The Architecture of Castles: A Little History
A place where every fairytale begins, castles are splendid structures that have found a place in many childhood tales around the world. Although there is no perfect requirement for what a castle looks like, there are scores of structures that have been categorized as castles. With time, many forms and styles of castles changed, but the royalty of the structure remained the same in essence.
A castle is defined as a personal, protected residential building. However, they were also used for defense, supervision, and domestic reasons among others. Though initially they were built just to serve a military purpose, afterward they came to be known as residential buildings. Sometimes, castles were even erected as prisons or as entertainment venues for soldiers. However, as soon as the castles were occupied as residential buildings, the owners (mostly the landlords and bishops) started paying more attention to the size and style of the exteriors. Later on, they were then tagged as “Kingly Residences.”
Understanding Castle Architecture
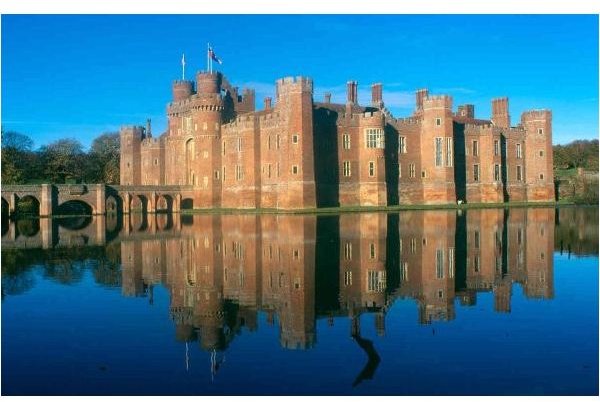

Lords of a particular kingdom originally had homes made of wood. However, these homes were prone to fire both from kitchen accidents and attacking armies. In order to avert the danger of fire being used as a weapon, obstacles were created around the home. Along with practices like creating trenches and barricades, builders also would erect huge walls around the home.
Castles were not just restricted to Europe, but were found in the Middle East as well. Castles with huge walls were found in Japan too, although with their own distinct style. In order to build the castle, the lord must first choose a site. This might be in a key area in order to defend a piece of land. Then the building materials were chosen. While mud and timber were cheap and easy-to-use, stone was more costly.
Main Parts Of a Castle
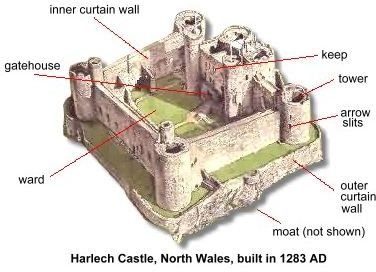
Although some styles changed throughout time, there were main parts of the castle that remained the same. One of them was Motte, which is a mound with a flat top and represents a defensive feature made of mud. Another was bailey, which was a protected zone; each castle had at least one. The keep above the Motte was reserved as the settlement for the landlord, while the bailey housed rest of the landlord’s family. There were multiple baileys created in time for different reasons.
Enceinte was the cardinal guarded zone and was the most unique feature in the entire castle. A huge tower or the chief defensive summit was known as the keep. Trenches along with banks were also made as an easy way to defend, however this construction without a motte was known as ringwork. A darkened jail was identified as dungeon. Curtain walls, which were high enough to reach and equally thick to withstand attacks were built around the bailey. The passage on the walls which permitted the warriors to attack the opponents was known as Moat, which prevented the walls from being sabotaged and was either dry or filled with water. Gateways, either of stone or wood, were used to control the traffic influx. Other features such as battlements, arrowslits, hoardings, etc. ensured extra protection of the castle.
As time passed, castles underwent scientific renovation and became adapted to modern armaments. Construction of castles also spread to other countries, providing them an advantage over their enemies. The introduction of modernization also added to the strength of the castles. With the advent of new technology, the cost to build these defensive structures also went up. All said and done, castles not only became immortal, but also heavily expensive. Architectural splendid, castles have found a place in each and every folklore, making them an important part of history.
