Computer Upgrade Guide - What are the Various Motherboard Slot Types?
Most computers can be upgraded, and their feature-set expanded, by installing a card into one of the motherboard’s expansion slots. Motherboard slot types support a wide variety of devices that run at various speeds, and provide a wide range of functionality. We will review some of the more popular mother slot types and their uses.
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP)
The AGP standard for slot types was developed as a high-speed channel between the graphics card and the computer’s motherboard.
The card slot is directly connected to the front-side system bus, which allows graphics cards to have direct access to the CPU and system memory, thus allowing for greater speed than is possible on PCI buses.
Data transfer speeds: up to 2133 MB/s
Developed by: Intel
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) local bus is a common motherboard slot type that is commonly found in modern PCs. The standard succeeded the ISA and VESA Local Bus standards as the most widely used expansion bus. While PCI supports a wide range of expansions cards including NICs, modems, TV tuners and disk controllers, the standard is not as popular today for use as a graphic port because of its bandwidth constraints That role has by and large been taken over by AGP expansion slots. However a faster version PCI is now available, namely the PCIe standard.
PCI cards are by and large self-configuring or plug-n-play compatible because they allow the CPU to automatically configure them using information the card gives about itself.
Data transfer speeds: 133 MB/s (32-bit at 33 MHz), 266 MB/s (32-bit at 66 MHz or 64-bit at 33 MHz), 533 MB/s (64-bit at 66 MHz)
Developed by: Intel
PCI Express
The PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express or PCIe) standard was developed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP standards. PCIe differs from earlier bus topologies because of its use of point-to-point serial links rather than the parallel bus
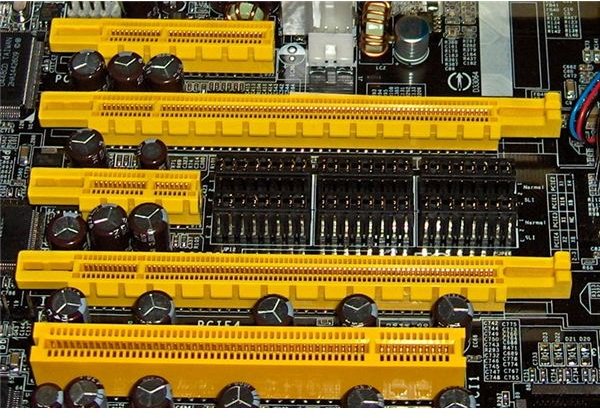
architecture.
PCIe preserves backward compatibility with PCI, at least at the software level. This allows for a PCIe device to be configured and used in legacy applications and operating systems that are not capable of handling the newer PCIe standard, even though a PCIe card cannot be inserted into a PCI slot.
Data transfer speeds:
v1.x: 250 MB/s
v2.x: 500 MB/s
v3.0: 1 GB/s
16 lane slot:
v1.x: 4 GB/s
v2.x: 8 GB/s
v3.0: 16 GB/s
Developed by: Intel, Dell, IBM, HP
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) – Legacy Card Slot
This is an older motherboard slot technology from the days of x286 machines. A few of these slots can still be found in new machines to provide backward compatibility to older cards such as modems, which don’t need lots of bandwidth in any case. They are easily spotted; they are the long black slots.
Data transfer speeds: 8-bit ISA slots are capable of a 0.625MB/sec transfer rate, and 16-bit, slots are capable of 2MB/sec.
Developed by: IBM
Enhanced Industry Standard Architecture (EISA)
These are typically found in servers. The enhanced ISA standard was developed to allow for computers to deal with workloads that ISA
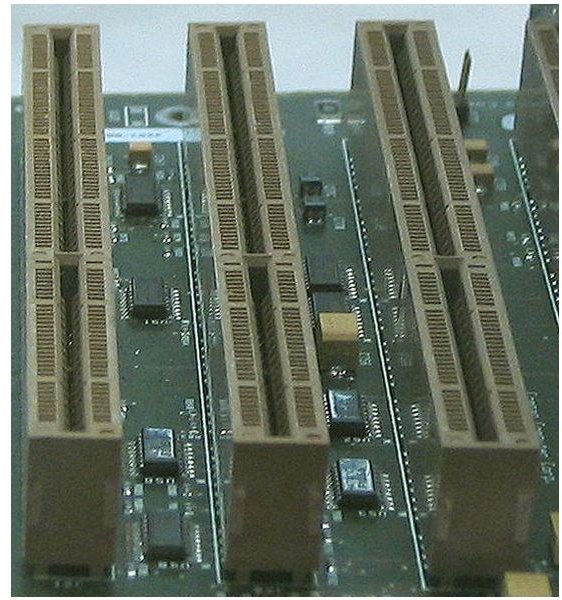
could not handle, as well as a response to IBM’s MCA standard. The EISA bus architecture is also capable of bus mastering; this capability allows computer components to communicate with each other without using CPU processing time. EISA slots are not widely used today, though one or two slots may be included on some computers to facilitate backward compatibility.
Data transfer speeds: 8.33 MHz
Developed by: The Gang of Nine (AST Research, Compaq Computer, Epson, Hewlett-Packard, NEC, Olivetti, Tandy, WYSE and Zenith Data Systems.)
Video Electronics Standard Association (VESA)
Basically, VESA buses are ISA slots with an extra slot at the end. This motherboard slot type was primarily developed to support video cards that required more bandwidth than ISA could provide; at the time VESA slots were considered to be a very fast interface. This slot type is not used anymore; newer video card solutions use PCI and AGP interfaces.
Transfer speeds: 132MB/sec.
Developed by: VESA organization
Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA)
PMCCIA cards are also referred to as PC cards. This slot standard is primarily used on laptops though some manufacturers have installed them into desktops. PC cards support removable credit-card size devices i.e, extra memory, hard drives, modems, network adapters, sound cards, etc. The PCMCIA socket uses a 68pin interface to connect devices to the motherboard and is usually accessible from outside the system case.
PC cards come in three flavors:
- Type 1 slots are 3.3mm thick and accommodate devices such as RAM and flash memory.
- Type 2 is 5mm thick with input output capability. Typically, these are used for modems and network interface cards (NIC).
- Type 3 is 10.5mm thick, and is often used for add-on hard drives.
Data transfer speeds: 133 MB/s
Developed by: Industry-leading companies
Summary
As motherboard manufacturers integrate more features into their boards, the need to purchase dedicated expansion cards to add new features and functionality to computers will diminish. However, the inclusion of expansion card slots allows for easy upgrading of computers should owners decide to do so, and the available motherboard slots support the upgrades.
Credit
Images:
“PCI Express - PCIe - Motherboard slot type and expansion card.” w:user:snickerdo.
“EISA - Motherboard slot type and expansion card.” Appaloosa
“AGP and PCI - Motherboard slot type and expansion card.” Berkut
