Computer Motherboards Explained: What is a Motherboard?
The Main Piece of Hardware
The motherboard is the main piece of hardware in a computer. Everything else is connected to the motherboard; the CPU (central processing unit) is inserted in a socket on the board, as is the RAM (random access memory). External expansion cards like video and sound cards also plug into motherboard expansion slots. The power supply, which provides the electricity the computer hardware needs to function will also plug into the motherboard, which then supplies power to the components plugged into it (there are a few exceptions: high-performance video cards which need more power to function may also plug directly into the power supply, as do hard drives and other disk drives.) Even keyboards and mice, when you plug them into your computer, plug into the motherboard.
Motherboards are used in all computers, and come in a variety of form factors to fit in different size computers.
Booting Up
The motherboard connects all the other hardware in the computer. When you press your computer’s power switch (which is connected to the motherboard), it sends a signal to power the computer on. The computer’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), located on a chip on the motherboard, proceeds to initialize the computer’s hardware and do some basic POST (Power On Self Test) functions, before handing off to the computer’s operating system (Windows, for example) which boots up.
Now the computer is ready to use, and all the hardware components on the PC are communicating with each other through the motherboard. The hard drive is loading things into RAM, the CPU is processing things from RAM, the keyboard and mouse are sending signals which the CPU is processing, and so on. All these functions are mediated by the motherboard, which also provides a system clock for precise timing information.
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons/Jaimz height-field
Motherboard Components
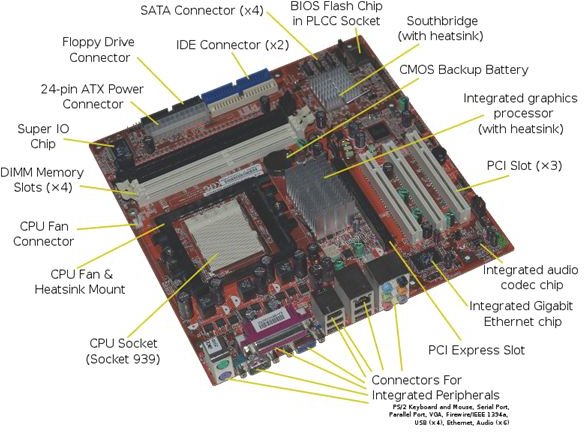
Motherboards have a variety of components, including:
- CPU Socket
- Memory Slots
- Expansion Card Slots
- BIOS Chip
- CMOS BIOS Backup Battery (Allows BIOS settings to be stored even when there is no power to the motherboard)
- Power Connector (To connect the motherboard to the power supply)
- SATA/IDE Connectors (To connect hard drives or disc drives to the computer)
- Integrated Peripheral Connectors: Keyboard/Mouse PS/2, USB, Ethernet networking, Sound Jacks, Video Output (Depending on what functions are integrated into the particular motherboard)
Many formerly separate functions are also being built into motherboards, such as sound and video. This is what ‘onboard sound’ and ‘onboard video’ are. While onboard video does not provide the level of graphics performance needed for the latest games, it’s a good option for users looking for mobility and low power consumption that don’t need that level of performance. In contrast, onboard sound should be more than sufficient for most users, and dedicated sound cards are now nowhere near as popular as dedicated video cards.
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons/Moxfyre
