Amniocentesis Pros and Cons
Amniocentesis
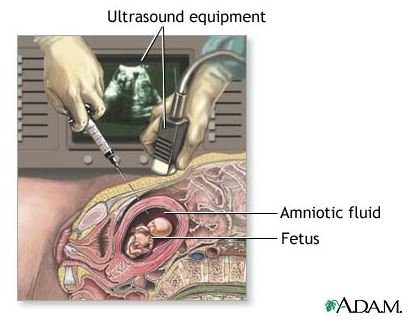
Amniocentesis is a procedure in which amniotic fluid is removed from the amniotic sac through a needle inserted in the abdominal wall in conjunction with ultrasound. It is one of the most valuable studies available for the management of the pregnant woman.
Click on image to enlarge.
Amniocentesis Pros and Cons
Pros
The amniocentesis can be used in early pregnancy to detect genetic defects in the fetus due to chromosomal abnormalities (like Down syndrome), sex-linked defects (like hemophilia), neural tube defects (like spina bifida), inborn errors of metabolism (like cystic fibrosis), and enzyme deficiencies (like Tay-Sachs disease). Indications for genetic amniocentesis include advanced maternal age, previous child born with a chromosomal abnormality, parent carrying a chromosomal abnormality, and family history of neural tube defects.
The amniocentesis can be used in determining Rh problems, in estimating fetal maturity, and in taking the L/S (lecithin/sphingomyelin) ratio, which measures surfactant levels in the fetal lung.
The amniocentesis can also be used therapeutically to relieve hydramnios (excessive amount of amniotic fluid) and to give an intrauterine transfusion.
Cons
Complications are rare but some can be serious. The placenta, fetus, or umbilical cord may be punctured inadvertently, causing injuries ranging from minor scratches of fetal parts to intrauterine hemorrhage, leading to fetal distress and intrauterine fetal death. Placental perforation could result in hemorrhage from the fetal circulation, which could lead to fetal anemia or to increased sensitization of a Rh negative mother. Other hazards include induction of preterm labor and intraamniotic infection.
The Procedure
A health care provider will inform the woman of anmiocentesis pros and cons regarding her situation and will require her to sign a consent form if she decides to be tested.
An amniocentesis may be done on an outpatient basis. The woman will have to lie very still during the procedure and may or may not receive a local anesthetic. The abdomen is scanned by ultrasound to locate the fetus, placenta, and an adequate pocket of fluid. Once located, a long needle is inserted through the abdomen to obtain the amniotic fluid. Rh negative women are given Rh-immune globulin after the amniocentesis, provided that they are not already sensitized.
Menstrual-like cramping is not unusual during or for a few hours after an amniocentesis. If no complications occur, the woman can go home shortly after the procedure. For the remainder of the day, the woman should avoid strenuous activity, lifting anything over 20 pounds, and sexual relations. Most women can resume normal activities the day after the procedure.
Results from the amniocentesis generally take 2-3 weeks.
Sources Used
WebMD: Pregnancy and Amniocentesis - https://www.webmd.com/baby/guide/amniocentesis
Medline Plus: Amniocentesis - https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003921.htm
Photo Credit
Image courtesy of the National Library of Medicine (NLM).