What is the Definition of a Dwarf Planet?
The Problem with Pluto
It was on a warm day in August of 2006 that more than 2500 astronomers gathered in the city of Prague to hold the 26th General Assembly of the International Astronomical Union. The IAU is an organization that was formed in 1919 to “promote and safeguard the science of astronomy in all its aspects through international cooperation”. It is made up of more than 10,000 PhD level astronomers from 90 different countries, and is the final authoritative body in the world of astronomy. That fateful day, a few thousand astronomers would enrage people the world over with something as pedantic as a definition.
For hundreds of years there was no need to create a definition of a planet. Early astronomers could see some planets with the naked
eye, and saw that they moved through the sky in a different way than the rest of the stars. The word planet actually comes from the Greek word wanderer. When telescopes were invented, a host of new objects were discovered. The last planet to be discovered was found in 1930 by an American astronomer, who named it Pluto. As time went on, some interesting things were discovered about Pluto. It was tiny. Really tiny. In fact, Pluto only has a diameter of 1,400 miles. On top of that, Pluto is made mostly of ice. The nail in Pluto’s coffin was the discovery starting in 2005 of several other objects in the Kuiper Belt that were about the same size as Pluto, or even bigger. Finally, astronomers had taken too much guff from Pluto. It was simply too different to consider it the same class of object as the other planets. A new class of object was invented: the dwarf planet.
What is the Definition of a Dwarf Planet?
When the IAU decided to create this new classification, they defined it by comparing it to planets. In the same assembly, a new definition

for planets was created. A planet is an object that is a) orbiting the sun, b) is massive enough so that its gravity has crushed it into a roughly spherical shape, and c) has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit.
A dwarf planet is an object that fulfills only the first two criteria for a planet, but has not eaten up all the debris that is around it. This creates a new type of object that is different from moons or satellites or the irregularly shaped asteroids.
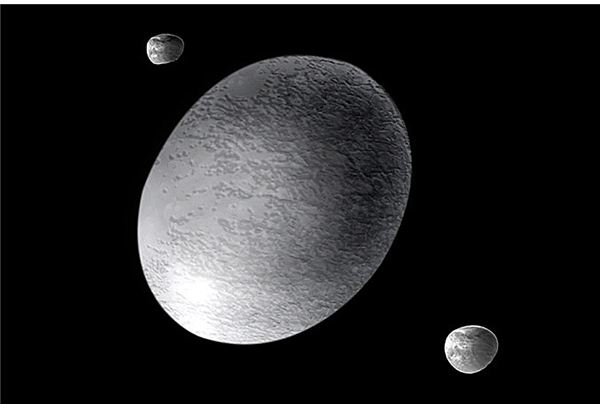
In 2006 the IAU only named three dwarf planets: Pluto, an asteroid named Ceres, and a new object in the Kuiper Belt temporarily named UB313. By 2008, the IAU has named a total of 5 dwarf planets: Pluto, Ceres, Eris, Makemake, and Haumea. The important thing to remember is that the International Astrnomical Union had no malicious intent when they “demoted” Pluto. Some people take it as an affront to the feeling of wonder they had as children, learning about our solar system and Pluto, the runt of the litter. Just remember, Pluto is in a better place now. It can finally feel at home, floating through space with its brethren.
Sources
https://www.iau.org/public_press/news/detail/iau0603/
https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/profile.cfm?Object=Dwarf&Display=OverviewLong
https://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/fap/image/0809/haumea_nasa.jpg