What are Some Business Strategies for Mobile Phone Security?
Password Protection and Encryption
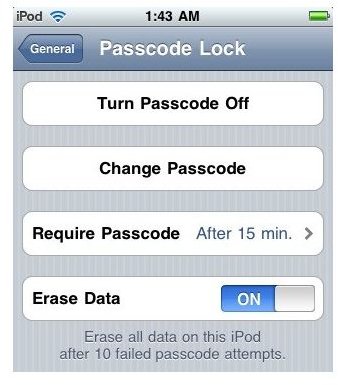
Enabling a PIN number or password on a phone can save users a tremendous amount of hassle. Users may be able to set security attributes on the phone so when someone tries the wrong password a certain number of times it locks phone access or even wipes that content. That operation can protect data.
While password protection is a good step, a better one is encryption. It scrambles the words so they are unreadable, and a key will unscramble them. This is a good way to secure data stored on cell phones. With the right security software, you may be able to wipe the phone remotely if it is lost or stolen.
Image Source
See Also: How a Cell Phone’s Security Policy Can Prevent Security Threats in the Office
Security Patches and Antivirus Software
Apple, Google, and Blackberry release new patches or new versions of their operating system. This is for new features that they want their customers to have. However, another is for security. Security patches come along to make the mobile phones more secure. So users should make sure to have the latest version on the mobile device.
Then, of course, is the use of antivirus software. Because mobile devices have a lot of power and capability, users should treat them as small PCs. That means that protection from viruses and malware, like a PC, is a priority.
Image Source
Malicious Sites and Phishing
Warnings go to PC users not to go to certain websites because malware may be present. The same warnings go for phone numbers. First, if users receive an unsolicited SMS text, even if they believe they know the point of origin, they should not click the links contained in the message. The link could lead them to malicious websites where the phone could end up infected with malware. Second, but less obvious, users should never place a call to a phone number that originates from an unsolicited text message, even if it appears to come from someone that they know and trust, like an employer, bank, or mobile phone company. If they do need to make the call, users should find the employer’s or bank’s number independently to make the call.
Phishing attacks (getting someone to do something because they think you are someone else that they trust) in recent times have affected Twitter. This happens often as users access the Twitter site with their smartphones and they “follow” a tweet. That could be a contact disaster.
Users should know enough not to input their personal information or passwords to any site or service unless they went there themselves, instead of following a link in an email or text. Similarly, avoid phone numbers or any phone call that the user did not first find the number independently–for example by looking it up using directory assistance or by visiting a company’s website.
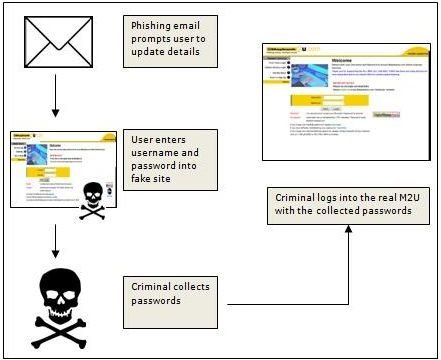
Image Source
Summary
Business strategies for mobile phone security should start with a healthy dose of common sense. This will alert the smartphone user that his behavior can have hurtful consequences to his business. Avoid gimmicky calls or text that wants to guide you to a location that you think you know. Legitimate sites do not send messages like,“We need to verify your account” or “You may be the victim of identity theft, click here to verify your address.” The best business strategies reflect the PC security features that they have taken on. Treat the mobile phone as a PC and use the same mobile phone security policy as you would use on the PC. So if possible have one security policy for both.
See Also: Establishing a Corporate Smartphone Policy for Security