Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Genotype
An amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) genotype is a technology used in the investigation of this condition. In a 2007 study conducted by the National Center for Biotechnology Information, it was determined that there was not a single locus definitively related to an increase in a patient’s risk of developing this disease, however, there were potentially related candidate single-nucleotide polymorphism’s identified.
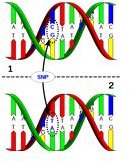
What is a Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism?
Also, referred to as SNP’s, they are DNA sequence variations that happen what there is an alteration in single nucleotide within a genome sequence. For any SNP to be labeled an SNP, at least one-percent of the population must be affected.
What is ALS?
ALS, also referred to as Lou Gehrig’s disease is a severe neurological disease that leads to disability, muscle weakness, and eventually death. This disease affects approximately 3 people for every 100.000 people and about 5 to 10 percent of all cases are inherited. In the cases that are not inherited, the cause is not known for most people. Some non-inherited causes that are currently being studied include free radicals, autoimmune responses, and glutamate.
Symptoms of ALS
The early signs of this neurological disease include footdrop, twitching and muscle cramps (in the shoulders, arms, and tongue), weakness (in the feet, legs, or ankles), slurred speech, clumsiness, trouble swallowing, and hand weakness.
As the disease progresses patients will experience progressive weakness leading to paralysis, trouble speaking, trouble chewing, and difficulty breathing.
ALS Diagnosis
In its early stages, this condition is often difficult to diagnose because its symptoms are not exclusive. Diagnosis often involves diagnostic tests to rule out other conditions that cause similar symptoms. Such diagnostic tests include electromyelogram, MRI, nerve conduction studies, urine and blood tests, spinal tap, and muscle biopsy. Then, some patients may choose to take part in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genotype studies.
ALS Treatment
There is no cure for this condition so the goal of treatment is to make patients more comfortable and to slow down the progression of the disease. There is only one drug approved to treat this condition and it is riluzole. Medications may be prescribed to treat a patient’s muscle cramps, depression, constipation, pain, fatigue, excessive phlegm, and excessive salivation. Therapy may also be used to help make the patient more comfortable. These types of therapy include occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech therapy.
Resources
Human Genome Project Information. (2008). SNP Fact Sheet. Retrieved on January 28, 2010 from the US Department of Energy, Office of Science: https://www.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/faq/snps.shtml
Mayo Clinic. (2010). Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Retrieved on January 28, 2010 from the Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.com/health/amyotrophic-lateral-sclerosis/DS00359
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2007). Genome-Wide Genotyping in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Neurologically Normal Controls: First Stage Analysis and Public Release of Data. Retrieved on January 28, 2010 from PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17362836
Image Credits
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism: David Hall – Wikimedia Commons