Photovoltaics off grid
Introduction to an Off-grid Photovoltaic (PV) System
There are quite a few third world countries that would benefit from a stand-alone PV system, but the people living in these often inaccessible places are too poor to have such a system installed. However, various world charities are making inroads to this, although unfortunately in today’s economic climate, rather slowly.
On the home front, PV arrays have becoming the most popular means of electricity supply for off-grid applications; especially so when supplying power to a homestead or cabin in remote areas. The initial cost for installation of a PV system is high, but this is well offset by the costs of having a grid connection made, not to mention the unsightly pylons and cables.
This is an article on renewable energy in which we will examine a PV array fitted to a homestead in a remote location, where there is no grid supply. We begin with a quick overview of the operation of a modern PV panel and go on to examine the different components required to install a stand-alone PV system.
Overview of a Typical PV Panel Operation
A PV panel consists of two different layers of semiconducting materials, usually silicon treated with a dope to produce a negative and a positive plate.
The negative (N) plate is doped for example with phosphorous, creating free moving negative electrons. The positive (P) plate is doped with boron, creating free moving positive charges called holes. When the plates are joined up as in a PV cell, the P and N electrons are attracted to each other, creating a magnetic field at the joint known as the junction.
When exposed to sunlight the electrons flowing across the junction causes a voltage of 0.5V with a small current to flow to and from the contacts on the plates through a resistance, causing an electric circuit.
PV Mounting Systems
The optimum mounting system should face south at an angle equal to that of the latitude of the building.
- Roof of building
Sloping roofs are a great location for the PV arrays, but remember these arrays can be heavy.
Therefore, the roof must be capable of supporting the array, as well as the stainless steel/aluminum angle section supports on which the PV panels are mounted.
South/East or South/West facing roofs are ideal, but a gap should be left between the base of the panel support and the roof tiles. This will allow any heat to dissipate as PV panels work better when cool and the gap will also allow limited orientation adjustments to be carried out by the installation contractor.
- Outside on a fixed rack
If you have the room in an un-shaded location facing in a Southerly direction; a fixed rack will allow correct orientation, as well as access for maintenance.
Remember the PV output cables have to run back to the building, so there is a power loss/distance to consider. Therefore, the PV rack should be located as close to the house as possible, so allow for this when locating an outside rack. Running the cables underground from the rack to the building is perhaps the best option.
- Tracking Rack
This will give the optimum power output from the PV system, as the rack tracks arc of the sun as it moves across the sky, picking up the maximum sunlight. However, a tracking system is expensive to purchase and, uses power to operating the tracking machinery.
Reference Web : windandsun - PV Mounting Systems
Related: Bright Hub - How to Build a Dual-axis Solar Tracker
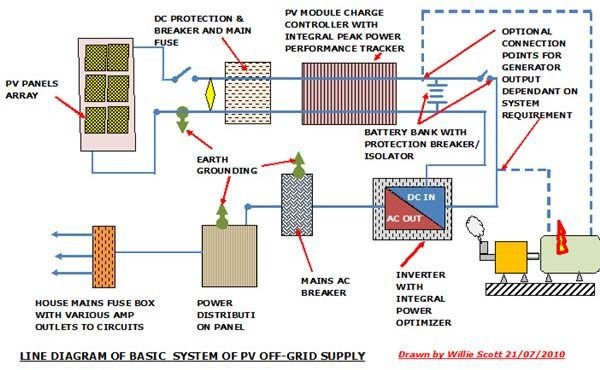
Please see page 2 for information on PV Off-Grid components and wiring diagram.
Components Used in a Stand-alone PV System
The components used in a typical PV system are shown below along with a brief description of their operation.
- PV panels
The panels are made up from PV modules that have been assembled from individual PV cells. The panels are grouped together to form arrays of 12, 24, 36 or 48 volts. The normal building requires between 12 and 20 panels.
The types of materials used in the plate’s construction affect the efficiency of PV panels as noted below;
- Ø Amorphous Silicon – 5% efficient
- Ø Cadmium telluride – 7%
- Ø Copper Indium Diselenide – 9%
The type of materials also effects the costs of the panels, the most efficient being the most costly to purchase. It is therefore advisable to weigh up the pros and cons of the different materials, which are changing rapidly as the technology advances, choose the industries recommended or award-winning PV panels such as:
Award winning PV panels in USA are manufactured by Sunpower USA selling at $4/W, with Revolution.uk also manufacturing panels in the UK, gaining awards, and selling PV panels for £3.50 ($6/W).
- Inverters
Inverters are available from 100W to 10,000W, and play a very important role in the off-grid PV system. The inverters convert the array Direct Current (DC) output power from the PV array into Alternating Current (AC) at 120 or 240Volts.
AC is the most practical current to supply the building, but DC power from the array can be used (but most household equipment such as kitchen appliances, TV, and computers run on AC).
- Control and Safety Components
Integral to the inverter, or attached to it, there can be a Power Optimizer (a DC/DC converter) or a Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) unit which control the system.
These components continually monitor PV output and ensure that in the event of a module failure or sudden changes in irradiance or temperature (all three detrimental to output), the best current and voltage is maintained.
Other controllers guard against overcharging the batteries, and gauges such as LED ammeters and voltmeters show the condition of the current being generated.
Electric fuses are located in each major component as a safety measure.
Reference Web: Windandsun - efficient multi-function off-grid PV array inverters and controllers
- Batteries
A bank of batteries should supply the house with power for at least a day, depending on the amount of power being used, and the output of the batteries.
Modern batteries are mostly deep-cycle batteries; these are becoming more efficient, of higher capacity, and lasting longer. This is mostly due to developments of the electric or hybrid car industry that is continually researching new battery technology.
Unfortunately, the prices of the batteries are still high, as I recently discovered when I replaced my Bruno electric disabled scooter batteries; $150 each! But the original batteries had lasted 10 years, so you get what you pay for.
Remember batteries give of fumes, so store them off the floor in a dry, well-ventilated area and check them regularly. Although the majority needs little maintenance, look for heat spots or the appearance of cracks, but do not touch them and, to keep the kids away from them, provide a locked access.
- Diesel Generator
A diesel or petrol genny will be required as an extra back-up to the battery bank in the winter months when days are shorter and more clouds reduce the PV system’s output.
The PV system installer will estimate the capacity required by the generator at peak loads and work back from there.
Try to get a generator with a decent sized fuel tank as you don’t want to be wandering about in the outback in your pajamas in the middle of a snow storm to top up a fuel tank!
Reference Web: smps.us - batteries and standby generators information.
Costs Associated with an Off-grid PV System
The overall costs of a stand-alone can range from $10,000 to $40,000 depending on the power requirement of the building.
This is a lot of dollars but if you consider that it costs anything up to $60,000 a mile to provide 3 phase electricity supply from the national grid to an inaccessible location, a PV system soon pays for itself.
Other benefits of your own power system are no more electricity bills- ever- and un-spoilt views due to the lack of pylons and cables marching across your land. PV systems are considered to be the most reliable form of electrical power supply.
They are environmentally friendly (saving 1 ton of CO2 emissions/year) and require virtually no maintenance. All these benefits add up to make the installation of an off-grid PV system the ideal source of power for homes or businesses in remote locations.
Reference Web: wirefreedirect - Off-Grid power systems costs and analysis.