How to Recover Deleted Data
How to Recover a Deleted File – Is it Possible to Retrieve Data?
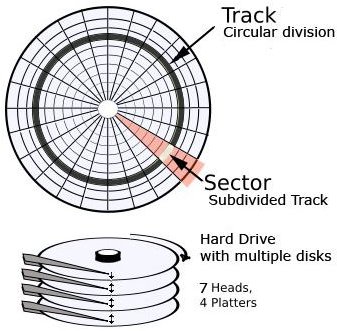
Before discussing how to recover a deleted file, let us speak about how data is stored on hard disks. Once you know how data is stored, you also know how to recover a deleted file. All the information about the different files and folders are stored in the file allocation table of your operating system. The file allocation table has undergone several changes in its format. The first was simply FAT (File Allocation Table), FAT16, FAT32, and finally NTFS: New Technology File System or NT File system. We will be referring to the table as FAT in this article. The FAT keeps a record of the pointers to all the files in form of the tracks and sectors on the storage device. Most of the magnetic devices such as the Hard Disk and Floppy are divided into tracks and sectors (see Fig 1).
Tracks can be considered as different parallel rings on each plate of your HDD (a HDD has more than one magnetic plate similar to the single plate in Floppy). If you have an old unusable floppy disk, break it open to see a black, round plastic plate. The plastic plate is coated with magnetic material to store the data in form of scratches on the disk. While the floppy has a single plate, the HDD has several plates almost similar to the floppy plate for more storage space.
The FAT contains the location of files by noting down the track and sector number. The innermost track is 0 and the number increases for each track outwards. Each track is divided into sectors so that the innermost sector is 0. Thus a file stored at the second track’s third sector would be recorded in the FAT as (2, 3). You may wonder how this is related to file recovery.
When you delete the file, FAT will not delete the file. It will simply remove the pointer from its database, marking the space as free. This means that your data is safe and sound until you perform any write operation that may overwrite the data present at that point. In other words, it is safe as long as you do not use the commands “SAVE” and “SAVE AS”, your file is safe and can be recovered.
Note: Sometimes, defragmenting the volume where your file existed prior to deletion may also reduce the chances of recovering the file. This is because the defragmentation process tries to use the empty space (a deleted file is marked as empty space) to reduce the fragments of a file. Hence, if it recommended that you do use defragment or CHKDSK (which creates log files that may overwrite on the empty space) until you successfully restore the file.
The next section offers a look at how to recover a deleted file if it is still safe, that is, not written over by any other data. In case you use any shredder program to delete the file, your chances of recovering the file are minimal even if you call in the best expert for data recovery.
Recovering Deleted Files – Using Data Recovery Tools
If it was DOS, there was a command called “undelete” that if used immediately, restored the file as such or in chunks that users could combine. However, with the complex operating systems, recovering deleted files on Windows XP needs some programming/codes to find the position of the deleted file and to retrieve the data. As everyone is not an expert, there are plenty of tools available that help in file recovery. These tools can be freeware, free to try (shareware), or paid software.
One such freeware is Restoration Freeware. Being a freeware is an advantage in itself. However, its functions are also worth using, and it isn’t very high size program either. It is just 406 kb, and it may easily fit your floppy drive, however, you may like to run it from your hard disk. It is better to run it from hard disk, and keep a floppy/CD as a back-up option.
Another tool is File Scavenger Data, available for download from CNET at a cost of USD49. The tool is easy to use and like the above mentioned Restoration software, is easy to use and does not use much memory. It runs on all versions of Windows and cannot be used from the command line. However, it does recover recently deleted files among which, you may locate the accidentally deleted file provided it has not been over-written.
While the above tools are for individual use, you may use Bart PE Disk Recovery for commercial use too. Bart PE is actually a collection of software tools that helps in several system tasks apart from data recovery.
Finally, if nothing works, you may have to call in systems expert who may help you retrieve data using sophisticated programs. Even then, no one can guarantee hundred percent data recovery unless your computer was not used at all after you deleted that important file that you want to recover.
Note: To avoid such circumstances, it is advisable to go for regular backups. There are plenty of online backup tools that also offer continuous backup at every few minutes. If you are using any of such program, you need not worry about recovery of data as you would have a recent copy stored online. I would recommend using Idrive online backup that offers free continuous backup up to 2GB of data. For large data, they charge a nominal fee. However considering the loss in case of you not being able to recover data from deleted file, the fee is worth it, as the tool backs up newer version of files as soon as it detects one.