How Do Computer Trojan Horses Work and How to Avoid Them in the First Place
Understanding Trojan Horses
Computer Trojan horses are one of the most insidious forms of malware the user might run across while surfing the Internet. It is noteworthy that they share a few distinctions that make it easier to understand just how Trojan horses work:
- Trojan horses do not self-replicate
- This form of malware mimics the functionality of a desirable program
- A Trojan program opens a backdoor access to the user’s computer on the system level
How Do Trojan Horses Work?
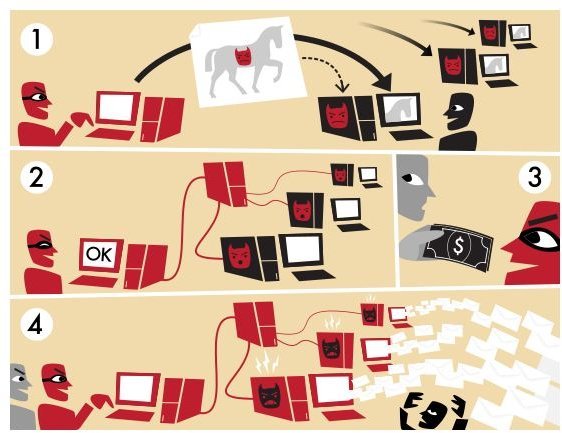
The urgency to remove Trojan horses becomes obvious when the computer user understands that this malware allows a hacker remote access to the operating system. A common function of an infected computer is its inclusion in a botnet.
Hackers turn the machine into a zombie computer that may now – at the hands of a bot herder – send out spam emails that carry a reputable email return address. Small business owners in particular are frequently flabbergasted when receiving angry emails or phone calls about alleged spam emails their computers sent out.
Other Functions a Trojan Program Fulfills
Another good reason for Trojan removal is the hacker’s ability to access data. Files may be uploaded or downloaded, the user’s screen becomes visible to a third party, additional malware may be installed at the hacker’s convenience and keystroke logging assists in stealing access codes and sensitive data.
It is interesting to note that the hacker who accesses the user’s computer and the creator of the Trojans do not have to be the same person. In fact, hackers routinely use port scanners to probe network hosts in an effort to find ports that have been opened by Trojan malware programs. Although more commonly associated with computer worms, port scanners nonetheless offer the same access for Trojan-infected machines.
Avoiding the Backdoor Trojan
Following the belief that an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure, finding out how computer Trojan horses work can help slam the door shut on this form of malware. There are usually four avenues of attack:
- A hacker uses a weak program and exploits a security flaw. Messaging programs are notorious in this context, but so are browsers and even media players. Updating security patches automatically and choosing more secure programs – even if they come with a price tag attached – saves time and money in the long run.
- Shareware in general and download sites in particular are well-known sources of Trojans. Sharing files should be curtailed as much as possible and downloads should only be accepted from trusted sites.
- This goes hand in hand with the email attachments that might be hiding this malware. Frequently these emails come from trusted sources, even if they were not sent by them. The odds are good that a hacker-controlled botnet sent out emails containing the Trojans. When the files are opened and the download is finished, the Trojan is deployed into the system.
- ActiveX controls are a sore spot for software developers. Microsoft Windows relies on ActiveX for animation displays and even data gathering. Hackers are abusing ActiveX functionality to create malware downloads the user believes to be required for properly viewing a website. In case of a doubt, click ‘no’ and do not install the ActiveX.