Common Types of Green Construction Materials & Their Uses in Building Construction
The Need for Green
The majority of Green House Gases (GHG) in a city comes from buildings, not from cars or trucks. It has been estimated that 1/4th of the world’s wood and 1/6th of its fresh water are used up in building construction. As the population increases, the need for more buildings increases, thus using more building materials and finally creating more pollution.
The conventional “drywall” material used in construction is made up of gypsum, which requires a huge amount of energy and several stages to produce. In fact, gypsum is the third largest producer of GHG, after steel and cement, among the construction materials.
Greener Building Materials and Construction Techniques
Fly-Ash: The recent trend is to use “fly-ash,” which is a residue from coal fired power-plants. These are used in the making of cement. Usage of fly-ash decreases the cost of the concrete and results in a higher quality product. When cement is produced, huge quantities of carbon-dioxide are released, and this results in air and water pollution. Usage of this residue will lessen GHG.

Bamboo: Often misunderstood as a light, slender wood, bamboo is lighter than steel, but five times stronger than concrete. It absorbs four times more carbon-dioxide than most trees. It can grow faster than any normal tree (usually several feet/day), and has a great cooling effect too. Certain parts of southeast Asia have houses made of bamboo, and there is no problem in using it except for the problem of joining two bamboo sticks together. The main positive aspect is that it is a renewable source.

Evaporative Cooling: This cooling technique is used in plenty of places near the tropics. It is very similar to the production of sweat from our body. As we feel the heat, our body produces sweat to cool itself. In the same way, the water content in the plant evaporates, taking away the heat from the surrounding air or the atmosphere, thus making it cooler. It is also very similar to the cooling effect that is produced when a drop of alcohol is held in our hand. The alcohol vaporizes taking away the heat. This cooling effect is known as “green roofs.”

Straw bales: They can be used as a main structural component or as a soft insulation. These are packed as closely as possible and made hard so they can withstand considerable amount of load and impact. One may think that these straw bales are a fire hazard, but they are not. They provide three times more fire resistance than conventional homes.

Earthen Rocks: The main property of earthen rocks is “thermal mass.” These rocks posses a high degree of thermal mass thus can be a better substitute for insulation. Insulation may sometimes be made of toxic material or harmful material, but these rocks are natural and are eco-friendly. So thermal mass is the property to absorb, store, and release heat energy. These are best suited for desert climates.


Green Roofing
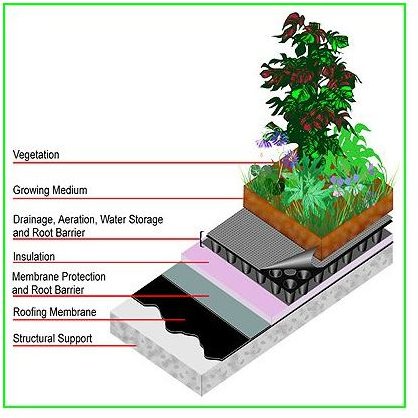
The picture to the left shows the simple technical details for “green roofing” or “roof vegetation.” Civil and structural engineers play a vital role in green roofing, as they have to estimate the load bearing capacity of the roof structure. On the roof structure, a primary coating of roofing membrane is applied. There is a separate layer called the “membrane protection and root barrier” which is very important to avoid destructive effects. This layer prevents the roots growing and getting in touch with the main roof structure. Some designs are capable of storing a certain quantity of rain water or collecting waste water, usually “grey water,” which is used for the vegetation irrigation. Finally medium sized, selective plants are grown in the growing medium, which has soil and fertilizers in it.
Some Green Construction Tips:

1. Buildings can be constructed on the basis of East-West axis, thus allowing us to take full advantage of the sunlight.
2. Tall buildings, theatre halls, corporate buildings, and other structures can have transparent glass substituted for concrete walls.
3. Transparent glasses reduce the weight of the building and do not contribute to urban heat islands.
4. These glasses can be recycled and reused.
5. The “Brise-Soleil” system can be adopted. In this, the transparent glasses are coated/designed in such a way that they take the sunlight in and block the solar heat back.
6. “Ecotels” are desirable instead of hotels/motels. One desirable criteria for ecotels is having swimming pools placed at the rooftop so that the heat entering the roof can be eliminated, thus reducing air conditioning usage and providing a smaller carbon footprint.
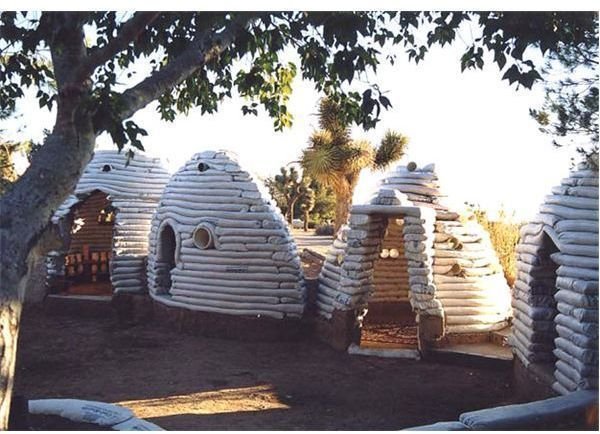
7. Instead of using polyurethane tents or temporary shelters, sand bag homes can be used.





Image Credits:
