Military Satellites, Communication & Spy Satellites: Learn More about the Purposes of Military & Spy Satellites
Military Satellites Explained
Military satellites are state-of-the art, artificial satellites. Between 1957 and 1999 around 4000 satellites were launched without fail. Of the 4000 satellites, about 50 percent have been used specifically for military purposes.
The major functions of military satellites include reconnaissance and surveillance, positioning and navigation, analyzing and recording information about the surface of the earth (remote sensing), geodesy, research and analyzing weather and weather conditions (meteorology). Here it would be important to note that a satellite is rarely military nor civil exclusively. The payload it carries determines whether it is of civilian or military character. Although military communication satellites differ from commercial satellites, there are some civil commercial satellites used for several military tasks, including command assistance and military logistics support. A satellite with purely military uses, having certain capabilities and multiple systems that differ from commercial ones, is what would be considered a true military satellite.
The best example of a military satellite is the NAVSTAR GPS (Navigation Signal Timing and Ranging Global Positioning System). The NAVSTAR GPS network is operated by the US Air Force. It contains an accurate and reliable satellite navigation system that determines the position of military forces on the ground, air or at sea. The network is also used for many commercial purposes. Its 25 spacecrafts (of which 21 are operational) provide worldwide coverage, including the north and south poles. The spacecrafts are semi-synchronous orbits inclined at 55 degrees to the equator at 18700 km (11,600 miles) altitude. Russia operates the GLONASS navigation system, a less reliable system, compared to the US version.
Military satellites are also used for Geodesy, the study of Earth’s shape and size. Data from geodesic surveys is important to the military, as it is used for map making, positioning, navigation, and a variety of other missions. The Defense Meteorological Satellite Program is a US DoD (Department of Defense) group of satellites that provides complete coverage of the Earth at various times. These satellites maintain an altitude of 833 Km (517 miles).
(Above, Right: The NAVSTAR satellite, image courtesy, https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/17/Navstar.jpg__)
What are Spy Satellites?
Spy Satellites, also referred to as military reconnaissance and surveillance satellites, operate in many parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. These advanced military satellites are used to observe deployment of military forces, weapons development, assessment of damage caused by bombs and also provide intelligence on enemy capabilities.

The development of reconnaissance satellites was officially demanded by the United States Air Force on March 16, 1955. The main reason for the demand of military reconnaissance satellites was to have a continuous surveillance of some areas to determine the weapons-making capabilities of some potential enemies. The first generation spy satellites were Corona and Zenit.
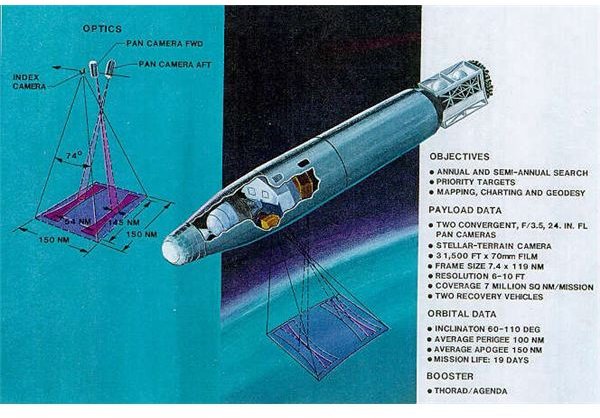
The Corona was a US military spy satellite system used for photographic surveillance of China, the Soviet Union, and other areas between June 1959 and May 1972. The Corona was operated by the CIA Directorate of Science and Technology, with assistance by the US Air Force.
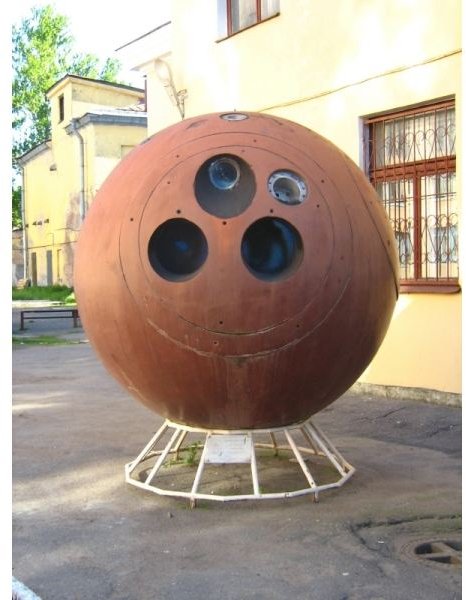
The Zenit program was a successive launch of military spy satellites between 1961 and 1994 by the Soviet Union. However, the main reason for launching satellites was kept secret.
Reconnaissance satellite missions are varied. The missions range from covert operations and communications to monitoring the nuclear test ban compliance and detecting missile launches.
Long before digital imaging systems came into use, reconnaissance satellites sent vital photographs via canisters. The ejected canisters floated down on parachutes and were retrieved in mid-air. With the transition in technology and imaging systems, spacecrafts started employing digital imaging systems, and the images were downloaded via encrypted radio links.
From Napoleonic times, when the French used observational balloons to scan enemy development, to the current state-of-the-art spy satellites used by powerful nations, the importance of such artificial satellites will always be in great demand for political and military state of affairs.
(Image above, Right: The Zenit Space Vehicle, Photo credit: Maryanna Nesina, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Zenit_space_vehicle.jpg)
(Image, Left: The Corona US military spy satellite image courtesy https://www.nro.gov/corona/recsys.jpg)
Credits
https://www.spaceandtech.com/spacedata/constellations/navstar-gps_consum.shtml
https://www.answers.com/topic/military-satellite (SciTech Encyclopedia)
https://rst.gsfc.nasa.gov/Intro/Part2_26e.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corona_(satellite)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zenit_spy_satellite
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Military_satellite
