Networking Basics for Beginners in a Plug and Play World
Basic Concepts
A network is a way to interconnect data resources so that they can be shared. The most common impetus for the creation of a network is
Internet connectivity. Rather than having every device in your home connected to the Internet with its own Internet account, you can share one connection using a network. Other functions of networking are game play, printer sharing, file sharing, media streaming, and voice over IP phone service. Once you have networking in place, you have the backbone to which all your other devices can connect.
Components and Terms
Before you get started with networking, try to familiarize yourself with some of the essential components and terms.
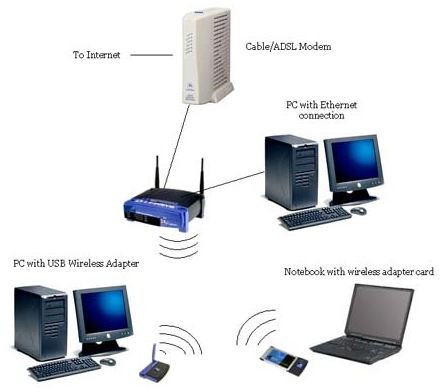
Cable / DSL modem – This is a box that sends and receives data on your ISP’s network. If you have cable service, you’ll see a coaxial cable going to the box. If you have DSL, you’ll see a phone cable going to the box. Also, you’ll see an Ethernet jack that is used to connect the modem to your computer or router.
Cable / DSL router – This box has a WAN port that connects to your cable / DSL modem using a network cable. Your router will also have jacks on it that you can use to connect computers, Network Attached Storage (NAS) drives and other network devices. Often these routers will have wireless capabilities.
Hubs and switches – This is a separate box that usually doesn’t have a WAN port that has four or more jacks for network cables used to connect devices to the network.
Network Cable – This is a cable that has a connector that looks like a phone connector only larger on both ends. This is usually a category 5 or 5e Ethernet cable. These cables are used to connect devices to your router.
Network Adapter – A connector on a computer or other network enabled device that allows it to be connected to a router, hub, or switch via a network cable. Wireless network adapters are often in laptops and other devices that don’t require a connector as they connect via radio waves.
Firewall – A program that runs on your computer or a physical box to provide [security](/tools/Security http:/www.brighthub.com/computing/enterprise-security/articles/65221.aspx) for your network.
IP Addresses
Some other networking essentials basics invovle IP addresses. Your router should be configured with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) enabled. This allows it to assign IP addresses to the other devices on your network automatically. An IP address is a specially formatted unique number that identifies each device on the network. Every device needs an IP address to access the network. Be sure that each of your networked devices are set to obtain an IP address automatically. Usually, an IP address looks something like 192.168.0.9. Advanced users can define the addresses allocated by DHCP by logging into the router. When a computer receives an IP address automatically, it usually also gets the default gateway address. This is usually the IP address of your router. The default gateway tells each device where to go when it needs to access the Internet.
Hooking it all up
Connect the all devices to your router and/or switches and then run the automated setup on your cable/DSL router to configure your network. Be sure to follow the directions that came with your wireless router and you should end up with a functioning network. Just in case though, keep the support number nearby.
More reading
If you get the techno bug, you won’t be happy just letting your network run by itself. Click here to read more about IP addressing. For more about wireless networking, click here. Then there’s more about setting up a Windows 7 network here.