How to use Strong Encryption for Data
Learning about Encryption
The point of using strong encryption for data is to safely protect the individual’s privacy and/or the data itself. The concept of data encryption is to help make the contents illegible for others. In short, the only secure way to safeguard data is to “encrypt” them.
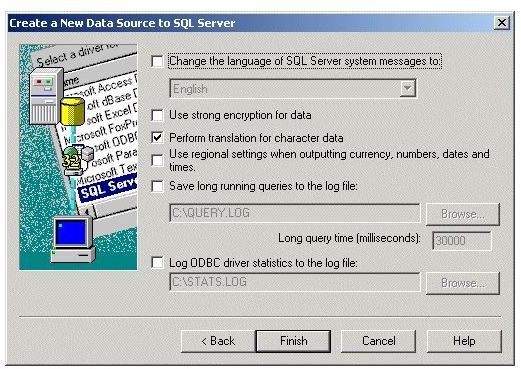
Note: Only those with the correct encryption/decryption key are able to read the contents of the data. To be able to give authorization to a client to view encrypted data, a computer user must enable encryption for a specific client. For example, to make an SSL encryption connection to a computer running SQL Server, a user must navigate to the Microsoft SQL Server DSN Configuration page and Select: Use strong encryption for data, and then click Finish. See the images section below to see what the screen looks like at the point of selecting to use strong encryption. For those that need assistance, Microsoft TechNet is available.
How Encryption Works
Data is encrypted and decrypted (or encoded and decoded) with encryption software, a cryptographic key, and by enabling encryption on a computer. The encryption process is the same. An encryption algorithm and a key are used to transform the original information to another form. To learn more, see: Types of Encryption - Conventional Methods.
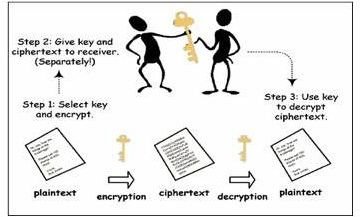
Note: Plaintext is the original data without encryption; while ciphered text is the encrypted data.
* The Encryption Process is based on the science of cryptography (i.e., encryption is done using cryptography).
To verify that information comes from a trusted source, data should be authenticated by public and private key encryption. See the images section below to understand how it works.
Note: Public (non-secret) and private (secret) keys are used to encrypt and decrypt data.
There are two encrypting techniques: Symmetric and Asymmetric. With Symmetric, both the sender and receiver use a shared key to encrypt/decrypt data; whereas with Asymmetric, the sender and receiver use separate keys. Note: For stronger encryption of data, use both techniques.
How to use Encryption
For strong encryption of data, use one of the following technologies (or a combination of each):
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate to encrypt the message. It helps secure online end-to-end messaging.
- PGP (pretty Good Privacy) encryption to help secure emails.
- Ddigital Certificate (e.g., VeriSign) to ensure authentication of the data, and provide privacy against eavesdroppers. VeriSign is good for authentication, encryption and digital signing.
- E-mail encryption to digitally sign electronic documents.
To use strong encryption for data, consider buying or downloading online a software program that already has the encrypted data stream. Here are 5 of the more popular encryption programs: (1) MEO Encryption Software 1.1 (Freeware), (2) Dekart Private Disk Light 1.2 (Freeware), (3) Emsa EZ Encryption Tool 1.0 (Freeware), (4) Comodo Disk Encryption (CDE) (Freeware) and, (5) High Power Encryption 4.0 (Shareware) $39.95.
For Mac users, give either MEO’s “Free” Data Encryption Software a try, or consider Kremlin for MacOS (Shareware) $29.95. Before buying it, check out the reviews: “Kremlin Security Suite Review.”
For Windows 7 users, there’s EFS and BitLocker to encrypt and protect data.
There are many more software programs available for encrypting email messages and data files; just ensure you “Choose Encryption Wisely.”
Best Advice: For an overall secure way to safeguard data, use strong encryption (i.e., use either SafeBit, TrueCrypt, or Dekart Disk Encryption) and digital signature technology. And, when needing to secure e-mails, use an email encryption program.
To use encryption for emails, before sending email, select “Encrypt” from the security options menu. The data will be sent from the sender to the receiver who will be able to open, view, and read the message only if they hold on to a shared public or private cryptographic key.
What’s needed for strong encryption for data is…
- to set up a secure messaging system (use email encryption)
- to set up file encryption (use F-Secure FileCrypto)
- to secure transactions (use SSL encryption)
Note: Microsoft Office 2007 includes built-in encryption for single-user or for group distribution.
Also, for those people who want or need to encrypt ZIP files, there’s SecureZIP.
Useful Web Sites
How to Choose the Best Encryption Software for Your Organization: https://blogs.sans.org/windows-security/2009/08/17/how-to-choose-the-best-drive-encryption-product/
NetAction’s Guide to Using Encryption Software: https://www.netaction.org/encrypt/reviews.html
Related Articles
Small Business Data Protection: Dos and Don’ts of Encryption
Images by Southern Illinois University and FunctionX, Inc.
This post is part of the series: Learning Everything About Encryption
Utilizing encryption will safely protect and secure computer information. There’s lots to learn about the topic, as well as to know which encryption software programs will work best.