What is Windows 7?
A Short History of the Development of Windows 7
Microsoft has developed operating systems since the 80s, starting with DOS, Disk Operating System. Every two or three years they make modifications to the OS. Sometimes the changes they make are tweaks, minor improvements that make working with it easier. Other times the improvements are major, like when they went from the DOS world to the Windows world with Windows 2.0. It’s been a Windows world ever since.
The biggest reason that Microsoft makes changes and upgrades the OS is to keep up with hardware demands. In 1975, the Intel Chip, the 8088 was a single 8 bit processor. Today the processor chip comes in many forms, with a quad-4 chip set and 64 bits. That is a lot of processing power.
Windows 7 comes from a long line of workstation operating systems. Windows for Workgroups (1992), Windows 95 (1995), Windows 98 (1998), Windows Millennium (1999), Windows 2000 Professional (2000), Windows XP (2003), and Vista (2006).
Besides hardware changes, Microsoft has been keen to make the user interface, the desktop, more user friendly. This happens as a result of requests from users, and as a reaction to Apple. User input has made a big impact on Microsoft. Changes in icons, the use of the windows explorer, and search operations were big. Perhaps the biggest change was the introduction of the Wizard.
While it is taken for granted now, the introduction of the Wizard as a consistent installation interface allowed new users to work effortlessly with their computer. The Wizard is a series of screens that allow a user to install programs easily and quickly. If you don’t know how to install a program, just accept the defaults and it will do it for you. This was a big advance in making computer applications user friendly. Another Wizard that was important was a printers Wizard. This Wizard allowed users to easily install a printer, both local or network.
Apple also had a large impact on Windows development. The first Window like interface came on the MacIntosh in the early 1980s. Microsoft soon had its own Windows applications, but it didn’t make the move to an operating system independent of DOS until 1995. Apple was always one or two steps ahead of Windows type development compared to Microsoft. When Windows XP came out, however, it was heralded as a success; it was what an OS should be. It was stable and fast. But still the GUI was not up to Mac standards. For a large segment of users, the GUI was a nice flash, but they were interested in stability and speed. Windows XP had those two features.
Vista was the next OS to be release by Microsoft around 2006. It took many features from Apple. The user interface was snazzy and fun. It had a new kernel, the same one that Server 2008 had, so it could work with any of the new processors. It was scalable up to 256 processors.
But Vista was slow; it took a long time for it to boot up and begin to function. It had to many user blocks. It assumed that all users were first time computer users and needed guidance. It was hard for administrators to manage. Programs that were in the start menu in XP were now missing. Drivers for printers, audio and video cards were not available; there was a lack of backward compatibility. Because of these problems Vista was seen as a commercial failure. While updates followed, and fixed a number of problems, it was not enough; a large segment of the PC user community remained loyal to Windows XP, especially in the business world.
Key Features of Windows 7
Because of the problems with Vista it received more than a face lift and an upgrade. Vista became Windows 7. The same operating system kernel is still present. But there are significant modifications to the user interface.
First the boot up time is significantly improved. The number of programs automatically launched has been reduced. Also the desktop has changed. The task bar can be customized. Web operations were improved: they are faster, easier and safer with Internet Explorer 8. With the new Media Center you can watch TV shows for free when and where you want with Internet TV. Here are some other features:
- Home networking, something that has been difficult with all version of Windows, is made easier with HomeGroup. This application finds or assigns an IP address to complete the network installation. Connection to other computers and printers is done quickly and effortlessly.
- XP support is enhanced. This feature means that you don’t have to abandon Windows XP. You can run many Windows XP programs in Window XP Mode.
- Security has improved since you can prevent theft or loss of data on the PC or portable storage devices with BitLocker, an encryption mechanism.
- New ways to work with Windows are available. For instance, two windows can be placed side by side and evenly spaced automatically. You can also maximize a window by dragging it to a corner and it will maximize. On the lower right hand side of the task bar is a small rectangle; click it and the desktop content clears. Click it again and the content reappears.
- Themes are Microsoft’s desktop background and they now offer 34 different settings. They range from countries like Mexico, and France on the International setting, to Ferrari and Lexus on the automobile front. There are beautiful looking landscapes as well. While the themes don’t improve your productivity, they are pleasant to look at. This is part of the Windows7 Mac-like experience.


Voice and Speech Recognition
Windows 7 supports voice commands and these will allow you to control your computer or programs. Speech recognition software is built into Windows 7.
The computer listens and responds to spoken commands using a microphone. An initial configuration setting is used at the outset where the user will speak a sentence into the microphone. The Windows 7 OS will identify the user voice, diction, and speech patterns. This will enable the speech recognition program to make guesses and approximations to words that the speaker uses in the future. While this is not Star Trek territory, nevertheless, you can use the speech software to run programs and interact with one or multiple applications. The create and edit features allows you it to dictate words into word-processing programs like Word or to fill out online forms in a web browser or cells in a spreadsheet. No special computer is needed for this, although it is recommended that a good microphone be used.
Touch Screen
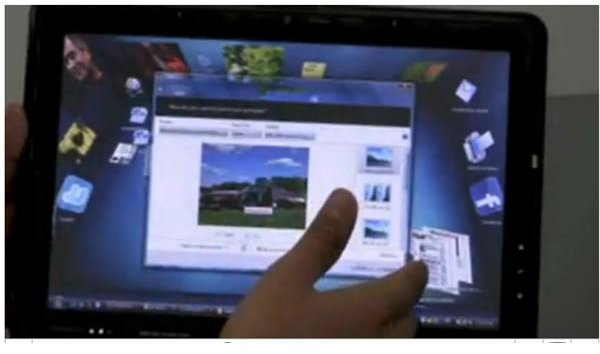
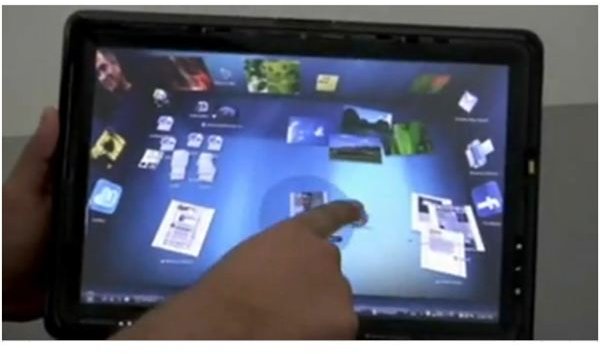
If you have a touch screen monitor, you can access programs from anywhere on the screen without using a mouse. Touch screen monitors are special monitors with built in capabilities for touch applications. All you need are your fingers. You can expand, click, double click, minimize, maximize, launch or close any application.
The multi-touch feature includes gestures in photo galleries like two-finger zoom, flicking, and panning. The multi-touch paint program allows you to draw with your fingers. There is also a multi-touch piano application, this means that you can play a piano on the screen by touching the piano keys.
User Satisfaction
Windows 7 improves the user interface and is designed to make the computing experience fun. To make it fun, Windows borrowed a lot from the IMac. But there are things that Windows 7 does that the IMac does not do. Windows 7 out performs the Mac OS because it provides better previews and navigation right from the taskbar with jumplists, it allows an easier organization of open windows on the desktop and touch-screen capabilities.
One of the biggest complaints about Vista related to the compatibility of software programs. Many did not work with Vista. But compatibility with other programs is available. The following applications worked without any problems Adobe Reader, Apple’s iTunes and Safari, Mozilla Firefox, and Google’s Picasa and Chrome.
On the whole, users should find that Windows 7 lives up to most of the hype and publicity it has received.