What is my DNS server number and what does it do - Domain Name Server Troubleshooting
Understanding TCP/IP
All computers that use the Internet have one primary thing in common. Computers use the protocol TCP/IP. TCP/IP is a suite of many different protocols. Some of these protocols include TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), IP (Internt Protocol), FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, and DNS.
All computers have a different IP address, allowing them to move across networks and across the Internet. In the early days, computers had modems that were used to dial up bulletin board services. Computers dial directly into the other computer and did not have to navigate across a web of networks across the globe (today with Twitter, computers travel across the web to MARS!). IP addresses route the computer across the world wide web. With the power of routers, these packets are redirected to their intended destination.
The Role of DNS Servers
DNS Servers (Domain Name Servers) provide a friendly name to IP address resolution. In other words, if you type www.brighthub.com, this URL (or address) is translated by your ISP (Internet Service Provider) from www.brighthub.com to 66.165.142.74. This makes life easy as an Internet user. Without DNS Servers, you would have to write down every IP address of every website you were going to visit.
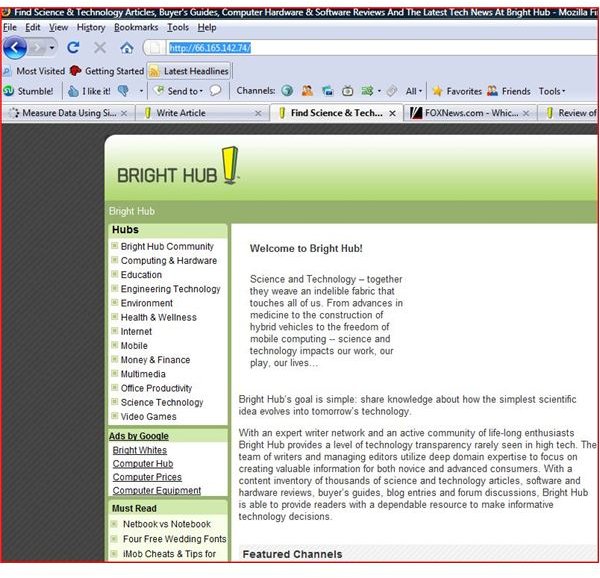
Below is an example of how DNS works (note the ip address in the address line). After opening Internet Explorer, enter the IP address and hit enter. You will instantly be transported to your destination. This actually is faster (going to a website) than typing the address. Remember, if the address is typed, Internet Explorer, Firefox and all other browsers take the request to the DNS server where the ’name’ is traded out for the IP address. Packets are then routed from router to router until your website is returned.
DNS Servers have databases and relay to one another the information that is in them. With a few root servers in the world, websites that are purchased (www.yournewdomain.com) are entered into these servers where the name and IP address are registered together. These servers then talk with other DNS servers so that web browser requests that come in will be translated to the IP address.
How to Find Your DNS Server Numbers
Most ISPs provide at least two DNS Servers so that your Internet connection will be uninterrupted. To find out what your DNS Server numbers are, Go to Start or the Windows Logo and type CMD. At the command prompt, type ipconfig /all. This will show your DNS Servers.
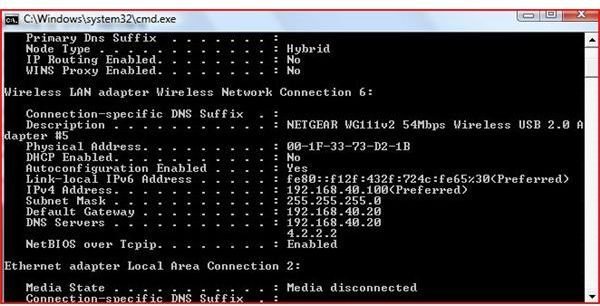
This picture shows the DNS servers provided on my computer. DNS numbers are often given out automatically by your ISP through a DHCP server. If you are connected to a router, you may have a DNS server number in the 192.168.x.x range. Your router will have public DNS ip addresses assigned to it automatically.
Without DNS servers, your computer would be lost on the Internet and you would have to remember IP addresses instead of friendly URLs.