What is the Difference Between Server Software and Desktop Software?
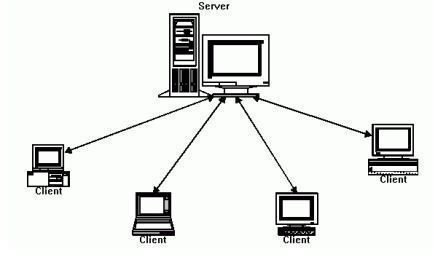
Client-Server Operations
Server software vs Desktop software gets its initial distinction by what operations are performed where. To start with, a Server is a powerful computer that may look like a desktop computer but it has many features that a desktop PC doesn’t have. For one, the CPU will be more powerful; it will be at the upper end of CPU processing in speed and technology with quad-core chips or higher. The amount of memory will also be at the upper limits of current technology. There will be a RAID hard drive technology for on the fly-hard drive replacement in case of failure, and a tape backup system running incremental or differential daily backups. And it will manage the software network and all of the clients on the network. That is just on the server side.
On the client side the hardware will be less robust; the hardware technology doesn’t need to be state of the art, after all it is not a network manager, and it typically performs only one software task, say accounting, or spreadsheets, or Powerpoint.
Source: JavaWorld
Server Software
Typically a hardware network is made up of cables, network interface cards (NIC), routers, switches, and hubs, maybe wireless access points if it is a wireless network. A typical hardware network would be a Cisco network.
On the other hand, the software network is typically a Microsoft, or Linux network. The software controls the operations between the clients on the network and how they exchange information.
Source: hqsoft
So what is server software? It is a manager. It will manage the hardware components via the network configuration, and it can manage the software sets. For example, Active directory is the server side network manager for a Microsoft domain controller. The Domain Controller is the master computer that operates and controls the network, both the hardware side and the software side.
Active directory is Microsoft Network Manager. It controls the users and computers joining the Domain, which is the group of computers. But there are other server software managers. SQL Server 2005 is Microsoft’s SQL manager control program. You can write SQL programs, distribute them throughout the network, have processing occur on the client side and have the results stored on the server.
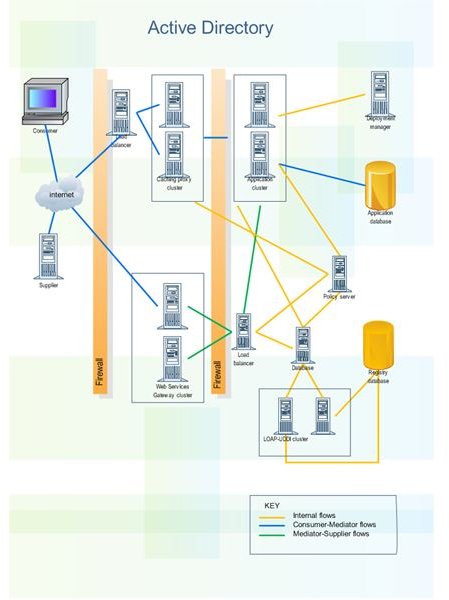
Source: edrawsoft
Other programs such as finance, engineering, science, accounting are typical examples of server programs that work with clients to perform operations between the client and the server.
Source: Non Microsoft Network Management Software
Desktop Software
Desktop software will fall into two main categories; it will be a part of the client-server structure where at least two computers are working together. The other desktop software is a standalone program that runs exclusively on the computer. It is called desktop because an icon can be created and stored on the desktop to run. But it can be stored anywhere on the C drive.
Some examples come to mind here. The Microsoft Office suite, with Excel, Word, or Power point are desktop programs that are installed on the PC and run there independently of any server operations, with the exception of printing which could be on a network server.
Another example would be graphics programs that are designed on the PC, and then ported over to a server for operations to be run on the network, especially those attached to the Internet. If the design is at the PC-client end, but the final operation is on the network-server end, this would still classify as a desktop program.
Other examples are dashboards, which are management information systems. They monitor programs that are on the system. Computer simulators are programs that implement computer operations and run them as if they were the real system.
Summary
In a desktop program the design for a program is done exclusively on the client side, and the operation is done exclusively on the server side. When one is finished the other takes over. If changes need to be done, the client does the changing, and the results are uploaded to the server.
In a client-server operation, both the development and operations can occur on the server side, and they interact simultaneously with the client program never being out of the picture.