Can Gleevec Effectively Treat Neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatoses affect the nervous system and are classified as genetic disorders. The growth and development of neural cell tissues is primarily affected. Current treatments, for both types of this disorder, aim to control the symptoms, but the disorder itself cannot be cured or effectively treated. However, Gleevec, an anti-cancer medication, has shown promise in possibly being the first effective treatment for this disease.
What is Neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatoses affect the nervous system and are classified as genetic disorders. The growth and development of neural cell tissues is primarily affected. Tumors grow on the nerves causing a variety of symptoms, depending on the nerves they grow on. Patients can also experience other abnormalities, such as bone deformities and skin changes. Other symptoms can include hearing loss or ringing in the ears. Headache, facial numbness, or facial pain due to tumor pressure can occur. Poor balance can also occur.
What is Gleevec?
Gleevec, also referred to as imatinib, is a protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor that helps to stop cancer cells from spreading. It does this
by blocking an abnormal protein’s action that tells cancer cells to multiply.
Of course, no medication is without side effects or other precautions. The common side effects include:
- Diarrhea
- Gas
- Vomiting
- Indigestion
- Muscle cramps
- Anxiety
- Teary eyes
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Joint pain
- Depression
- Night sweats
Serious side effects can also occur and should be immediately addressed by a medical doctor. These include:
- Under eye puffiness
- Weight gain
- Heartbeat that is irregular, pounding, or fast
- Fainting
- Increased urination, specifically during the night
- Fever
- Jaundice
- Abnormal bleeding or bruising
- Severe weakness or fatigue
- Dizziness
- Swelling of the ankles, feet, lower legs, or hands
- Shortness of breath
- Insomnia
- Coughing up bloody or pink mucus
- Chest Pain
- Blisters or Rash
- Blood in the stool
- Signs of infection
- Headache
All patients must also tell their doctor about all current medications and medical conditions to avoid potentially life-threatening complications.
Using Gleevec for Neurofibromatosis
Gleevec is used to help stop cancer cell multiplication. When cells (both cancerous and noncancerous) multiply, they become tumors. Gleevec for neurofibromatosis is showing promise because it has been proven to help slow down or completely stop cells from multiplying and becoming tumors. Neurofibromatosis is characterized by tumors growing on the nerves. So, the studies are being done to determine if Gleevec can prevent neurofibromatosis tumors, like it can help to prevent certain cancer tumors. This drug is already FDA-approved and considered relatively safe for most cancer patients who take it. Studies are still being done to confirm its effectiveness in treating this genetic disorder, but current studies are showing great promise in helping to decrease neurofibromatosis tumors, some by a very drastic percentage.
Current Neurofibromatosis Treatment Versus Gleevec
As of today, there is no effective treatment method for preventing neurofibromatosis tumors. The current available treatments only help to alleviate some of the symptoms of this genetic disorder. Radiation, chemotherapy, and other anti-tumor drugs have proven ineffective in treating the tumors associated with this disease. Surgery is another current treatment method used to remove disfiguring or painful tumors, and certain NF1 bone malformations. However, surgery is not a permanent treatment method because the tumors can grow back, and in some cases, in greater numbers.
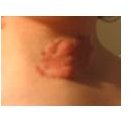
While Gleevec for neurofibromatosis, was still being researched using animal models, Riley Hospital for Children, had a three-year old neurofibromatosis patient, who was critically ill, come in with a plexiform neurofibroma (a type of tumor seen in neurofibromatosis) and this tumor was compressing her airway. Gleevec was given to her, under a compassionate use protocol. Her tumor, due to the administration of Gleevec, was decreased by approximately 80 percent. This patient was later removed from treatment and is being monitored.
Resources
Science Daily. (2008). Gleevec Holds Potential As First Drug to Successfully Treat Neurofibromatosis, Scientists Report. Retrieved on June 23, 2010 from Science Daily: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/10/081030123837.htm
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (2010). Retrieved on June 23, 2010 from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/neurofibromatosis/neurofibromatosis.htm
PubMed Health. (2007). Imatinib. Retrieved on June 23, 2010 from PudMed Health: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0000345
Image Credits
Plexiform Neurofibroma: Gerrit – Wikimedia Commons
Pills in Bottle: foxumon – sxc.hu
