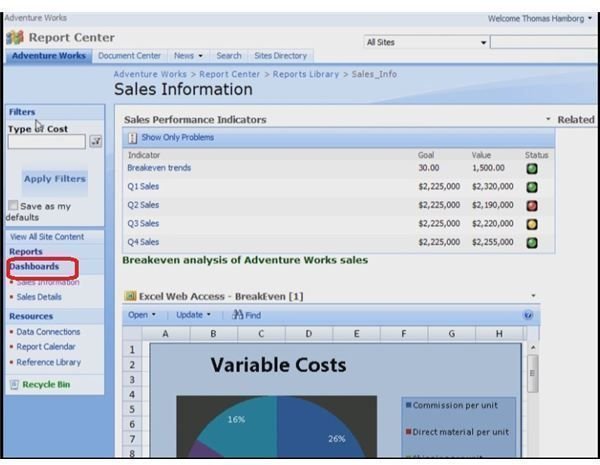
Summary
Collaboration is the central idea behind SharePoint. The name says it all. Users share a task or tasks that have one or more points in common. Here we have seen how those points can be represented. They are collaboration, portals, search, enterprise content management, business processes, and business intelligence. To understand SharePoint and to learn how to use SharePoint, one must understand each of these operations.
Source: Roadmap to using SharePoint Server 2007
This post is part of the series: SharePoint - How It Works and What It Does
SharePoint is a collaborative program designed for document and project management across an enterprise. It is a browser based application which can be used to create websites for internal and external business operations.