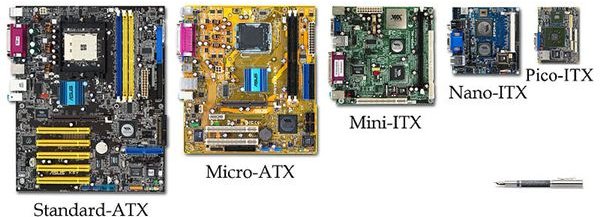
Motherboard Form Factor Comparison From ATX to Nano ITX
Motherboard form factors are generally accepted manufacturing standards that ensure that products from different manufacturers can fit seamlessly into the same spaces, by using the same physical dimensions and mounting points. These dimensions speak to the overall size of the board and also the specifications for components that can be used with the boards.
There are quite a few form factors in use today for use in appliances, personal electronic devices and computers to name a few. While most form factors were developed by Intel to support its products, other manufacturers such as IBM, VIA and Aopen have also developed their own form factors standards. Some of the more popular form factors include: ATX, Micro ATX, Mini ITX, Nano ITX and Pico ITX. Here are their descriptions and a comparison of their intended applications and dimensions.
ATX Form Factor
ATX motherboards use the most popular motherboard form factor standard available today. It was created by Intel in 1995. The typical
board measures 9.6 × 12, however, some companies have extended those dimensions to 10 × 12 in. Since its release in 2007, it has become one of the most popular form factors among computer retailers and persons wanting to upgrade their motherboards.
Developer: Intel
Created in: 1996
Dimensions: 12 × 9.6 in (305 × 244 mm)
Micro ATX Form Factor
When compared to an ATX form factor, Micro ATX boards are about 25% shorter on one side. They are compatible with most ATX cases, but due to their reduced side, they support a fewer number of slots than ATX boards and use smaller power supply units as well. They have become very popular among consumers who want desktops with a small footprint.
Created in: 1996
Dimensions: 9.6 × 9.6 in (244 × 244 mm)
Micro ATX Form Factor
When compared to an ATX form factor, Micro ATX boards are about 25% shorter on one side. They are compatible with most ATX cases, but due to their reduced side, they support a fewer number of slots than ATX boards and use smaller power supply units as well. They have become very popular among consumers who want desktops with a small footprint.
Created in: 1996
Dimensions: 9.6 × 9.6 in (244 × 244 mm)
Mini ITX Form Factor
Mini ITX boards are even smaller than Micro ATX boards. As a result, they have many computer functions such as communications and video integrated onto the board to reduced the number of slots that will be need to build a fully functional computer system. This form factor was specially designed for small devices such as thin clients.
Created in: 2005 by AOpen
Dimensions: 5.9 × 5.9 in (150 × 150 mm)
Nano ITX Form Factor
ITX boards are even smaller than Mini ITX variants and were designed for use in small and smart digital entertainment devices such as Personal Video Records, set-top boxes, media centers and thin devices. They measure 4.7” on both sides and was developed by VIA.
Created in: 2003 by VIA
Dimensions: 4.7 × 4.7 in (120 × 120 mm)
Summary
Using standardized form factors ensures parts are interchangeable across competing developers, manufacturers and vendors. It also ensures that the overall dimensions of motherboards from different manufacturers will fit into standardized cases and mounting racks without a problem, with the screw holes and mounting points lining up perfectly on whatever they are mounted.
While the choice of standards isn’t overwhelming, a motherboard form factor comparison is recommended to ensure that the right solution is purchased.
Credit
Image: “Motherboard Form Factor Comparison.” VIA Gallery