Rice Plant Husks and Efficient Rice Husk Stoves
Introduction
There are several kinds of rice, namely long grain, short grain, and medium grain. Long grain rice takes a longer time to grow and is costly to mill. This rice has a special taste when cooked. Medium grains are cheaper to mill. Its growing season is short and has longer harvests. It is very popular in the US. Short grains are known as Japonica and are liked in Japan. Rice from Taiwan and Korea have several different colors such as white, brown, red, purple, blue, and striped.
Rice Plants contain all the parts of the rice seed – the embryo, cotyledon, and endosperm. The embryo at the end of the seed becomes a rice plant. Cotyledon helps the growth of the rice plant.

Multiple-purpose Applications of Rice Husk Ash
Rice husks can be used as fuel for the boilers to produce power or for further processing at a rice plantation.

Rice Husk Ash (RHA) is used in the cement industries. It bonds well with cement, and it reduces the amount of cement content required. RHA-mixed concrete products are ecologically sound and sturdy. It can be used as a replacement up to 20% of the cement in concrete. It is a valid economic solution. It strengthens concrete and minimizes corrosion by decreasing its permeability.

RHA is an excellent insulation medium. It is exclusively used for insulation lining of the molten metal in tundish and in slab casters. The molten metal temperature in the ladle is 1400 C and its temperature drops to 1250 C. In order to prevent breakdown of the slab caster, RHA is coated over the tundish and the ladle as an insulator.
The packaging industry uses RHA-generated silica. It has an anti-blocking property which solves the problem of bonding low density polyethylene films. This is because RHA silica has smaller particle size and higher specific surface area.
Precipitated RHA Silica has special physical and chemical properties. It blends firmly in vulcanized rubber formulation enhancing tensile and tear strength with an increase in hardness and abrasion resistance. (There must not be any confusion between RHA-generated silica and silica extracted from sand.)
RHA silica is widely used in tire and shoe industries. Precipitated silica serves as filler for paper industry. It is a cleansing agent used in toothpastes and cosmetics.
Our body uses natural silica for maintaining and promoting good health. A shortage of natural silica causes acute health problems. The best remedy is to eat steam cooked Bamboo shoots. It has 95% natural silica. Health recovery is very fast. Silica is used for health care applications. Bamboo silica prevents premature aging.
Ground rice husks impregnated with silver iodine nano particles serves as a safe drinking water filter. The Tata Swach Magic water filter is a new cost-effective innovation, and it runs without electrical power.
Rice Husk Plants and Efficient Wood Stoves
A typical rice husk burning furnace consists of a rotary kiln with a heat resistant steel plate platform on which the rice husk is charged. The lift-able chimney is of conical shape, and its small end serves as an exhaust port. The high temperature heat energy is used to generate superheated steam fed to a turbine engine for producing electricity on a continuous basis.
The large opening of the cone snugly rests over the finely perforated platform. When ignited, the husk converts into carbonized husk at a temperature of 3000 C – 4000 C. This facilitates self-burning of the carbonized husk, creating rice husk ash [RHA] which is white in color. When the entire husk is carbonized, the temperature of the kiln is increased to 7000 C for a specific time with respect to volume of RHA. The output ash has 90% amorphous silica of large surface area, which is desirable. RHA is collected at the bottom container.
The rice husk is never wasted as it has many useful applications. The rice mill generates 22% husks. 78% of the weight of rice and of broken rice and bran is obtained by milling. Steam is generated by burning the husks as fuel. The husk has 75% organic volatile matter and the rest 25% of husk is burned into ash in the firing process. This ash is known as RHA – rice husk ash. RHA contains 85% - 90% amorphous silica.






Rice Husk Stove

A rotary kiln is used for converting rice husk into carbonized charcoal. It is called charcoal because the husk becomes charred when heating at 4000 C. Japan uses this charcoal in bulk quantity for cooking and heating water by stove. When ignited, the carbonized rice husk charcoal generates heat sustained for several hours continuously.
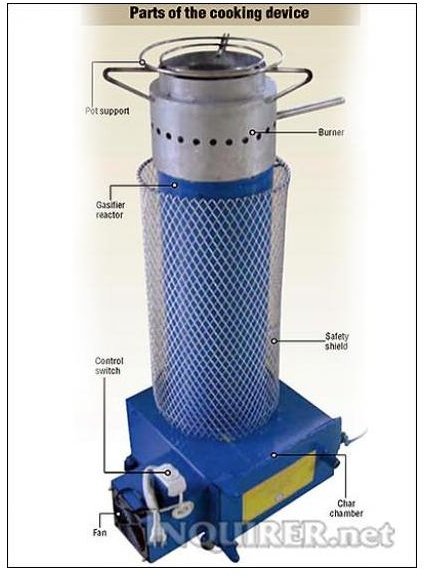


Rice husk charcoal is costly because of process costs in creating the charcoal. Rice husks are cheaper and are useable in stoves. The ash has good sale value because it contains 90% precious silica. Please do not throw away ash as waste. A rice growing country like Japan can very well use free rice husks for stoves.
Additional Resources
Identifying Plant Disease and Advice for Treating the Plants
Newsweek – Clean Stoves for All
