The History of Windows Mobile
Since the early 1990’s technology has evolved to such an degree that computing and communications are now possible from the smallest, pocket sized devices, while delivering fantastic visuals and speed. In order to embrace this shift in technological capability Microsoft has been at the forefront of software development, creating applications and operating systems that fit the specific requirements of the mobile device. One such operating system is Windows Mobile. In essence a basic os, based on the Microsoft Win32 API, Windows Mobile was designed specifically for handheld devices, originally the Pocket PC, then Smartphone’s and Portable Media Centers. In its earliest form the windows mobile operating system was similar in look, feel and functionality to Windows 98, delivering basic application delivery and minimal third-party support for common hardware and software components.

Today however Windows Mobile is more in tune with the ‘Live’ suite Microsoft are pushing, which has a dazzling array of onscreen informatics - e-mail messages, tasks, apointments and ownership details. As with Windows XP, the taskbar holds the current time, volume connectivity status, and resource processing. The notification bar holds all the standard desktop iconic representations such as running programs, connectivity, etc. In terms of application productivity the Mobile Office suite delivers impressively similar functionality to its big brother Microsoft Office. Word, Excel, Outlook and PowerPoint all deliver excellent functionality and while there are some gaps in functionality, for example table and image insertion are two areas that are missing, you won’t see much of a drop off. Windows Media Player also has extensive operability providing users with the capability to play WMA, WMV, MP3 and AVI files, however MPEG’s are not supported and WAV files require a separate player. There is also an abundance of personalization settings, from configuring background images and themes. Most importantly however is the development of ActiveSync and improved server interfacing for fast and secure synchronization of data to any desktop application.
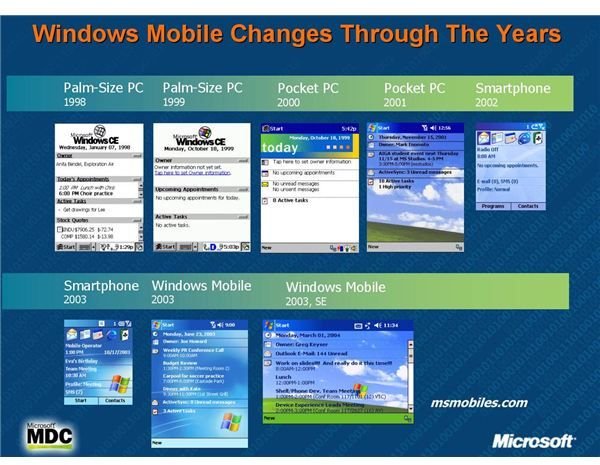
The Windows Mobile operating system is now available on multiple platforms, but the first devices to use Windows Mobile were Pocket PC’s. Driven by Pocket PC 2000 operating system and powered by Windows CE 3.0. It was soon realized that such an operating system brought real value, and with successful integration into handheld devices it became the os of choice on many Pocket PCs. Being the first release brought the obvious limited functionality and problems, the most limiting being Pocket PC 2000’s ability to only support screens with a resolution of 240 x 320. Other than that, the operating system gave great encouragement for the future of mobile computing os delivery with such functionality as Pocket Office, Pocket Internet Explorer, Windows Media Player, Microsoft Money, Microsoft Reader, Notes, Character Recognition and Infrared file beaming.
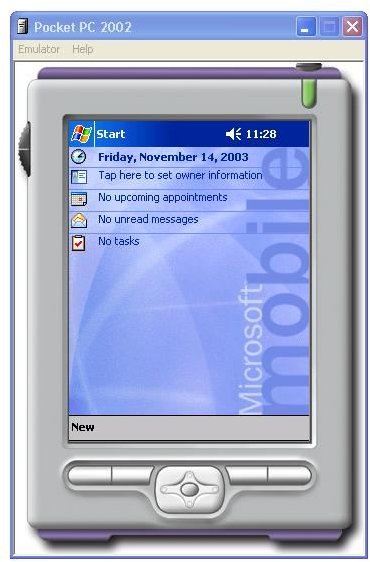
Following Pocket PC 2000 came the enhanced operability and Smartphone compatibility of Pocket PC 2002. These Smartphone devices were developed to aid user interactions via one hand, bringing mobile computing to handheld communications devices for the first time. While Pocket PC 2002 still didn’t resolve the issue of only being able to run at 240 x 320 resolution it did have improved navigability and slicker operability. This enhanced user interface also incorporated greater configurability, GSM communications and enhanced Pocket Office tools, bringing it more in-line with desktop versions. There was also an extension to the services on Pocket PC 2000, including virtual private networking, synchronization, MSN messenger and digital rights management. All of which were available for the first time via Pocket PC and now Smartphone’s.
As Smartphone’s advanced to incorporate greater multimedia capabilities, advancements were made in the area of Portable Media Centers. As such Microsoft focused its integration with Windows Media Center, Windows Media Player, and developed the Windows Mobile 2.3 operating system architecture. This enabled users to carry extensive media libraries and manage multimedia via a simple operating system, on one unit. Windows Mobile 2003 introduced the first multi-version consumer choice mobile operating system platforms. These were Windows Mobile 2003 for Pocket PC Premium Edition, Phone Edition, and Professional Edition, and Windows Mobile 2003 for Smart Phones. Catering for such a wide range of handheld devices, the Windows Mobile operating system was making considerable strides into the handheld market. With such a range of operating systems flexibility came enhanced communication support, keyboard facilities, games, image delivery, MIDI file support, messaging and further enhancements to the Pocket Office suite.
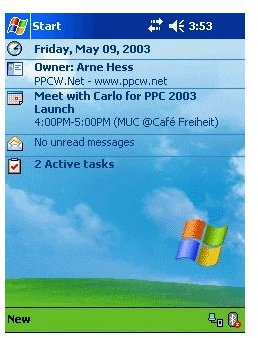
With the added diversity of hardware manufacturers, Microsoft then released the 2nd edition of Windows Mobile 2003. This brought enhanced viewing on VGA screens of 240 x 240 and 480 x 480 resolution, Wi-Fi security and an enhanced look and feel which included for the first time portrait or landscape viewing options.
As more hardware devices came to market, offering greater multimedia, communications and office type productivity there became a greater need for operating system flexibility for working (and playing) on the go. Thus Microsoft developed Windows Mobile Automotive. Enabling communications, entertainment and information systems to be interlaced for seamless operability on one sophisticated device. Having a need for such functionality in transit dictated the need for two different versions of the Mobile Automobile, the basic version had USB interfacing and Bluetooth connectivity, whereas the standard version also had built-in GPS, GSM and greater security. Windows Mobile did require a higher spec processor, memory and microphone but it was a considerable step towards mobile computing for the roaming user.
In 2005 Microsoft launched Windows Mobile 5.0. Driven be Windows CE 5.0 and incorporating a .Net compact framework it delivered further compatibility with communications infrastructures and the first breakthrough cooperation with Microsoft Exchange Server architecture. This created tremendous potential for data synchronization, compatibility and greater capacity for storage. Which in turn saw major upgrades in improved battery life through Persistent Storage capacity where flash memory is used for primary storage as opposed to the previous memory intensive volatile RAM which had been used in the past.
Also available via Windows Mobile 2005 were major improvements to application software, such as the introduction of ‘Mobile Office’. Along with Word, Excel and Outlook, the Mobile Office suite also incorporated PowerPoint, enhanced graphics and tables. Windows Mobile 2005 also offered photo caller ID, greater communication support for Bluetooth and GPS, default keyboard support, error reporting, ActiveSync and the aforementioned persistent storage for enhanced battery life.
Now in 2008 the current version is Windows Mobile 2006. Coming in three different iterations there is Windows Mobile 6 Standard for the Smartphone market, Windows Mobile 6 Professional for the Pocket PC with mobile phone capabilities, and Windows Mobile 6 Classic for the Pocket PC without mobile phone capabilities. In the next part we will look closely at Windows Mobile 6 and its development.
Next »> Windows Mobile 6 Developments
This post is part of the series: Windows Mobile: Taking the Windows OS to a truly global audience
Windows Mobile has come a long way since its introduction in 2000. Here we look at the History of Windows Mobile. How it has developed and embraced technologies such as Pocket PC’s and Smartphones, and how it now delivers an array of applications, services and communications.
- How Redmon Took Windows on the Road: What a Long, Strange, Mobile, Trip
- Windows Mobile 6: Reviewing Microsoft’s Mobile OS Platform
- Windows Mobile 6: New Release Developments
- Best Windows Mobile Communications Software
- Windows Mobile Apps for Multimedia and Business
- Best Windows Mobile Games Software
- Best Windows Mobile Utilities Software