Brief History of Cisco Systems Inc - What Does Cisco Stand For?
Cisco in the 1980’s
Cisco was formed by the married couple, Len Bosack and Sandy Lerner, who worked as computer operations staff at Stanford University. In 1984 they were joined by another computer engineer Richard Troiano. They formed the company that would sell computer networking products. The name Cisco, comes from the city name San Francisco.
The early work on the router was the ability to use multiple routing protocols, i.e., instructions sets to guide traffic. Think of a router as a traffic signal at an intersection. All it does is move traffic forward, to the left, to the right, or stop. That is what a router does. But this is not trivial. Each network has its own address, and it works with a routing protocol. The Cisco router combines those elements and redirects traffic, like a Web Page, or e-mail, or a file or document across a network. It can direct traffic from one location to another; continent to continent.
The Executive Team
While the first years showed little growth in the company, this may have been due to the fact that networking operations were not driving computer sales the way they are now. The two founders Bosack and Lerner were managers of different departments at Stanford University.
The early days were difficult; at times making payroll was a challenge. It was not until 1988 that Donald Valentine was approached that things changed. Valentine was a venture capitalist and agreed to capitalize Cisco. In return he would be given stock ownership control of the company. This meant that the old management team was replaced. First he brought in John Morgridge as President and CEO. Over the next few years, while the Internet grew, the demand for Internetworking devices also grew. Cisco was, as they say, in the right place at the right time.
In 1991 John Chambers joined the company. He was brought in after having done management stints at IBM and Wang Computers. In 1995, however, he was named CEO. This was the beginning of the rise to new levels for Cisco. Since 1995, the company has exploded in growth, and it has been the acquisitions plus the basic R&D that Chambers insisted on that made the product brand a success.
Timeline of Significant Events and Company Acquitions
Growth has been Cisco’s underlying motive; most of it was done through acquisitions of other technology companies that directly tied into the type of product that Cisco was interested in. This also included new technologies that were nascent, like voice over IP, and wireless. Here is a quick timeline of the company.
- 1984: Cisco Systems, Inc. is founded by the married couple Leonard Bosack and Sandra Lerner; both work at Stanford University.
- 1986: The startup company ships a router for the TCP/IP protocol suite for the first time.
- 1988: Donald T. Valentine, is brought in as a venture capitalist, and gains stockownership control of the company; He brings in John Morgridge as president and CEO.
- 1990: The company goes public; Lerner is fired and Bosack quits.
- 1993: Cisco acquires Crescendo Communications, its first hardware acquisition.
- 1994: 10 years after being founded Cisco revenues exceed $1 billion for the first time.
- 1995: John T. Chambers from IBM and Wang computers is named CEO.
- 1995-1996 the company completed 11 acquisitions.
- 1996: Company acquires StrataCom, Inc., for 4.67 billion; a maker of switching equipment.
- 1997 and 1998, 15 more deals were completed.
- 1998: Cisco’s market capitalization surpasses the $100 billion mark.
- 1999: Cisco acquires 17 more businesses, spending over 12.1 billion.
- 2000: The Company’s market capitalization reaches $450 billion.
Market Value
The acquisitions that Cisco made had a lot to do with it’s growth in market value. Here are some significant facts about its market value.
Starting in 1994, ten years after being founded, Cisco revenues exceed $1 billion for the first time. In 1998, Cisco’s market capitalization surpasses the $100 billion mark.
In 2000, Cisco’s market value went past the $450 billion mark. It ranked third in worldwide company value behind Microsoft and General Electric. And for a short period in late March, Cisco actually reached a total market capitalization of $555 billion and was the highest ranking company in the world. Earnings reached $906 million for the second quarter of the 2000 fiscal year. Much of this had to do with the worldwide Internet explosion (before the bubble burst).
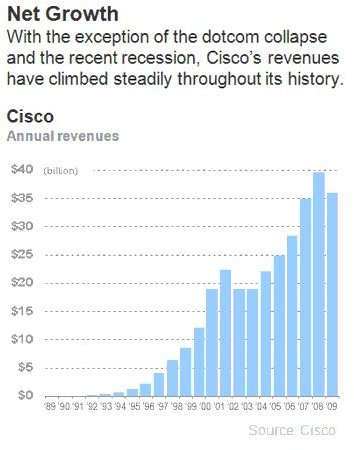
Since then the goal was to increase Cisco Systems’ revenues to $50 billion by 2005.
Image Source: Cisco’s Silver Anniversary: A History of Reinvention
Summary
The history of Cisco shows that it grew from a very small company in northern California, and it was present when the Internet was just getting started. Cisco has been an extremely successful networking and Internetworking company. It was there before the Internet took off as a giant industry, and it grew with the Internet. Its devices, routers and switches, are the backbone to a large percentage of the structure of the Intenet. It grew by the acquisition of companies that it saw representing the future technologies.
Source: History of Cisco
