Display Processes Consuming Most Memory Linux - Showing the Memory Used by a Process
The top Command
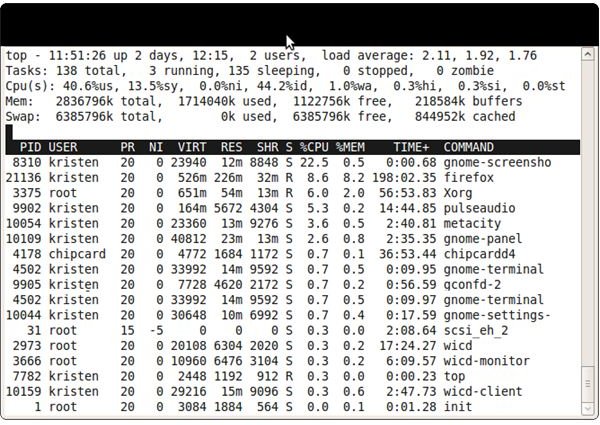
The top command shows valuable real time information for each process currently running on your system including cpu and memory usage. The command display is separated into two sections. The upper part of the window contains the entire system usage. The first line shows the total uptime, the number of users and the load average. The second line shows the number of tasks including running, sleeping, stopped and zombie processes. The rest of the lines show the CPU, memory and swap usage.
The lower section shows usage by process. They are listed in terms of process id (PID), user, priority (PR), nice value (NI), virtual memory used (VIRT), physical memory used (RES), shared memory (SHR), status of the process (S), percentage of CPU usage (%CPU), percentage of memory usage (%MEM), uptime of the process (TIME+), and the name of the command (COMMAND).
The command is sorted by process id by default, but different sort options can be specified. Options that are useful for monitoring memory usage are:
m – sort the processes by memory usage
U – monitor the processes by user name or uid
n
o – the order in which the values are shown on the screen
s – display the swap usage and purgeable memory.
These options are invoked from within the top command by typing the appropriate letter. If the option requires an argument, a line will appear between the top and bottom sections of the command where you can type the information required.
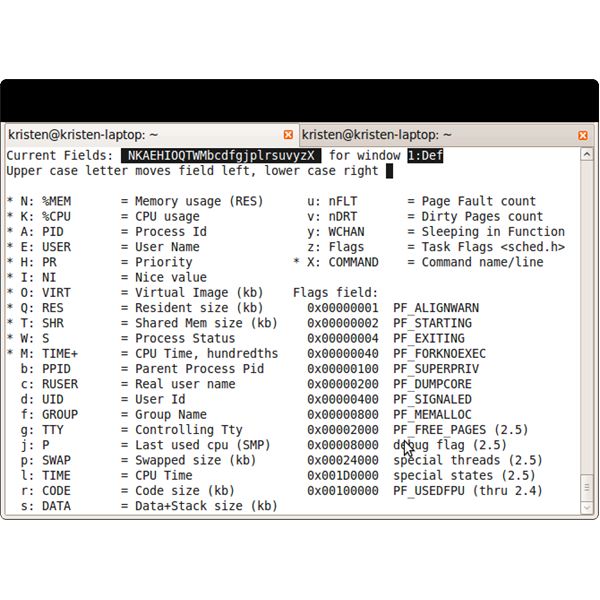
To organize the display so that you can quickly see the memory usage and cpu usage of a particular process, type “o” while the command is running. A new screen will appear, with the list of variables the command can show. Type uppercase “N” a few times to move the memory usage to the first column, then type uppercase “K” a few times to move CPU usage to the second column. Press Enter to go back to the regular display.
When you want to see how much resources a particular user is consuming, type the uppercase “U” while the command is running. The line “Which user (blank for all): ” will appear about 1/3 of the way down the screen. Type the user name press Enter. The display will update with the processes used by that user.