What to Do When You Are Unable to Access HTTPS Sites
HTTPS Security
Most online merchants, financial institutions and other online services are now use a hypertext transfer protocol secure HTTPS to provide safety and privacy for end-users and network web servers. Websites that will store or collect any personal or financial information will use a HTTPS protocol so that online transactions will be protected against spyware and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Internet Explorer, Firefox, Opera, Safari and other web browsers include certificate authorities that allow Internet users to visit a secure website. Any URL that uses HTTPS should carry a valid certificate, but if the certificate isn’t valid, the end-user will see a dialogue box or a security information alert within the browser asking if they want to continue using the website.
In some cases, a browser will fail to load or access certain secure websites. If you come across this type of problem, check out the following solutions.
Error Messages
You may receive any of the following error messages or dialog boxes when using your preferred browser to connect to a secured website:
- The document contains no data.
- The connection was refused when attempting to contact https://{exampleURLhere}.com.
- The server could not be found.
- The connection has timed out.
- Internet Explorer cannot display the webpage.
- Security Warning: Do you want to view only the webpage content that was delivered securely? This webpage contains content that will not be delivered using a secure HTTPS connection, which could compromise the security of the entire webpage.
- Secure connection failed. An error occurred during a connection to {exampleURLhere}.com. Can’t connect securely because the site uses an older insecure version of the SSL protocol.
First Steps to Fixing the Problem
There are several reasons why a browser might not be able to load, connect or access a secured webpage, but the first thing to do is to troubleshoot your computer using the following steps:
-
Using the same browser, visit another secured website, such as Windows Live Hotmail, Yahoo! Mail or Google Gmail.
-
If the browser is able to visit any of these web-based email providers which are using a secure connection, the secure website that you couldn’t visit is possibly experiencing a server problem. Try again after a few hours have passed, or report the problem to the website administrator by accessing the non-HTTPS webpage, if one is available.
-
If the browser also fails to load the secured websites of Hotmail, Yahoo or Gmail, start fixing the problem using the guide in the next paragraphs below.
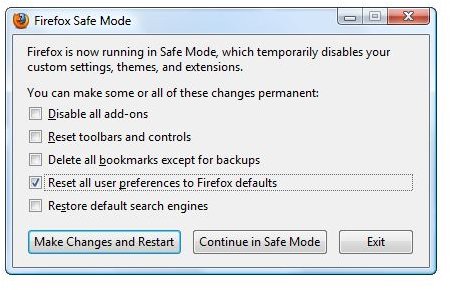
You may also try to reset the browser’s settings to their default. You may install Microsoft Fix It 50195.msi to reset IE. Firefox users can reset the browser by opening Firefox Safe Mode and select “reset all user preferences to Firefox defaults.”
The browsers’ connection settings may have changed without your knowledge or consent. This is especially true if you installed a program that can modify the connection settings for the browser or operating system. You should try to visit the secure website by using another browser on your computer. If the other browser is able to load the secure website, compare or verify that both browsers have the same connection settings in the relevant settings menu. If you are not connecting using a proxy server, uncheck the option to use a proxy server or select the “no proxy” option, and then click OK to apply the changes. Try visiting the secure webpage again.
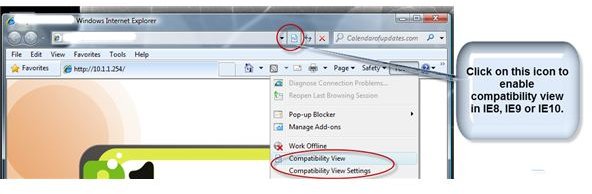
For end-users of Internet Explorer v8 and higher, you should also try to enable the “compatibility view” because the website may not be fully compatible with the new version of the IE browser.
More Solutions
If none of the above solutions will help you access secure sites, you should try the following courses of action:
-
Time and date settings – Verify that the computer’s time and date settings are correct.
-
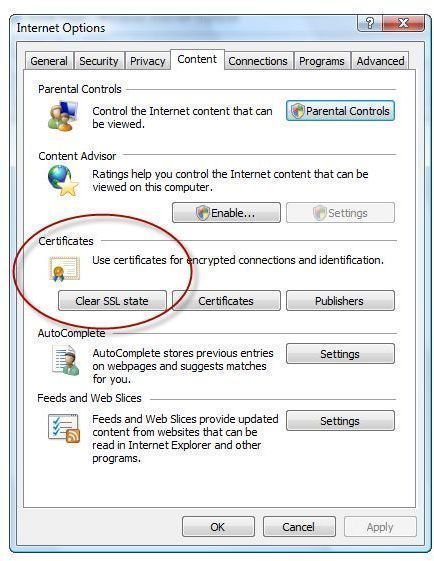
Clear the SSL state – IE users can clear the secure sockets layer (SSL) state by opening Internet options, selecting the Content tab and clicking “Clear SSL state” button.
If you are using another browser, such as Firefox or Opera, you can only clear the SSL state by deleting the browser’s recent history.
-
Re-register .dll files for IE – Simply download and install the Microsoft Fix It 50191.msi to automatically re-register the .dll files.
-
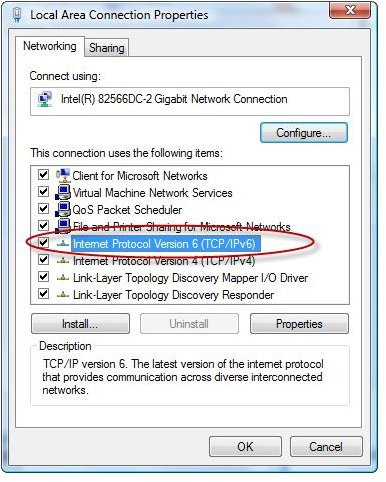
Disable IPv6 – Firefox, IE and other browser will use Internet Protocol version 6, if available. If your Internet environment or local network is not equipped to handle IPv6, you can disable IPV6 by typing about:config into the URL bar of Firefox. Then type network.dns.disableIPv6 in the filter section. Disable IPv6 by double-clicking on network.dns.disableIPv6 in Firefox. You can also disable IPv6 in Windows by opening the Network and Sharing Center in Vista, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 and then opening the Local Area Connection properties. Uncheck “Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) in the list.
-
Disable prefetching - Firefox and Google Chrome users should try to disable the use of DNS prefetching. In Chrome’s under the hood sub-menu, uncheck the box for “use DNS prefetching.” Firefox users must type about:config into the URL bar and then right-click an empty space. Hover your mouse to “new” and then select “Boolean.” Type network.dns.disablePrefetch in the Preference name box. Click OK and then select “true” for the value.

-
Recreate cert8.db file in Firefox – The cert8.db file in your Firefox profile may have become corrupted. Close Firefox and open the profile folder in Firefox and then delete cert8.db file in the list. The cert8.db file will be re-created the next time you opened Firefox.
Malware and Router Issues
Some routers provide an option to filter access to secure sites, so make sure that your router is not configured to block visiting HTTPS webpages. Also, if you are using the router to block or filter some websites, make sure that the secure site that you are trying to visit is not listed in the blocked list.
When a computer is infected with malware, there is also a possibility that you will not be able to access some websites, including secure webpages. Scan the computer using an on-demand scanner, if your resident anti-virus program doesn’t find any malware infections. You can use any one of many free on-demand scanners, such as Microsoft Safety Scanner, Malwarebytes Anti-Malware or EmsiSoft Anti-Malware.
Do you have other tips or solutions for how to access blocked HTTPS sites? We would love to hear from you! Simply post your comments below.
References
- Re-register .dll files for IE: Microsoft Fix It 50191.msi.
- Image credit: Screenshots taken by the author.
- Article based on author’s experience.
- Resetting IE browser: Microsoft Fix It 50195.msi.