How to Make Your Hard Disk Drive Faster? Just Use This Software
Slow Loading Computer - Problem With Hard Disk Drive?
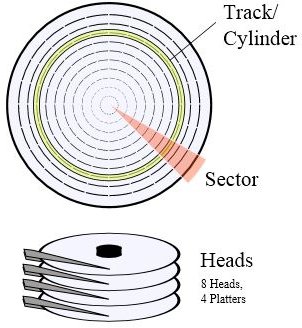
Your hard drive is nothing but a set of magnetic disks that are stacked one atop another with small air spaces between them. Each disk has several tracks and sectors on both sides that serve as addresses for your files and programs. The format of data identification should not present problems in accessing files or programs without delay, yet still you experience delays- often to the extent that you get irritated.
Considering that you are using the latest NTFS format and SATA drive connection, you may wonder if the use of the File Allocation Table (FAT) is still the best way to speed up access to programs. File access delays occur when files are fragmented and programs are cluttered all over the hard drive. For example some portion of your program might be on the first disk and the remaining part on disk three or four. In many cases, a file may span several dozen segments on your hard disk.
When you save a file or install a program, Windows looks for the nearest free space and tries to save your file there. If the file size exceeds the free space, it looks for the next free space chunk and stores the remaining part there. To allow “file access processes” to retrieve the remaining data, it leaves a pointer to the next segment at the end of the data chunk. This process continues until the Windows “write process” encounters an EOF (End of File) character**.**
How Does Windows Access Files On Hard Disk
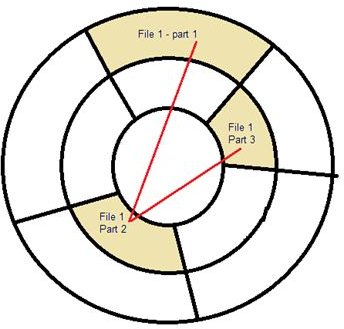
When you access a file or program, a Windows process consults the file allocation table for the address of the file and then goes to the address shown. As the process tries to load the file or program into memory, it notices that the file has further portions (indicated by the pointer previously mentioned). The file access process moves ahead to the appointed address and loads this portion only to find out that the file still has some portion stored elsewhere (see Fig).
For both data files and programs, Windows employs a cache so as to reduce the access time. As this cache lies in between the hard disk and main memory, a Windows “read operation” need not repeat the entire process of accessing the file from the hard drive again and again. For write operations, too, the data is kept updated in the cache until you “save the file,” whereupon the Windows write process accesses the hard disk to store your data.
Please note that in the case of any application, Windows needs to cache at least the basic code so that you can use it to initiate further processes**.** For example, if you are opening MS Word, Windows will have to read the hard drive using the above method and load these basics into the cache: the GUI and blank page so that you can start working and initiate other processes of MS Word.
This is the primary reason why you need to wait for long while loading any application. In case of MS Word, it already took time to gather all the cluttered portions to get the basic GUI into cache. Once you issue the open command, the entire read process is activated for the file that you wish to open. Same is the case with other commands such as “Save” or “Insert Image,” etc. Also, if you wish to apply a theme or page border, it will again have to initiate the read operation to locate and load the theme into the cache.
Tips on Increasing Speed of Hard Disk
Formatting the hard disk drive (HDD) is a temporary solution. Plus it involves plenty of other tasks such as backing up your data, reinstalling all your programs, customizing Windows settings, and restoring data. Even after this, if you do not care to spend some time on HDD maintenance, it will be the same case within few months of the format. The following tips about how to increase the speed of your hard drive also include some “setup and forget” methods for HDD maintenance.
How to Increase Hard Disk Speed – Clean and Defrag the HDD
Defragmentation: As stated previously, the only cause that slows down your HDD is high fragmentation and clustered programs and data files. It is recommended that you defrag the HDD so that all the different portions of different files are bought closer, if not completely together.
There is a built-in disk defragmenter in Windows XP, but it consumes substantial resources while the HDD is being defragmented. I never use the built-in Windows disk defragmenter. Instead, I suggest that you download the free Smart Defrag. This program has plenty of features, including auto-defragmentation. By default, its auto defrag is turned on– it initiates defragmentation when the system is idle for five minutes. You can change it to suit your needs. Once configured, you can forget about defragmenting the HDD. It loads with Windows and runs silently to monitor and defrag your HDD.
TIP: While speaking of defragmenting HDD, I would recommend another program in addition to Smart Defrag that takes care of the pagefile. Pagefile fragmentation leads to slow boots. Page Defrag (download link) defrags pagefile while your system boots thereby keeping all of the pagefile contiguous.
Clean up the Computer
Among other factors that slows down access to the HDD are temporary files, leftovers from uninstalls, cookies, logs and many more unnecessary files occupy precious space on your hard drive- giving a boost to fragmentation. It is necessary that you get rid of these files so that your data files are stored contiguously. Though there is a built-in Disk Cleanup Wizard in the Accessories submenu under All Programs, it offers limited cleaning. The only advantages I can see with Windows Disk Cleanup are compression of old files and removal of old System Restore Points.
Though a useful feature, System Restore consumes a considerable part of your hard drive for storing settings for each restore point. I recommend turning off System Restore on all drives except for the system drive (often the C drive) by right-clicking My Computer to select Properties. In the resultant window, click the System Restore tab. Click on each drive other than root and click on the Settings button to turn off monitoring of that drive. Finally, select the C drive, click the Settings button and limit the space used by System Restore. This will free up more space for your programs while also speeding up your computer.
For a full cleanup, I use and recommend the free Comodo System Cleaner (download link). It defrags your system registry, allowing resolution of keys to start programs faster, while removing all unwanted files and privacy settings. It has the option for safe cleaning and can be scheduled to run weekly or monthly so that your hard disk is uncluttered thereby speeding up your computer.
Once in a while - when you feel that your computer is working all fine - use the Windows Disk Cleanup Wizard to remove older System Restore points. A proper cleanup will give you ample space to create new files that are not much fragmented.
To sum up, a scheduled system cleaning combined with auto defragmenting helps you keep your HDD optimized for faster access so that you feel like you are working on a new HDD. The answer to how to speed up your hard disk drive could be using two additional software regularly: Ccleaner and SmartDefrag.
References
- SysInternals Screenshot by Author
- Fragmented Files Diagram by Author
- Hard Disk Diagram from Wikimedia Commons
- Courseware for DOEACC A level, http://doeacc.edu.in
This post is part of the series: Troubleshooting Windows XP - How to Fix Windows XP Problems
Windows XP is the best operating system till date. You have read much about advantages of Window XP. We will talk about Windows XP disadvantages: troubleshooting Windows XP; fix Windows XP problems, speed up Windows XP; how to make Windows XP run faster; and many other XP problems & solutions.