Web Browser Security for Internet Explorer 7 and 8
Introduction
Web browsers are perhaps the weakest link in the computer system, as they are the connection point through which a user accesses the Internet. There are a number of threats that can affect a computer with an insecure web browser through a multitude of reasons: web links are not always reliable and can take a user to an unsafe website; some websites require a program to be installed on the system to allow functionality; and many more reasons besides. Therefore securing a web browser is similar to setting up a firewall; basically securing the system’s first line of defence.
Internet Explorer is an exceedingly popular web browser, simply by the virtue of coming bundled with the Windows operating system. It is a familiar interface with the basic security functions of any web browser. However, there is usually a trade off between quality of browsing and security, and usually people downgrade security.
Internet Explorer has had its share of security breaches, the latest of which occurred in December 2008. A security flaw was discovered in its code by security experts, and the millions of Windows users that use the browser were at serious risk from hackers. Microsoft raced to release a patch to correct the problem, and secure the vulnerable file.
Setting security levels
The first step towards securing Internet Explorer against attack is the simplest. Under the Tools menu, there is an option
called ‘Internet Options’. Clicking on this option will open up a small window with tabs alongside the top. Click on the ‘Security’ tab.
The top pane has four categories in which the various sites are grouped. When anyone is selected, the
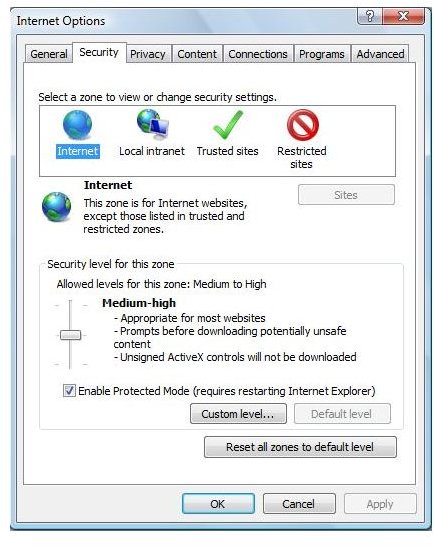
bottom pane shows the level of security for all websites that fall within that particular category. The best option for all the categories is to drag the slider up to ‘High’. Setting the security levels to high entails disabling any browser functions that are vulnerable to outside exploitation.
When a level is set, the Custom level button under it will allow the user to check and uncheck further options. These options pertain to various scripting languages and ActiveX controls, for example.
There is also an option to ‘Reset custom settings’ at the bottom of the security settings pane. Set this drop-down box value to High, and click the Reset button alongside. This option will set the most secure value for all the functions and features that the browser has for a particular category of sites.
Trusted Sites
Since most of the extra functionality that goes into making dynamic websites has been disabled by the High security level, the trusted sites zone acts like a neutral ground. A user can set the security level to Medium-High, and turn on all the functionality for this particular category of sites, if they are completely certain that those sites are free of malicious software and are exactly what they say they are.
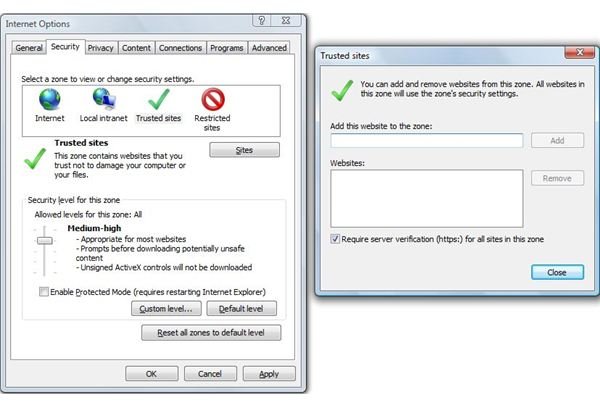
When the Trusted Sites icon is selected, there is a button just below the top pane with the label ‘Sites’. Clicking on this will bring another smaller window where the user can enter the names of sites where they are completely sure of being secure. There is an additional option of requiring verified sites (https:) for all the sites in the category, adding an additional layer of security.
Handling cookies
Cookies are small files left behind by websites to identify the user, or to save session data. Most websites require cookies to run, however cookies are one of the first places that store away passwords and sensitive information without user knowledge. Invariably, a hacker can read the cookies on a user’s computer, and glean quite a bit of information on the individual.
On the ‘Privacy’ tab of Internet Options, there is another slider for cookies. It isn’t possible to run some websites without cookies altogether, so it is best to leave it at Medium, and adjust the Advance Settings instead.
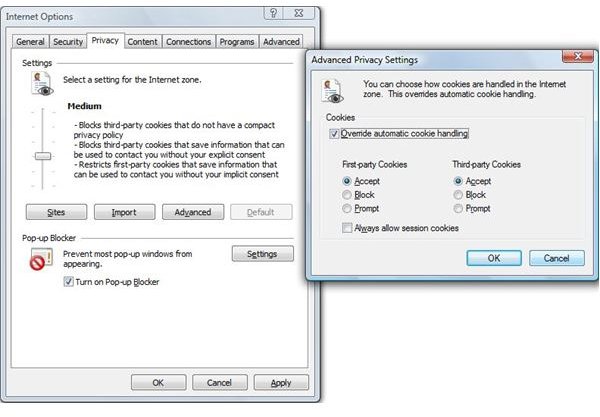
The Advanced Privacy Settings tab has the option of overriding automatic cookies handling. This essentially means that the user can set a response to first-party and third-party cookies. If the user selects ‘Prompt’ for both, the user will receive a message every time a website tries to write a cookie to the browser cache. While this is an excellent way to block websites tracking a user, it can become tedious for session data; therefore there is a checkbox for allowing session cookies without prompts.
Additionally, the Sites button allows the user to set certain sites that are allowed to save cookies to the cache without asking the user permission each time. The user needs to be absolutely certain that these cookies are safe, and do not store any personal information.
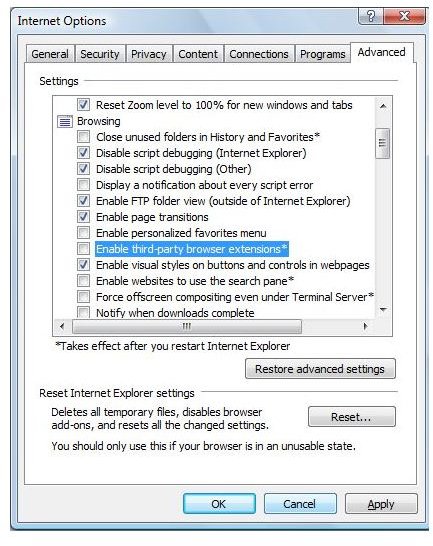
Advanced settings
In the ‘Advanced’ tab on Internet Options, there is a list of settings that apply universally to all the security zones. Over here, it is best to set the following checkboxes in certain ways:
1. Uncheck - Enable third-party browser extensions: this usually means the banner advertisements on a website. These can track the user Internet usage pattern for marketing purposes, and is not always entirely secure.
2. Check – Always show encoded addresses: Encoded addresses will show the user exactly which site they are going to, and avoid phishing scams in this way.
3. Uncheck – Play sounds in web pages: Sound is usually handled in an unsecure manner on websites, and it is rarely integral to the content. This option does not affect built-in multimedia players at all.
Conclusion
Safe browsing ensures the user’s safety from sites that track their usage patterns, or malicious sites like phishing sites which attempt to retrieve usernames and passwords without authorization. It is best to err on the side of safety although some of the resulting actions of the browser may be slightly tedious.
More Web Security Tips!
For more web security tips, see our articles How to Control Cookies in Internet Explorer, How to Block Third Party Cookies in Internet Explorer 7, How To Check If a Website Is Safe, and Using ZonedOut to Manage Internet Explorer Security Zones.