Denial of Service Attack: Examples Common Today
Operating System Attacks
Operating systems have flaws, and some come with the way the OS is written. They may create vulnerabilities unintentionally; hackers look for them and exploit them if found. There are several denial of service attack examples for you to consider.
One such vulnerability is a weakness that allows a hacker to enter the system and take it over remotely. Then all he or she has to do is prevent a legitimate user from accessing or working on the system.
Lockouts are possible, where the denial of service–DoS–prevents legitimate users from accessing their system. This comes from the fact that many systems have authentication features, such as a login name and password. It is also typical that there are a limited number of attempts that can be used in order to gain access, and reaching that limit locks out the user. So a hacker can manipulate the login account limit and lockout the user.
See Also: How Denial Of Service (DoS) Works?
Networking Attacks
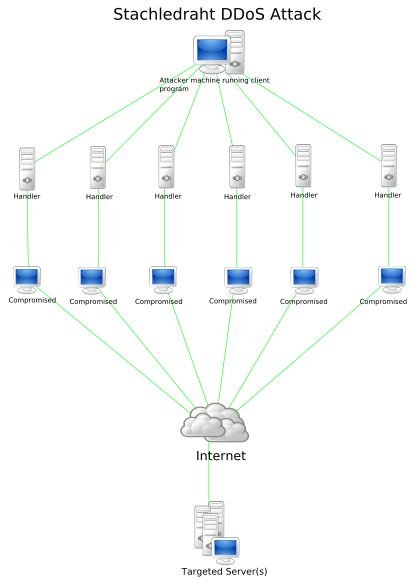
DoS attacks can also affect networks. One example deals with the physical destruction or alteration of network components. Connections between two computers may be disrupted or the disruption will occur among the multiple devices on the network. One way to do this is to flood the bandwidth with extraneous traffic. Legitimate traffic can’t enter or it travels at a reduced speed.
Another example is a “SYN Flood” attack, which prevents legitimate hosts from connecting to the network. The attacker starts the process of establishing a connection to the victim’s machine; however, the ultimate connection is incomplete, deliberately so. Then the victim’s machine has reserved one of a limited number of data structures required to complete the impending connection, but it will never complete it. So the real connections are never complete, while the victim is waiting for another, bogus, connection to complete.
Non-Renewable Resources
DoS attacks can also consume scarce, limited, or non-renewable resources. One example of a denial of service attack comes with the destruction or alteration of configuration information in the operating system. Such an attack may flood the system so that it is incapable of performing the normal operations. The CPU may be performing at the 100% level, which prevents other processes from running.
Another example is when programs are triggered to access more and more memory, thereby filling up the available space in the system. Generating excess mail messages may take up memory. This slows the system down, even to the point that other programs can’t run. Even after a re-boot the problem does not go away. In such a case the DoS attack now comes with malware that has infected the system.
Sources
For an article on legal cases involving hackers and cyber crime see: Busted Hackers and Cyber Criminals - Interesting Cybercrime Cases
Operating System Attacks: https://www.irchelp.org/irchelp/nuke/
Image: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Stachledraht_DDos_Attack.svg Common License
Networking Attacks: https://www.cert.org/tech_tips/denial_of_service.html