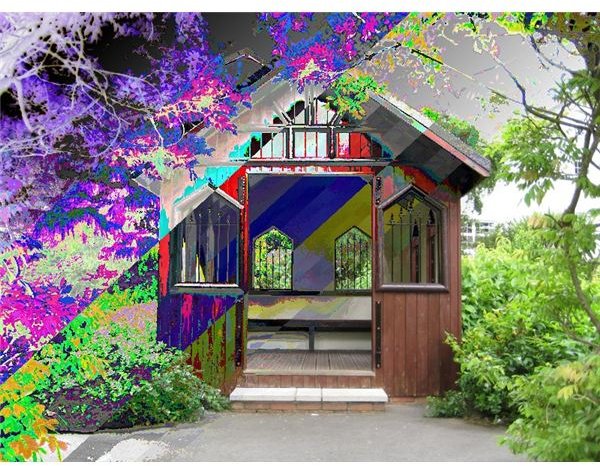
How to Use Blending Modes in Paint.NET - Definitions And Examples
When we speak of layers, there are two things that come to mind: Opacity and Blending Modes. Opacity is a way to control the transparency of a layer by setting an alpha value. This method does not achieve spectacular results, since it is applied to the layer as a whole, without taking into account the color intensity of each pixel. Blending modes are a much more complex and versatile tool, as they analyze each pixel separately and treat it differently according to its color intensity.
What are blending modes?
Blending modes are ways in which the colors in the foreground interact or “blend” with the colors in the background. We call “foreground” the top layer and “background” the layer immediately under it. The way the background blends with the foreground depends on the blending mode of the latter. Mastering these modes is important, because it opens new perspectives and creates new possibilities, enabling the user to do things that would be impossible otherwise. They might seem a little too technical to understand at the beginning but the keyword is experimenting until you get the “feel” of them.
Blending modes in Paint.NET
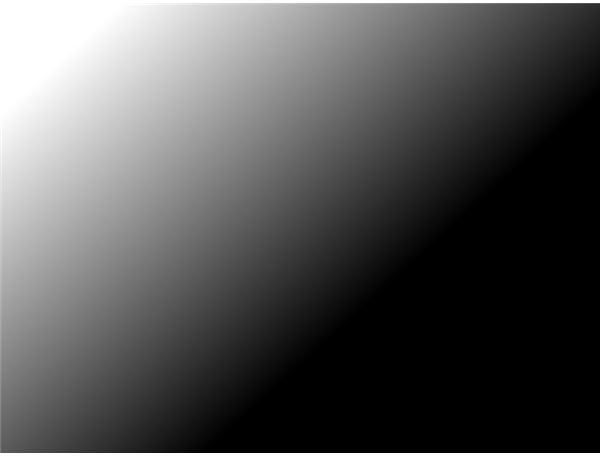
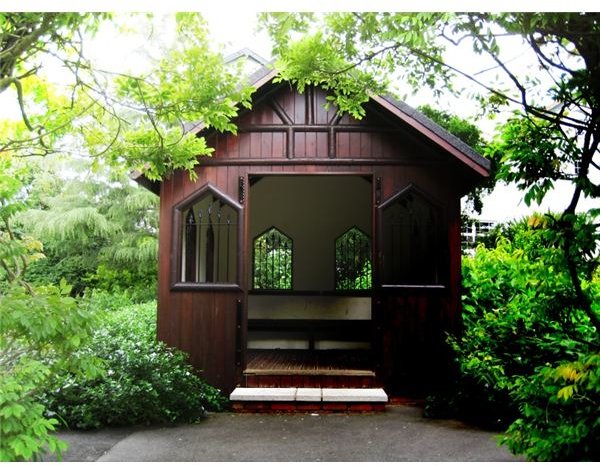
Paint.NET has 14 blending modes: Normal, Multiply, Additive, Color Burn, Color Dodge, Reflect, Glow, Overlay, Difference, Negation, Lighten, Darken, Screen, Xor. To change a layer’s blending mode, select that layer in the Layers window, press F4 to open Layer Properties and choose a blending mode from the drop-down menu. To illustrate the changes, we have chosen two images: The foreground is a black and white gradient filled with intermediate shades of gray.
The background is a color photo.
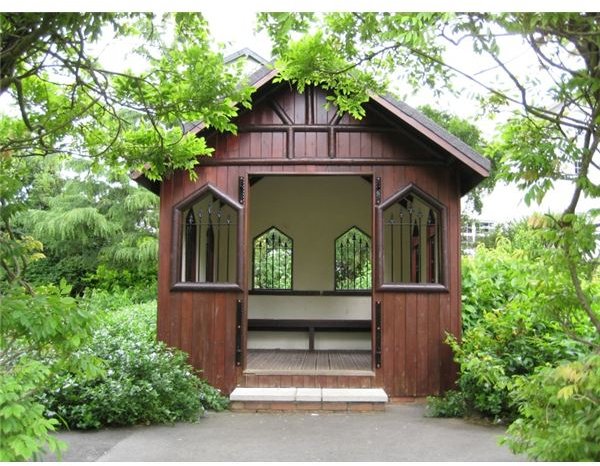

Let’s see what happens if we set different blending modes for the foreground.
NORMAL – is the default blending mode. In fact, it is improperly called a blending mode, since it does nothing else than leave all the job to the opacity value. If the opacity is set to its maximum of 255, the background (in our case the house) becomes invisible.
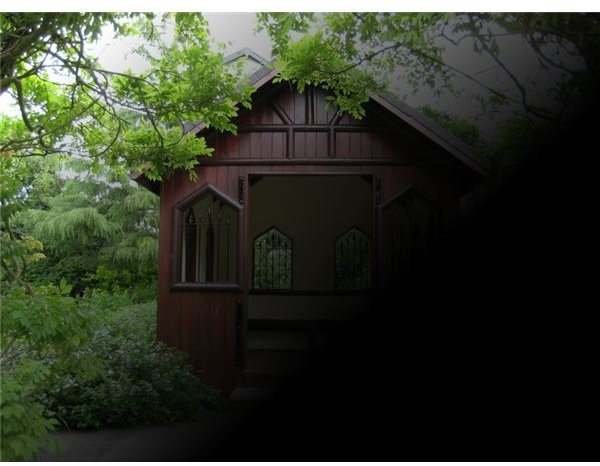
MULTIPLY – is one of the most commonly used blending modes. In this mode, the value of the pixels in the foreground is multiplied by the value of the pixels in the background. It can be used for darkening images, creating shadows and fixing faded photographs. The white is ignored, the black remains unchanged and all the other colors become darker.

ADDITIVE – Instead of being multiplied, the value of each pixel is added to the value of the pixels in the background. The colors become lighter.
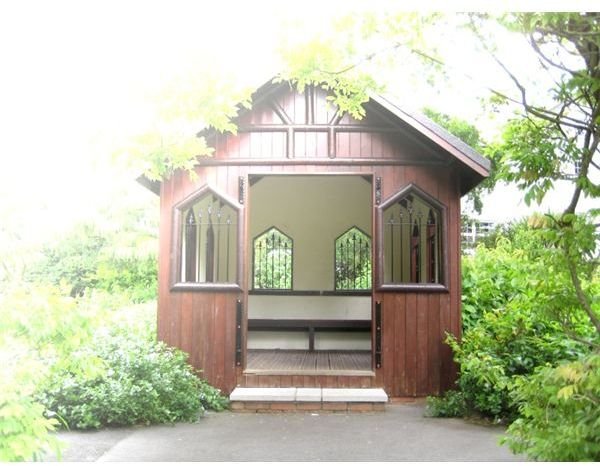

COLOR BURN – In this mode, the background is changed according to the color intensity of the foreground. The darker the foreground, the more the background gets darkened. White produces no change. It is used to make tonal and color adjustments.
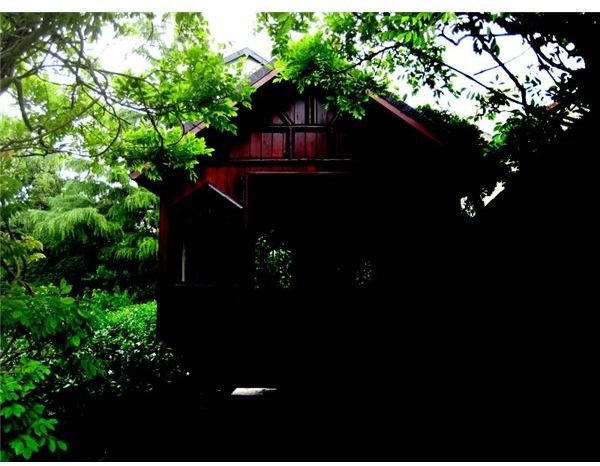

COLOR DODGE – Has the opposite effect to Color Burn. The brighter the foreground is, the more the background gets lightened. Used to make tonal and color adjustments. Black produces no change.
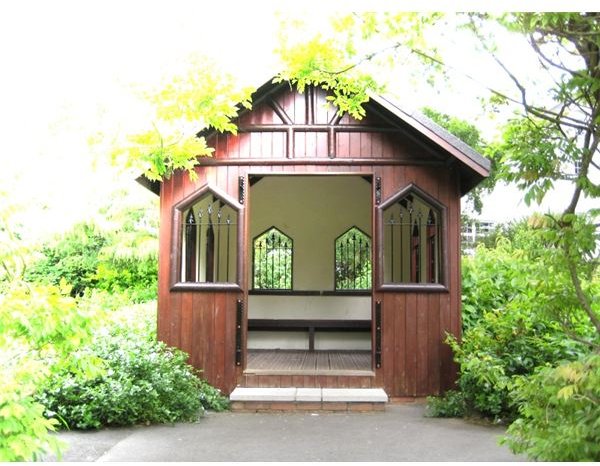

REFLECT – A blending mode used for adding shiny objects or areas of light.
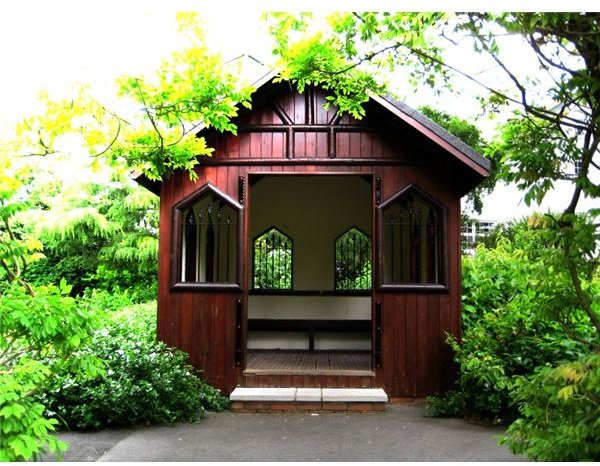

GLOW - Works the same as Reflect, only that the layer positions are swapped.
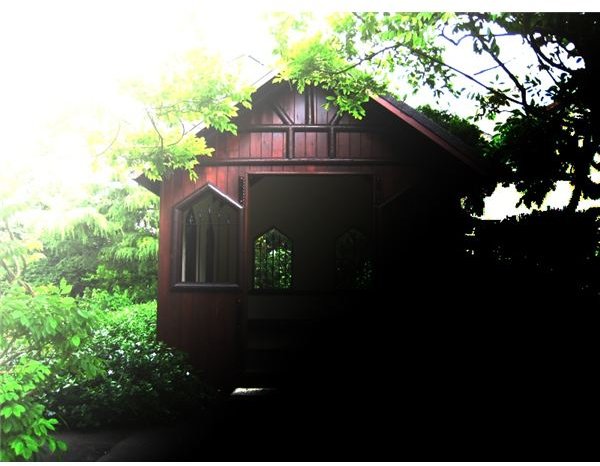

OVERLAY - a combination of Screen and Multiply. For darker colors, it acts like Multiply. For lighter colors, it acts like Screen. The result is that dark colors become darker and light colors become lighter. Used for increasing contrast and sharpening.

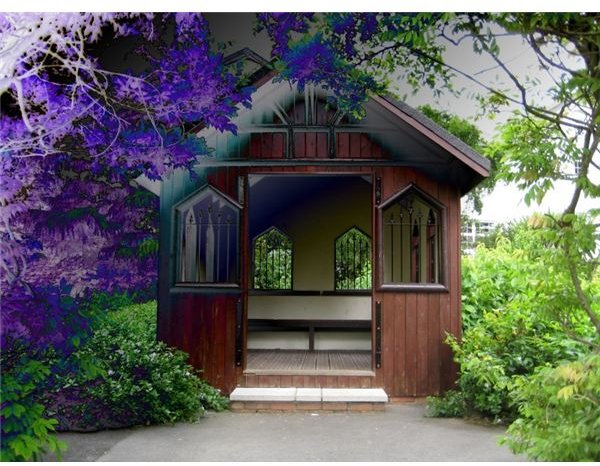
DIFFERENCE - Subtracts the value of each pixel in the foreground from the value of the pixels in the background. White minus any color results in the second color being inverted. White minus black and black minus white will both produce white. Black minus any color results in no change. Used for aligning images and for creating and enhancing a Clouds effect.

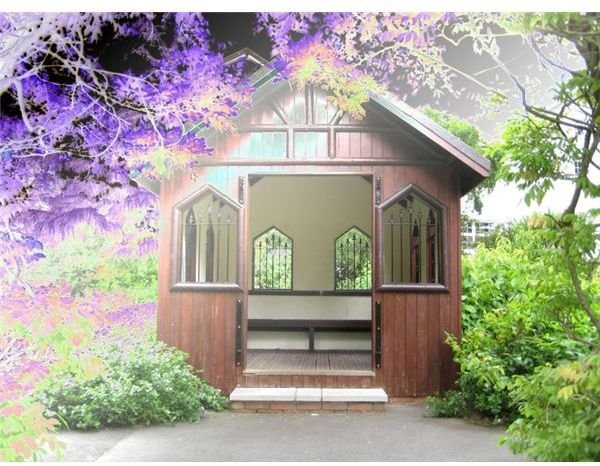
NEGATION - produces the opposite effect to Difference. Instead of making colors darker, it makes them brighter.

LIGHTEN - A mode based on comparing each pixel in the foreground to the one in the background and choosing the lightest of the two.
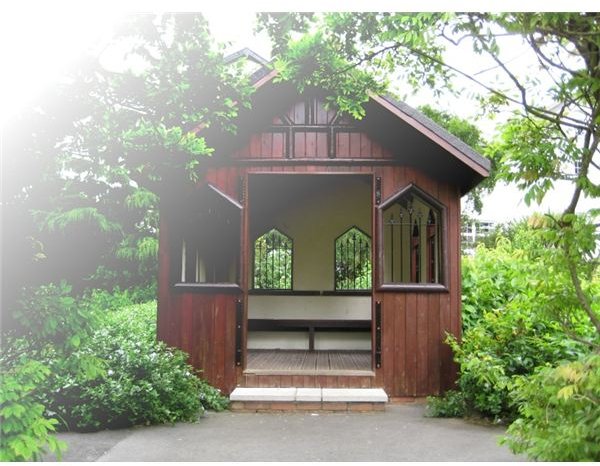

DARKEN - A comparative mode in which each pixel in the foreground is compared with the one in the background and the dark one is chosen.
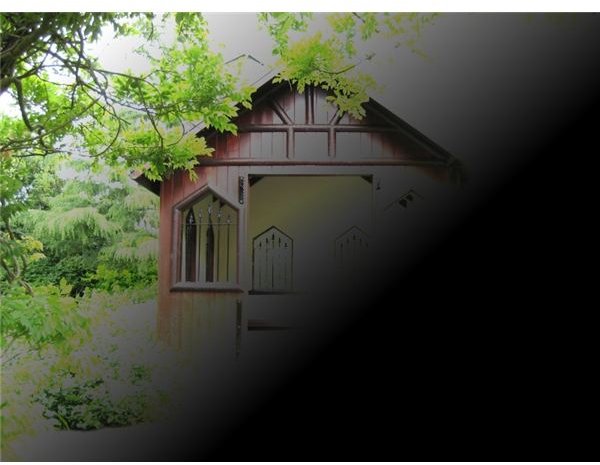

SCREEN - The opposite of Multiply. Black in the background remains invisible. White stays unchanged. The other colors become lighter. Used to brighten highlights and fix underexposed images. Screen was the blending mode we used for creating a snow effect in our tutorial How To Apply A Snow Effect To Your Photographs.
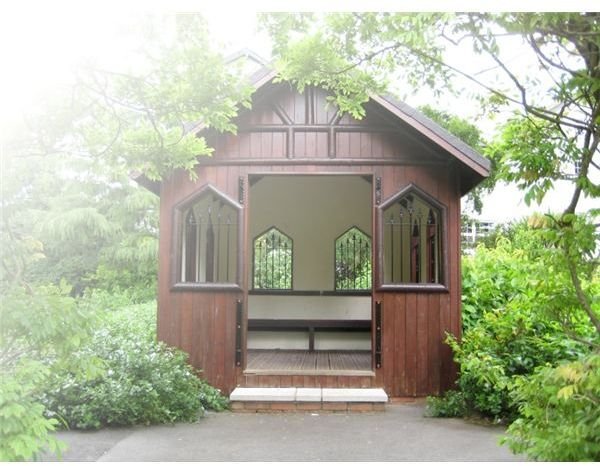

XOR - An advanced blending mode used for image analysis. Not suitable for image processing.

