What to Do about Regedit Unable to Display Security Information Issues?
Registry Keys’ Security Information
The Windows registry is the heart of Windows. It’s a database of settings in Windows, including where third-party application preferences are stored. Each registry key is allowed to be removed or modified if the current user has permission to do so. Administrator user accounts usually have full control over registry keys unless a registry key is hidden or not configured to be accessed by software that adds a particular registry entry. An example was a rootkit registry key added by Sony Music to prevent end-users modifying the permission of the Sony software in copying music. Some malware adds a hidden registry entry, which is a rootkit infection.
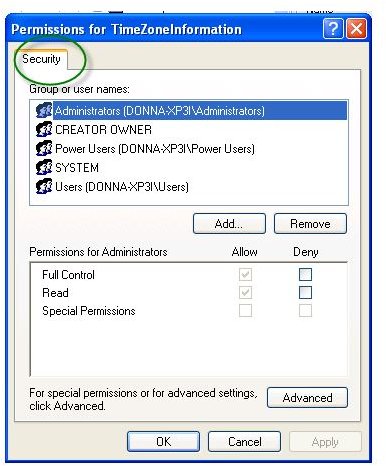
Each registry key has its own permission and when you open a registry key, you should find the security information or the users that have access to the particular registry entry. If the registry editor, aka, regedit is unable to display the security information, you need to troubleshoot or fix it using any of the below steps.
Unable to Display the Security Information
The image at the left shows the registry editor can display the security information or user accounts that have access or permission to access or modify the particular registry key. If regedit is unable to display the said security information, you may try to find a sub-key of a particular registry key to change the permission.
Note: Changing the permission or editing the registry key information means you may stop permissions or allow a new user to access software, or keep the software from running properly. Be sure to backup the registry before doing anything to it. A registry backup can be done manually or using free Erunt, registry program backup. If you’re not comfortable in using the registry editor, it’s best to seek help from a local tech guy or PC vendor, for support or guidance. Be careful in deleting any registry key as it can cause system instability, or Windows or other applications may no longer start.
If the registry editor is unable to display the security information of a particular key, try to fix it by doing the following steps:
-
Browse to the sub-keys of the main registry key where you need to modify a permission
-
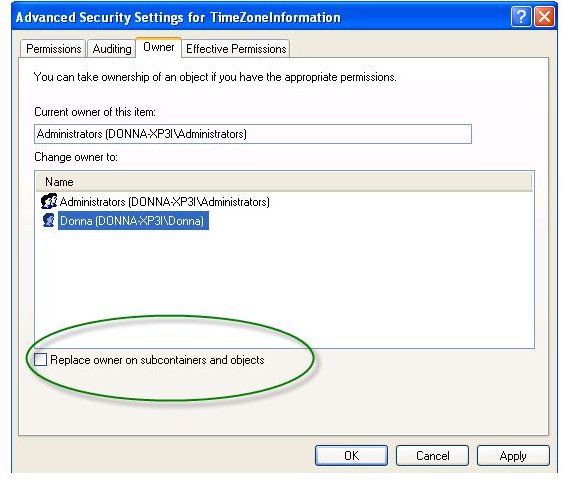
Right-click any or each sub-keys and click “permissions” until you find a sub-key that will display the security information. When you find a sub-key with security information, click the “advanced” button and then click the “owner” tab. Select the administrator user profile and ensure that the box before “replace owner on subcontainers and objects” is not selected.
-
Proceed by clicking the “permissions” tab and give the administrator user account a full permission.
-
Close the registry editor and try to do the same steps for each sub-key that displays security information for the particular registry key where you are trying to edit the permissions.
Old Service Pack and Registry Security Information
If the above steps did not help you to display the security information of a registry key, you may be using an old service pack for Windows. Microsoft has released a supported and new service pack for different Window editions with many fixes and improvements. Try upgrading Windows by installing the latest service pack. You should be able to download the latest available service pack for Windows via Windows Update website for XP or the Windows Update application in Vista and Windows 7.
Advanced Registry Editing
Another method to be able to display the security information of a particular registry entry is by accessing the registry editor using advanced mode. Use this mode only if you are comfortable in using the registry. The advanced registry editing is similar to the steps done in resetting the WIndows password, where a hive needs to be loaded and by entering a “key name”. Depending on the location of the registry entry that the security information won’t display, you need to use these steps:
- Configure Windows to show hidden files and folders.
- Open the registry editor
- Select HKEY_USERS key and click “File” in the menu. Next, click on the “Load Hive”
- In the Open command, navigate to the user accounts’ folder, where a user account needs modification, e.g. C:\Documents and Settings\
folder - Select the hidden NTUSER.DAT file to open
- Enter a key name, e.g. yourname or any name as long as it easy to remember, but it is best to enter the user logons’ key name to which you are trying to modify access.
- Start to expand the registry key hive to modify the permission or access.
- When done, unload the hive via File menu.
Image credit: Screenshot taken by the author.