Using Microsoft's Virtual Machine: Part 1
Why use virtual machines
Simply put, a virtual machine is a computer inside a computer; specifically it is an operating system application contained in a framework that resides inside another operating system. For example, you can have a Server 2008 virtual machine running on a Windows XP computer. Then in the Server 2008 virtual machine you can have many different applications running, for instance SQL Server 2008, or Visual Studio 2005. You can design programs, run simulations on different applications, and they will not affect your base platform. What makes virtual machines such good programs to use is that they don’t interfere with your base operating system, the one that runs your computer.
The idea behind using a virtual machine is that while the computing power of the system is idle most of the time, the virtual machine can be used to run other applications. So you can install Microsoft Office, and run PowerPoint apps from there, and still have your base platform run other applications like a financial program.
Another feature is connectivity. With the virtual machine (PC) you can even create a connection to other virtual machines and have a network of virtual machines as well. So you can test you applications, evening having a domain controller with clients. You can run active directory and other network programs. The advantage is that by having your work done in a protected environment, your main computer or network will not be affected.
You can download the virtual machine components from Microsoft’s web site. Go to www.Microsoft.com, select the Downloads and Trials tab, then select the Download Center. Type in Virtual Machine in the search box and you will get the Virtual PC 2007 link. You can download from there. You will download a file with a .vhd extension (virtual hard drive). You have to select either the 32 bit version or 64 bit version. If you don’t know which kind is right for your operating system download both. Whichever one becomes a disk icon when the download is complete, will be the one that you install. The other one will not be an icon.
VMC: the Virtual Machine Console
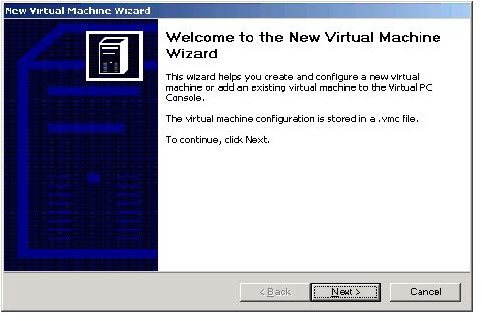
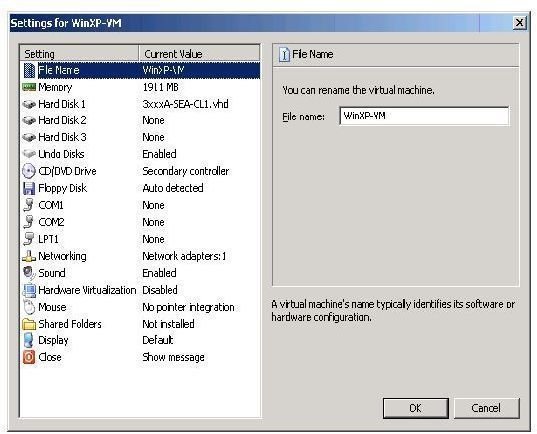
Once you have downloaded a vhd from Microsoft’s site, you can create a virtual machine. This will be your operational application. You create a vmc from the vhd. Let me say that again. The virtual machine console file is created from the virtual hard drive.
Here are the steps:
-
In the virtual console select File from the menu. Select Virtual Disk Wizard. Now a wizard starts, so select Next.
-
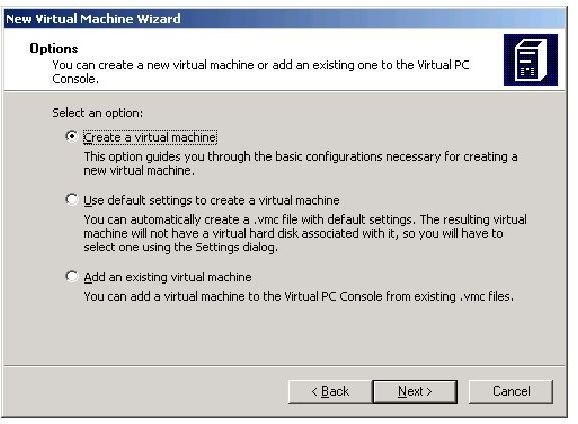
Create a new virtual machine
-
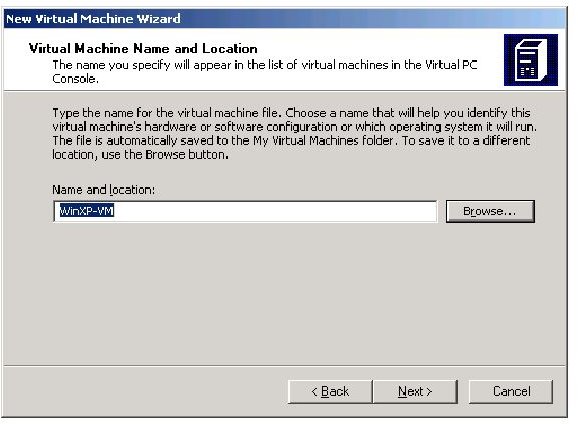
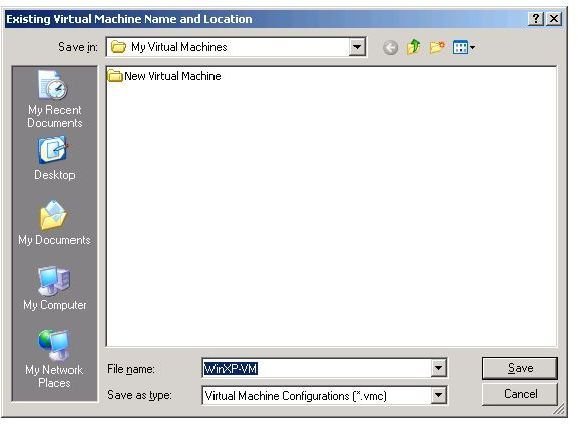
Add the Name and location, the path where the file will be stored at.
-
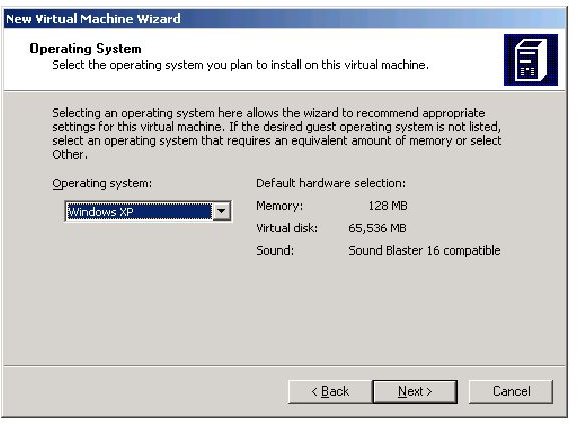
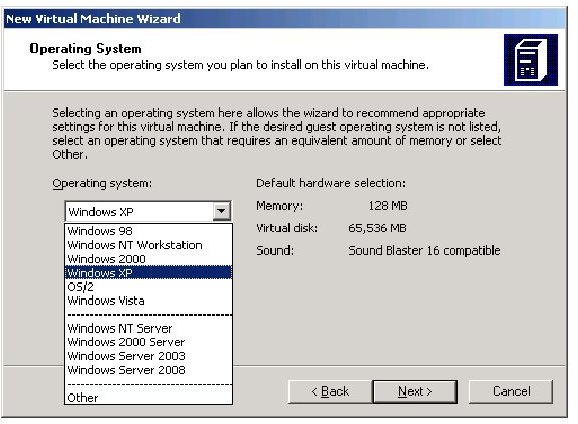
Select the operating system, and your options are win98 to Vista, and your servers are NT up to Windows Vista
-
Or you set up a server with OS selections from NT Server to Server 2008
-
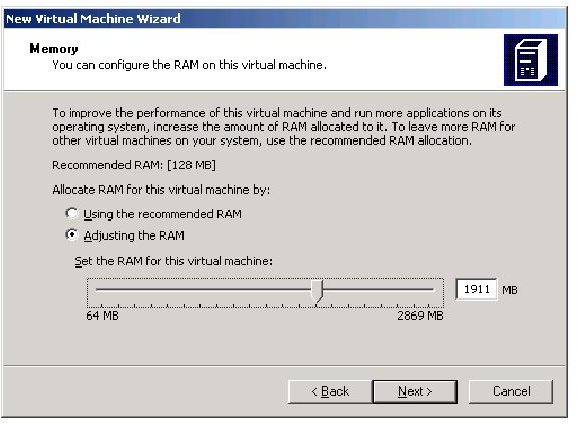
Finally you can choose how much RAM you want your VM to have. Note, your VM can’t have more RAM than your computer RAM.
-
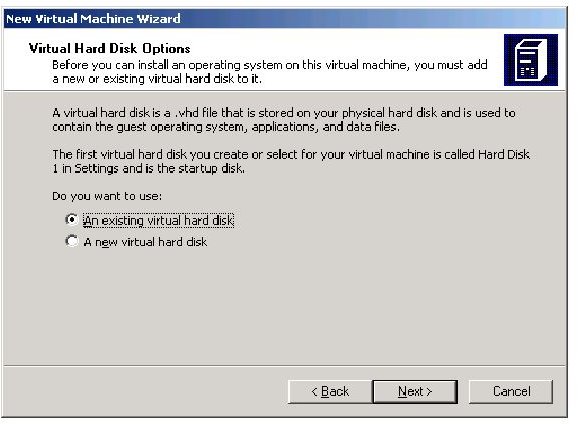
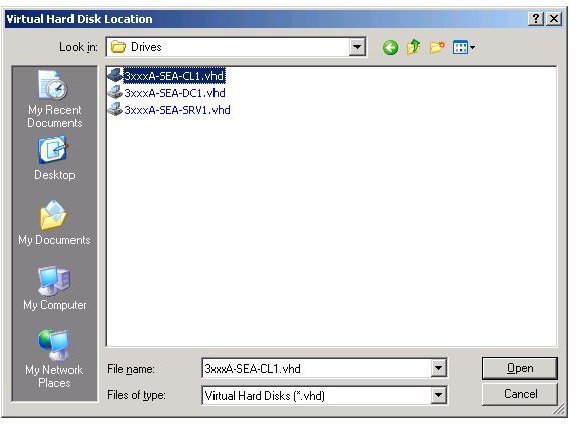
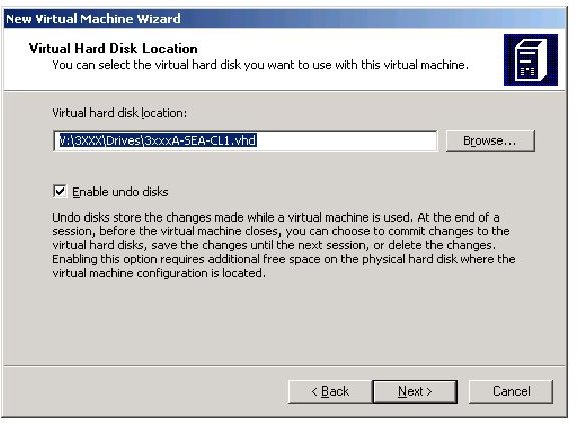
Now you select the VHD; browse to the location where your vhd resides.
-
You will also have to locate the Base file,that will be associated with the vhd. The Base file is another vhd file that can be used with multiple vhd files. That is why it is called Base.
-
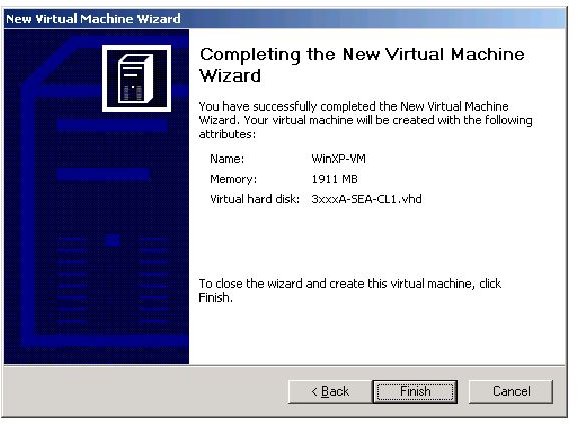
Now you are done.
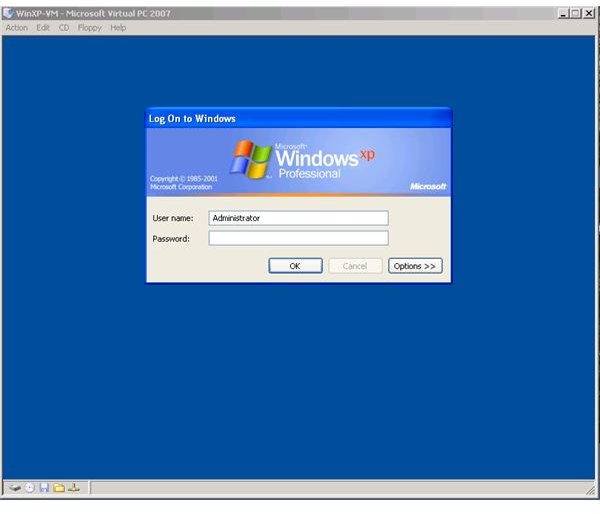
Now you can launch your VMC file and start the operating system.
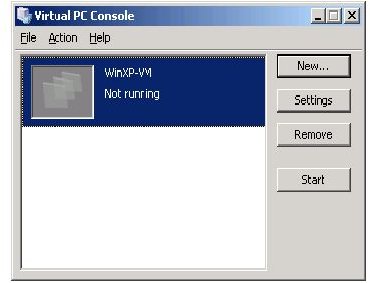
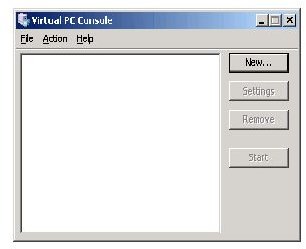
To see how the virtual machine set up works, images are included below to see the steps necessary. The images begin with the virtual machine console, without any virtual machines. The last image is with a virtual machine running Windows XP.
In Review
Using a virtual machine is a good way of testing software and applications in a real time format without using the production environment. Once you have created your virtual machine, you can then load any application on it to test to configure.
Images