Layers of Information Security
Firewalls
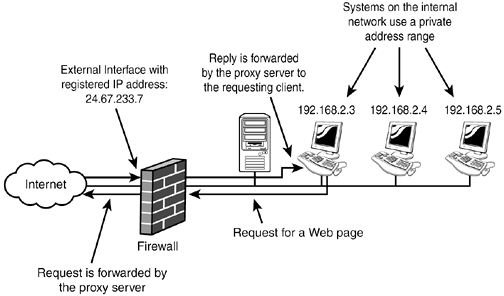
Hardware firewalls are appliances used to keep programs from entering the network. A firewall uses access lists, which are summaries of networks that have or do not have access to the system. For example, a network with an IP address of 150.31.x.x may be allowed in, but all other networks may be denied entrance into the network. Hardware firewalls also can be used to set up VPNs and free servers for other duties.
Image: Brainbell.com
See: How to Assess Information Security Vulnerabilities
Proxy Servers and Routers
Two other hardware devices can control information security for an organization. A server, via hardware such as a proxy server (pretending to be something else) can control what the outside world sees of the network. Since the Internet is an open system, anyone can have access to any device that has connections and access. So one way that protection comes about is by putting up a “smoke screen” on the network. That would be the proxy server. It hides the real network, by showing a minimal connection to the Internet.
A router is a different device that can control access to the network. Like a firewall, it can have access lists that allow or prevent access into a network. They are like a firewall; however, they do more than just monitor access: They route IP packets to other networks. No other device on the network or the Internet does that.
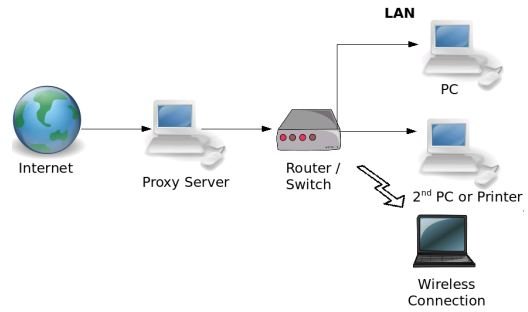
Both of these devices work to control access into the network, one direct (the router) and the other indirect (proxy server).
Image: AmitBhawani.com
Network Controls
Network controls can provide information security for an organization. This type of control occurs at the local level. Authentication involving logins and passwords are key. Every user must have an account that allows him to access the network.
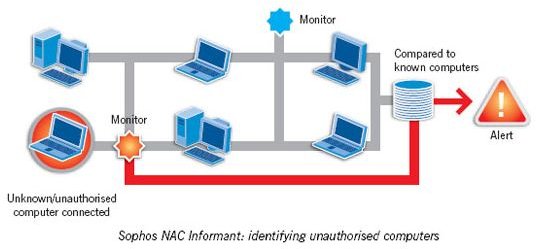
Furthermore, the user must have a password, structured with a sophisticated protocol, like a minimum of ten characters, no common names, like “password,” and a combination of letters and numbers. These network controls can affirm that only legitimate users will gain entrance to the network.
.
Image: ueses.com
Software Controls
Software Controls add another layer to information security by preventing viruses, spam, and other forms of malware from penetrating the system. If penetration does occur, then the controls should remove the infections and return the system to the pre-infestation state.
.
Image: FasterPcCleanClean.com
Encryption
The final layer of security information is encryption. This involves changing the characters of a file to make them unreadable unless a key to decipher the information is available.
Encryption comes in different formats as encryption tools have become more sophisticated. There is manual encryption, which uses software, and a user must initiate the encryption. Transparent encryption occurs automatically without the user intervention.
Symmetric encryption occurs by using character substitution with a key that is used to decrypt the information. On the other hand, asymmetric encryption occurs when two keys are used, a public and a private. Anyone can encrypt using the public key, but only the person with the private key can decrypt the information.
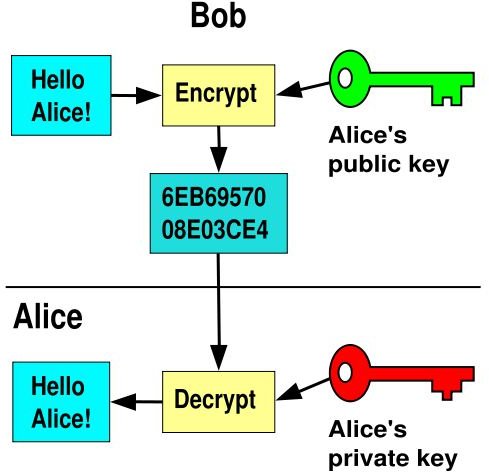
Image: rocketvox.com
Summary
Information Security is the responsibility of the network or security administrator in a company. The goal is to protect the business from unexpected and unwanted intrusions. There are multiple layers that the admin must be aware of, what they are used for, and under what circumstances they should be used. The top five layers of information security are firewalls, proxy servers and routers, software controls, network controls, and encryption. All of these layers must be understood by individuals doing information security for an organization.