This Day in Astronomy and Aerospace History: October 12
This Day in Astronomy and Aerospace History
1962
The United States and the Soviet Union enter into an agreement to combine their space-related efforts in the fields of meteorology and telecommunications systems.
1964
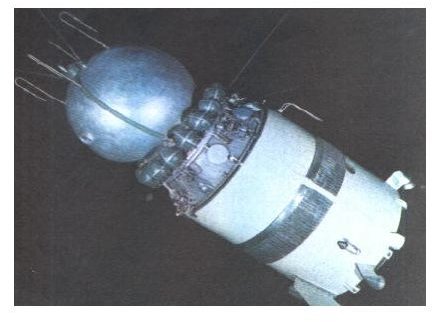
The Soviet spacecraft Voskhod 1 was launched on the first mission to carry multiple crew members (three), as well as the first to include physician or a scientist. Due to the time pressures of “the space race,” the Soviets launched the craft before the United States launched the Gemini series, Voskhod was launched without ejection seats for re-entry, an escape tower for evacuation during launch, or spacesuits in case of mid-mission emergencies. However, despite the lack of safety precautions, the mission would be a complete success, with the three-man crew returning after sixteen orbits over the course of twenty-four hours and seventeen minutes. Its success and the highly-publicized television footage it returned escalates the “space race” to a new furor.
1969
The Soviet spacecraft Soyuz 7 was launched. It failed to accomplish its mission due to equipment failures, though the USSR will not publicly admit the failure.
1972
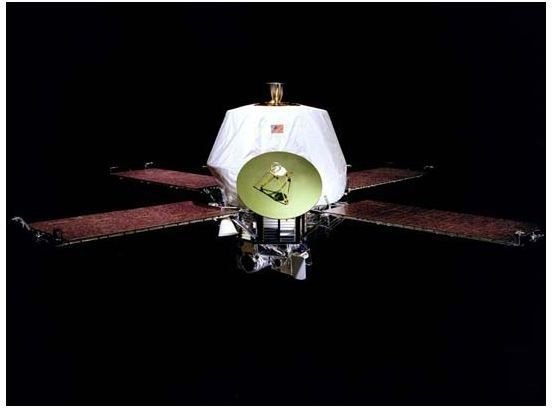

The NASA space probe Mariner 9 successfully photographs the north pole of the planet Mars, where far later missions will seek evidence of the presence of water. On November 13, 1971, it had become the first probe to orbit another planet. Until its deactivation on October 27th, the probe will continue to return high-resolution photos of the planet’s surface.
1975
NASA launched space vehicle S-195.
1976
The fifth Space Shuttle to bear the name Enterprise conducted an approach and landing test flight.
1977
The sixth Space Shuttle Enterprise underwent its fourth test. The Enterprise was built without a heat shield or functional engines specifically for the purpose of performing flight tests inside Earth’s atmosphere. NASA’s original intentions were to refit the shuttle for space flights, but during the course of the tests, the details of the final design changed.
1985
The Space Shuttle Challenger was moves to Vandenberg Air Force Base to be prepped for mission STS-61A. The mission will set a record for carrying the largest crew to date into space.
1994

NASA lost radio contact with the Magellan space probe during its descent into the thick atmosphere of the planet Venus. Over the course of the day and the next, the probe was presumably vaporized. Before its destruction, it returned unprecedentedly detailed photographs of much of the planet’s surface.
2005
The People’s Republic of China launched its second manned spaceflight, the Shenzhou 6, carrying Fèi Jùnlóng and Niè Hǎishèng on a five-day mission.