Why is GAAP Important to Every Financial Statement User?
What is it?
It is a set of generally accepted accounting principles, collectively known as GAAP. They are basic rules, principles and procedures observed in preparing and presenting a business entity’s financial statements.and prescribed by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). They were developed for the benefit of external users, who rely on financial statements, as bases for comparisons, analyses and evaluations for their investment decisions.
Adherence to the accounting principles is being required mainly from all public corporations registered and recognized by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). A reference to public corporations denotes companies whose shares of stocks are openly traded in over-the-counter stock markets or stock exchange floors.
Actually, the rules stem from another set of basic accounting principles set forth in accounting academics as fundamental guidelines, which accounting learners have to know by heart. In providing accounting information, there are four basic accounting principles that every learner should keep in mind about financial reporting, these are:
- Relevance or usefulness
- Reliability
- Comprehensibility, and
- Transmissible by way of financial statements.
However, there was one principle lacking, and its importance surfaced at a time when American commerce had started to flourish. Investing in businesses had become a common business activity, in which investors relied on financial statements as financial guides. However, there was no uniformity of accounting procedures applied in the preparation and presentation of the financial statements. Unfortunately, this came into focus only as an aftermath of the stock market crash of 1929 and the Great Depression during the 1930s.
The Establishment of Uniform Rules


The era of the Great Depression was brought about by the stock market crash of 1929 and was a major economic despair not only in the US but also worldwide. Prior to the depression era, speculators and investors dealt heavily on shares of stocks and relied on the financial statements of the different companies that boomed during the “Roaring Twenties”, a time of great economic prosperity.
Banks liberally lent out money entrusted to them by their depositors during an age when bank deposits were not yet insured. This was also the period when companies undertook all efforts in enticing the public to invest in their businesses with the promise of lucrative returns.
However, it was also a time when GAAP was still unheard of, in which accounting methods were used in ways that would best serve management’s purposes; but not necessarily for the good of all or to measure business performance. Back then, financial statements could possibly mislead whether intentionally or not, but to the detriment of the investing public or the lending institutions.
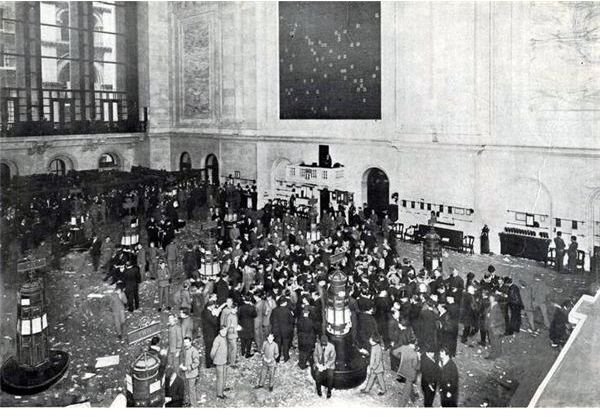


By and large, a lot of individuals were financially devastated when the stock market crashed and brought down with it a lot of businesses, banks and investors. The ensuing depression resulted to joblessness and heavy indebtedness.
In fact, some financial analysts and economists went as far as tagging the Great Depression as a contributing factor to World War II. It was also a period when other countries had a strong desire for world domination, thus seized the impact of the Great Depression as an opportunity to launch their aggression against major countries saddled with economic problems.
Emphasizing the Importance
After the implementation of the GAAP standards, accounting information presented in financial statements became more reliable as bases for economic decisions. Different users like managers, shareholders, investors, lenders, customers, suppliers, government authorities and even employees, became more confident with undertakings that involved furnishing money or rendering services or granting privileges to any business entity.
Adherence to uniform guidelines is important because this allows decision-makers to make financial forecasts about possible economic consequences when dealing with a business entity. Moreover, the rules and procedures are being formulated in consultation with private sectors based on their experiences and capacities as financial statement users themselves. Hence, there are reasonable grounds on which to conclude, whether or not, data interpreted are at comparable levels against those of other business entities dealing in the same type of industry or trade.
The Creation of the Securities and Exchange Commission


As an aftermath, Congress passed the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the creation of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The SEC’s initial objective was to restore order in the world of commerce.
The first of their many steps was to re-establish the integrity of stock market trading and the banking system, as possible sources of capital investments. Part of the actions taken was to require all publicly traded companies to register and be recognized by SEC; including those whose stocks and other forms of securities were held by more than 500 different shareholders.
In addition, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) was created to formulate the beginnings of the accounting standards, which SEC-registered companies would adhere to as requirements. Consequentially, the standards came to be known as the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.
Years later, this AICPA task was transferred to the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
As years passed, other government agencies, lenders, sellers, suppliers or any institution that base their judgements on financial reports saw the importance of GAAP accounting before any decisions were made. Although SEC was successful in implementing the rules, public corruption and connivance with unscrupulous business entities still undermined the integrity of financial statements as basis for evaluating and assessing the true financial condition of a business entity. Stock market crashes and economic crises, still occurred as the spate of accounting scandals rocked the business world several decades later.
The Importance of GAAP to Every Financial Statement User
The following are the basic reasons as to why GAAP is important to different users of financial statements
-
It enables investors to assess their risks and make projections about estimated returns on their investments.
-
Creditors can also asses their risks and can use the financial data to satisfy concerns over the repayment abilities of the entity.
-
Suppliers, as providers of goods for resale or raw materials for production are able to show proof that they can rely on their own capital resources, to sustain a business entity’s needs. In addition, suppliers can also impose the same requirements of financial proof from their customers as a prerequisite, before allowing credit instead of maintaining supply under COD. That way, suppliers can also keep a favorable financial position for their own purposes.
-
Business entities, as recipients of said supplies are being given the assurance that their operations will not be hampered by any failure in the delivery of goods. As customers, they have the prerogative to decide, which company to patronize by basing their decisions on the latter’s resources. It is a way of determining the supplier’s capability to furnish quality goods and to deliver in a timely manner.
-
Government agencies can also assess the ability of the company to pay taxes, provide employment, ensure the practice of fair trade and counter-check fair and reliable presentation of their financial position to investors, before any licenses are granted. Even the IRS, despite a separate tax accounting basis for income determination and allowable expenses, find financial statements prepared according to GAAP guidelines useful as reliable basis in assessing the income and expenses reported to them. The proportions of a business entity’s assets against its reported income may serve as indicators of fair presentations.
-
Managers and owners can measure their employees’ performances by evaluating costs incurred against productivity results, where overhead or operating expenses can be measured in proportion to the income generated. Financial statements prepared in the same manner by competitors can also provide relevant and reliable data to formulate plans and projections on how to create their own strategies for advancements.
-
Employees as represented by labor unions or other groups that take care of employees’ welfare also make use of financial statements to determine the businesses’ ability to provide better compensation packages. There is also the need to determine the true financial conditions of business organizations as providers of stable sources of income or livelihood.
Financial statements that carry the distinction of GAAP compliance are accompanied by audit reports issued by independent Certified Public Accountant. They serve as attestations that the material aspects of the financial statements are presented fairly in accordance with GAAP.
References
- Image: Gnucash 2 screenshot by Andrew_pmk - Wikimedia CCA-SA 3.0 unported.
- Image: Hendre-DduShareCertificate by Gwernol - Wikimedia under public domain.
- Image: Nonvaleur03 by Baltimore and Ohio Railroad company at Wikimedia under public domain.
- Business Accounting Guides: Basic Accounting Principles Rule – http://business-accounting-guides.com/basic-accounting/
- Stock Market Investing Guide : About Market Speculators – http://www.stockmarketinvestinginfo.com/smi_stockmarket_add_2.html
- Image: Stockexchange by Helen D Van Eaton,Wikimedia under public domain.
- Image: SEC by US-SecuritiesAndExchangeCommission-Seal.Wikimedia under public domain.
- Image: SocialSecurityposter1 by unknown author/ source: Franklin D Roosevelt Library website at Wikimedia under public domain
- SEC.gov. The Investor’s Advocate: How the SEC Protects Investors, Maintains Market Integrity, and Facilitates Capital Formation – http://www.sec.gov/about/whatwedo.shtml
- Image: U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission headquarters by AgnosticPreachersKid / Wikimedia CCA-SA 3.0 unported.