New High Tech Innovations to Healthcare: Cutting Edge Healthcare & Medical Advances
Healthcare technologies are advancing at a pace that rivals science fiction. Some of the latest breakthroughs allow for non-invasive ways to monitor the heart, scan the body, or do extensive colon scopes without the need of anesthesia. These new high tech innovations to healthcare reduce or eliminate the need for possible complications from invasive procedures and remove the chance of adverse reactions to anesthetics.
Five High Tech Innovations to Healthcare
Bluetooth Heart Monitors
The Bluetooth heart monitor records an electrocardiogram (ECG) and transmits the information to a patient’s cell phone. An application that checks the ECG signal for signs of possible cardiac failure analyzes the data and can be programmed to contact emergency personnel in the event of cardiac arrest. This little device is worn on a chest belt that holds the monitor directly against the skin. There are several models available from Polar including models with built-in GPS to lead paramedics directly to the location of the wearer when medical assistance is needed.
Portable Ultrasound Machine
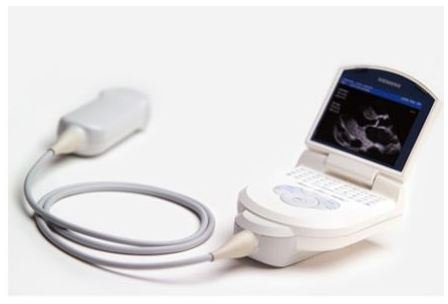
The discovery of ultrasound technology changed the face of medicine forever by drastically reducing the number of invasive operations and in turn lowering complications due to those operations. Now new high tech innovations to healthcare have taken the ultrasound from a room sized machine down to a handheld device no bigger than a cell phone. With the new handheld device ultrasounds can be carried from room to room and even on home visits! This new medical technology has the potential to re-revolutionize medical diagnostics and lower the instance of misdiagnosis because of the access it can give to the internal structures of the patient.
Endoscopy Pill Camera

Although the idea of a camera inside of a pill has been in development since 1981, scientific technology held it back until recently. The endoscopy pill camera is swallowed by a patient and sends 3 pictures of the gastrointestinal track a second for up to 11 hours allowing doctors to see into parts of the small intestine that were inaccessible before. There is no need for sedation, no swallowing of a scope (or in the case of an endoscopy no scoping the other end), and it can be done as an outpatient procedure because the camera sends the pictures to a wearable receiver!
Another application of these micro pill cameras is to have them tethered to an ultra thin fiber optic cord so that the doctor can physically manipulate the camera as it travels through the digestive system. This application lets the doctor stop and analyze anomalies on the spot.
Nexagon Gel
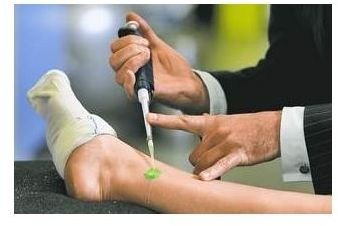
A wonder gel that uses DNA based technology to reduce the time it takes for wounds to heal. It works by interrupting how cells communicate and preventing the production of a protein that blocks healing. This allows cells to move faster to the wound to begin healing it. Laboratory tests on animals have shown that a cut that would normally take about a week to close heals in three days with the gel. It has proved effective on skin, brain tissue, and spinal cord wounds and the FDA has approved of its use on the cornea in the eye.
The scientists believe it could benefit patients undergoing cosmetic surgery, those with chronic wounds or spinal injuries. In particular, they believe elderly people could benefit from the gel, as they are more prone to slow healing wounds and infection. This could lead to the reduction of time patients stay in the hospital and allow health services substantial savings.
Rubber Based Artificial Skin

Stanford University has developed a prototype skin product made from a piece of rubber sandwiched between two micro thin layers of electrodes. The entire thickness of the skin is under a millimeter. It is sensitive enough to detect the weight of a fly. Currently the research team is working on models that can be integrated into the human body.
The first possible use for this new high tech innovation to healthcare is as a covering for robotic hands used during surgery. Surgeons already do remote surgery but a robotic hand covered with this artificial skin could feel the difference between rough tissue or soft smooth tissue allowing the surgeon a more complete picture using all of his senses.
