What is the meaning of TCP/IP - IP Address Definition & How Does DNS Works
Finding Your IP Address
Whether you are using Windows XP, Windows Vista or Windows Server, you can find your IP address by doing the following.
Method One
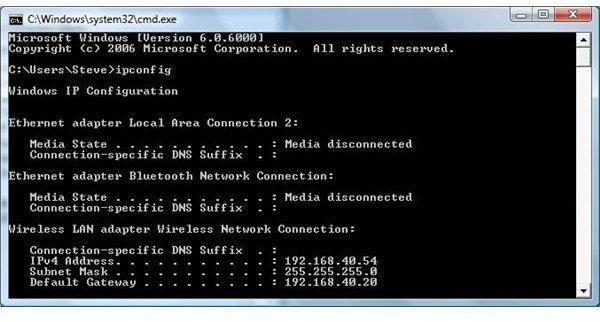
- Go to Start, Run (You may have to go to programs to find this command) and type ‘cmd’
The above command will take you to a prompt. This prompt is a core component used for internal windows commands.
- Now type ipconfig
Method Two
- Double Click on your network icon found by the click in the taskbar
- If the icon is not on your taskbar, you can right click on network places and check the box to show the connection on the taskbar. (General this is preferred by home users and network professionals)
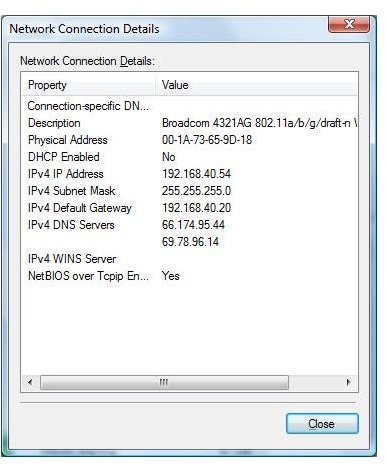
- Click on Details
Look at the example below. This gives an example of the IP address found on my computer. You may have a different IP address. Remember from the first tutorial in this series - no two computers or devices on the same network can have the same IP address.
IP Addresses
Understanding Your IP Address
You can now classify your IP address to see how many devices can be put on your network (This is determined by looking at the first octet or the first number in your IP address). After you see this IP address, (see instructions and pictures above to obtain your IP address) you can see your computer is in one of the following classes:
Class A 1-126
Class B 128- 191
Class C 192 - 223
From the first article in this series, these numbers determine the number of computers or devices you can place in your network.
Class A 16 million
Class B 65,000
Class C 254
Most home computers have the 192 numbering scheme. Therefore you can have 254 total devices. Remember, your router is probably the first device with this number. You can usually see its number by looking at the gateway IP address.
Detailed IP Address Information
More IP Information - DNS and Gateway
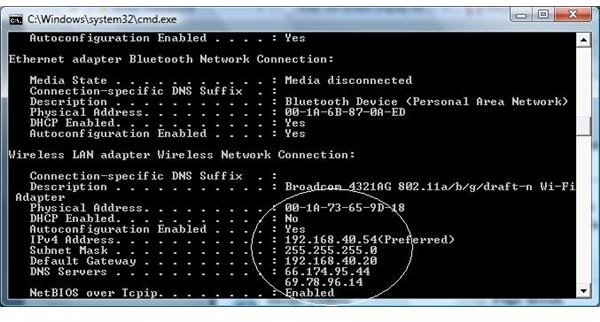
To get more information, use the commands above to get to your prompt (the ‘DOS’ window). Now type ipconfig /all and hit enter. This will return more information. (See pictures below).
The Gateway
The gateway IP address is normally your router or firewall. When you use your computer to travel to the internet, your computer goes to the ‘gate’ to travel outside of your network to its destination. Your private IP address of your computer is changed to the public IP address of the router so that it can travel outside of your network. Example: When you type https://www.brighthub.com into your browser, your browser tells your network card to travel to its destination (brighthub). The request you made goes to the gateway to begin its destination.
DNS Numbers
Your computer must ‘know’ how to take your request and route it to the appropriate computer. When you type the request of a website in your browser, the request travels out your network card to your router (gateway) and travels to DNS servers. These servers (the IP address you see in the last command you made) take the friendly name you typed in your browser (https://www.brighthub.com) and changes it to an IP address. This allows IP to route to its destination and returns information (the website) to you.
The next part in this series will cover the breakdown into networks and host.
Note: This article covers IPv4. Although IPv6 is out, most networks are behind a firewall or other device and use IPv4.
This post is part of the series: TCP/IP for Absolute Beginners
Has TCP/IP or IP addressing got you confused? Are you new to TCP/IP? This tutorial explains in layman terms the TCP/IP addressing scheme and the communications of this protocol.
- TCP/IP for Absolute Beginners
- TCP/IP for Beginners - IP Addresses, DNS & Gateway
- TCP/IP for Beginners - IP Addressing and DHCP
- TCP/IP for Beginners - Troubleshooting TCP/IP & IP Addresses on Networks
- TCP/IP for Beginners - Breaking Down an IP Address
- TCP/IP for Beginners - Change an IP Address & TCP/IP Settings