How Do Search Engines Google, Yahoo, MSN Services Collect Data? What are Search Engines?
Search Engines Are Not Browsers
While browsers use search engines, there are search engines that are independent of the browser. An example of a browser would be Mozilla Firefox, Opera, Internet Explorer, or Chrome. A browser is used to display information. A search engine, on the other hand, is a program that is used to find information.
The first browser was Netscape, designed in the early 90s, and it revolutionized the Internet. In fact, there was another development that helped spur interest in the Internet, and that was the http protocol designed around www, the World Wide Web. This made going from one web site to another easy. But it was the browser that turned text information into a graphics format and made it viewable. Thus the Internet, which was designed in the late 1960s by the US Defense Department, was only a curiosity used by scientists, techno-engineers, and military planners. But the World Wide Web and the browser made the Internet the communication engine that we know today.
What Search Engines Do
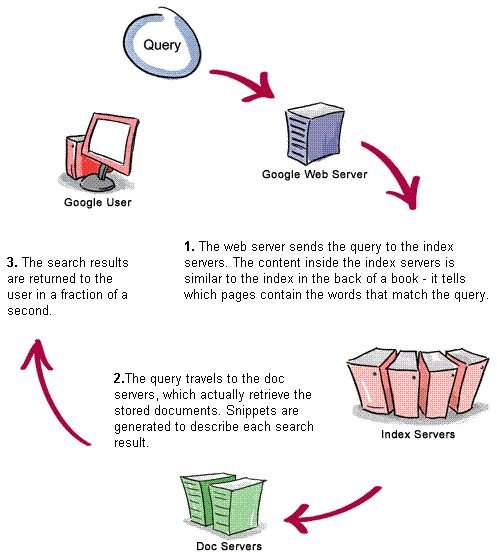
A search engine looks for web sites. It uses special algorithms, called crawlers or spiders, that search the World Wide Web. They index information about what kind of site it is they are visiting and look for key words about the site including the url. They send back information to their main database where it is catalogued. It then becomes available for anyone to search.
Google was not the first search engine company, but it far outranks the others. Here are some of its main characteristics: It can determine if a link is artificial or not, ie, finding a true editorial citation. It looks for natural link growth through popularity over time, the number of hits it has had. It is biased towards informational resources. Its crawl depth is determined by quantity, how deep it can go in a web site from one level to another deeper level, but also by quality. For example, if a website has references to automobiles, but the page is about a particular brand and its gas mileage, then the the quality is missing and it will not be indexed. In other words, if the website and its content are not on par, then the crawler will not index the site. How does Google find the right results? They use a PageRank technology based on linking hundreds of PCs together with querying capability to find answers to a search. That allows them to get the answers very quickly.
Yahoo
One of the earliest search engines, Yahoo, originally let other companies do the searching and it incorporated the results into its web site. Now it does its own searching. It has algorithms to determine if a link is a natural citation or not.
What is a natural citation?
Consider that some web sites may include words/tags in the SEO to permit it to be indexed into many categories, even if the website is not about that. For example, a website may be about French cooking, but the indexing tags include Spanish cooking, Chinese cuisine, Southern, and so on. These other tags are not natural citations, unless they clearly mention these other cuisines in the website.
Yahoo also includes paid content, skewing the results towards commercial interests, and ranking them higher than others.
Yahoo also tends to rank inbound links differently. When you perform a link check on Yahoo and then on Google, the Google results almost always tend to be lower. Google shows a snapshot of the “relevant” links, unlike Yahoo which shows all of the links regardless of relevance.
MSN Services
MSN is new to the search engine game. It is not very good at determining if a link is natural or artificial. They place a high value on page content, and not so much on link analysis. Their crawler algorithms place a premium on commercial results. There is also a tendency to trust sites that other engines would be wary of including in the index.
MSN indexes information that it finds, which includes web content, popularity, relevance, and true citation vs. artificial ones. Another feature is that their indexing occurs more frequently. Their crawling is done daily on some sites, weekly on others and monthly on the rest. Their view is that this is a more comprehensive approach and indexes more often and more completely than either Yahoo or Google.